The Human Excretory System - Mr. Aitken's Biology...
Transcript of The Human Excretory System - Mr. Aitken's Biology...

The Human Excretory System
The function of the excretory system is the excrete (get rid of) wastes that are not helpful to the body.

Cellular Waste
• Wastes that are removed include carbon dioxide, water, salt, urea and uric acid.
• All excreted wastes travel at some time in the blood.

Major Metabolic wastes:
• carbon dioxide, water– CO2 and H2O are from cellular respiration
• certain nitrogen compounds – Breakdown of amino acids from proteins produces
nitrogen compounds• Urea
• Ammonia
• Uric acid
• Mineral salts from metabolism– Sodium chloride (NaCl)
– Potassium sulfate K2SO4

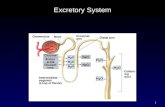
Structures of the Excretory System
1. Skin
2. Lungs
3. Liver
4. Urinary System
5. Large Intestine
Can you guess how these structures are a part of the excretory system? What makes the Large Intestine different from the rest?

Large Intestine
• The large intestine removes solid, undigested food from the body after it passes through the digestive system.
• Waste is stored in rectum until it is excreted from the body as solid waste. NOTE: This is NOT waste produced by the cells (cellular waste) as a part of your metabolism!!!!!

Skin
Wastes such as excess water, salt, urea and uric acid are removed from the body in sweat.

Skin2. Excretion-
– Small amounts of urea and salts in sweat– Removal of excess heat (Major Function)
• Blood vessels dilate bringing more warm blood to skin surface
• Sweat is produced by sweat glands• Sweat absorbs body heat and evaporates to water
vapor and body heat leaves the body in the water vapor
• Body cools as a result of the evaporation


Lungs
Excess carbon dioxide waste is removed from the body when we exhale.
CO2

Liver
The liver is a part of what other system?
The digestive system
Liver

The liver has many functions, including (but not limited to):
1. to produce substances that break down fats
2. produce urea (the main substance of urine)
3. make certain amino acids (the building blocks of proteins)
4. filter harmful substances from the blood (such as alcohol)
5. The liver is also responsible for producing cholesterol. It produces about 80% of the cholesterol in your body.

The Liver and Waste
• The liver produces urea and uric acid as a by-product of the breakdown of proteins
• Urea and uric acid are sent to the kidneys to be processed
Liver

Formation of Urea in Liver:
• Amino acids are broken down.
1) amino group, NH2→ changed to ammonia,
NH3 → changed to urea (less poisonous)
• Finally: Urea diffuses back into bloodstream and is filtered out by the kidneys.

Human Excretion
• Liver’s role
–Detoxification-
• changes harmful substances into inactive or less poisonous substances
• These inactive substances are returned to blood and are filtered by kidneys.

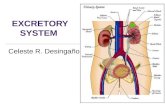
The urinary system
• The kidneys filter the blood to form urine, which is excess water, salt, urea and uric acid

Urinary SystemKidneys-> ureter-> urinary bladder-> urethra
Kidneys
2 main functions
1. Remove wastes from cellular metabolism
2. Regulate the concentrations of substances found in the body fluids
*****If kidneys cannot perform these functions a person will die.*****


Kidney structure3 layers of the kidney
• Cortex- outer layer blood is filtered to remove waste and excess substances
• Medulla- middle layer made up of tubes called collecting ducts that carry the filtered substances (filtrate) to the innermost layer of the kidney
• Pelvis- cavity that collects the filtrate and connects the kidney to the ureter which exits the kidney


NephronNephron- waste filtering unit of the kidney found
in the cortex and the medulla
• 1.25 million nephrons in each kidney


• Nephrons clean the blood in a three-step process.
• The first step is filtration of the blood.
FILTRATION
Water, electrolytes,
amino acids,
glucose, urea, and
other small
molecules diffuse
out of the blood,
creating the filtrate.
1Glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule
• Glomerulus:
Network of
capillaries
• Bowman’s
Capsule:
Encases the
glomerulus
• The body’s entire volume of blood is filtered every 45 min

• The first step is filtration of the blood.
• The second step is reabsorption of materials.
from body
to body
collecting
duct
from other
nephronsloop of Henle
REABSORPTION
As the filtrate enters
the rest of the tubule,
most of the materials
are reabsorbed into
the blood. Materials
not reabsorbed make
up the urine, which
flows into the loop of
Henle.
2

• The first step is filtration of the blood.
• The second step is reabsorption of materials.
• The third step is excretion of materials.
EXCRETION
In the loop of Henle,
water can be
reabsorbed one final
time to reduce the
volume of urine. The
remaining urine flows
into a collecting duct
that leads to the ureter.
3
from body
to body
collecting
duct
from other
nephronsloop of Henle

Filtration in Nephron1. Blood enters kidney through renal artery,
2. Small substances (water, salts and minerals) and wastes (urea) diffuse from the capillaries into the nephron of the kidneys.
3. Urea, excess water and excess substances travel to the renal pelvis to form urine.
4. Water and some dissolved substances are reabsorbed into the blood through the capillaries.
5. Clean blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein.

Urine- final waste fluid excreted
• Made up of water, urea and various salts.
• 1-1.5 liters of urine are produced every 24 hours
Structures Involved in Getting Rid of Urine!
Ureter- tube connects kidney to urinary bladder
•Function –conducts urine from kidney to bladder
Urinary Bladder- collects and stores urine for
Excretion
Urethra- during urination urine travels from the bladder to the
outside of the body

UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)• Is a very common disorder. If the bladder has become
infected, it is known as cystitis. If the urethra is infected., it is called urethritis.
• Symptoms include painful urination burning sensation), frequent urination (even if no urine present) and bloody or brown urine.
• This can lead to chills, fever, nausea, vomiting and upper abdomen tenderness.
Disorders of the Excretory System

NOTE :
• If left untreated, all UTI’s can lead to permanent kidney damage and possible kidney failure.
• The general treatment is by antibiotics. A person needs to maintain good personal hygiene when eliminating wastes (liquid and solid forms) from the body.
• Also, a person should drink lots of water.

Kidney Infections
• Result when an infection reaches the kidneys and becomes known as pyelonephritis.
• Common causes can be infection from elsewhere in the body or obstruction of the prostate gland (usually in older men).
• For children, infection can be caused by the tube that
drains urine from the kidneys and the bladder.

Kidney Stones
• 80% of those stricken are males.
• The most common crystals are:– Calcium Oxalates – Uric acid
• Crystals formed from minerals in urine.
• They can be found in the kidney, ureter or bladder.

Kidney Stones (cont)
• Symptoms include severe back or abdomen pain, blood in the urine, nausea and vomiting.
• Diagnosis involves a complete medical examination, including X-rays.
• Treatment may vary from letting the stones pass through the urinary tract to ultrasound shock (or lithotripsy) to disintegrate the stones to a small size that can be passed through the urinary tract.
• Real large stones require surgery for removal.

Kidney Stones (cont)
• Ways to avoid kidney stones:• Increase liquid intake (more than 2L /
day)
• Limit sodium intake
• Limit animal protein (link shown in men)
• Limit foods high in oxalate (spinach, strawberries, nuts, dark chocolate, brewed tea)