The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects...
-
Upload
alysha-sabine -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects...
The Human Body
The Skeleton provides…Support/Shape MovementProduces [White blood cells] Protects
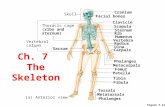
BonesUpper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, (Spine, Cranium, Metacarpals, Phalanges)Lower Body: Pelvis, Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Patella
Bone Types/Shapes: Flat, Long, Short, Irregular
Skeleton & Bones
A joint is a point at which two, or more, bones meet.
Types of JointFixedSlightly MoveableSynovial Joints
The Human Body
Synovial JointsBall and SocketHingePivotSaddleGlidingJoints are cushioned by
cartilage. Cartilage also reduces friction, and acts as a shock absorber.
JointsThe Human Body
Match the following joints to the joint type…
Neck
Shoulder
Knee
Ankle
Thumb
Ball and Socket
Hinge
Gliding
Saddle
CondyloidWrist
Pivot
Joints
Neck-P
ivot; S
hou
lder-B
all &
Socke
t; K
nee-H
ing
e; A
nkle
-Glid
ing
; Th
um
b-
Sad
dle
; Wrist-C
on
dylo
id
The Human BodySkeleton & Bones
Q1: Name the three bones in action when throwing a cricket ballQ2: If someone was said to have broken the longest bone in their body, which bone would they have broken?Q3: Name two long bones, and two flat bonesQ4: In which area of a bone is bone marrow situated? a. Outside, b. Centre, c. Spread throughout the bone structure
A: Q1Ulna, Radius, Humerus Q2Femur Q3See front Q4b
Front Back
The Human Body
Muscles-Involuntary: Work without conscious control-Voluntary/Skeletal: All conscious movement-Cardiac: Found only in the walls of the heart
Muscles are attached to the skeleton by tendons. The point at which the muscle tendon attaches to a fixed bone is the ORIGIN.The point at which the muscle attaches to a moving bone is the INSERTION.
Soft Tissues
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves toward the origin.
The Human Body
Body Systems
Respiratory System: Lungs (Bronchus, Alveoli) Nose, Mouth, TracheaCirculatory System: Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries[The pulse rate can be taken at: wrist, neck, groin]Digestive System: Stomach, Intestines, Esophagus, LiverEndocrine System: Hormones, Hypothalamus, GlandsReproductive System: Testes, Ovaries, Male and Female genetaliaNervous System: Nerves, (Spinal Cord, Brain – Central Nervous System)
Q1: Name 10 musclesQ2: Give another example of antagonistic effectorsQ3: Give another example of where fast twitch fibres are usedQ4: If the hamstring concentrically contracts, what does the quadriceps do?Q5: Is the insertion for the gastronemius at the knee, or ankle?
Soft TissuesThe Human Body
A: Q2hamstrings and quadriceps Q3clean and jerk weightlifting Q4 eccentrically contracts Q5 ankle
Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide and Water Vapour are all exchanged in the alveoliTidal Volume = the volume of air you inhale/exhale witch each breathRespiratory Rate = how many breaths you take in a minuteMinute volume = the volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a minute (min. vol. = tidal vol. x respiratory rate)Vital Capacity = the maximum amount of air which can be forced in exhalationVO2 Max =the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use in 1 minute. The fitter you are, the higher your VO2 Max
The Human Body
Gas Exchange
Front Back
Muscles: Isometric & Isotonic ContractionIsometric Muscle stays the same length.Isotonic Muscle changes length as it works, Concentric contraction = muscle shortensEccentric contraction = muscle lengthens
Tendons & LigamentsTendons attach muscle to boneLigaments attach bone to bone
eg. The cruciate ligament- behind the patella
The Human Body
Soft Tissues
Training
Principles of Training
S.P.O.R.T.Specificity- Make the training specific to your sport Progression- Ensure that each session, you further your abilityOverload- Concentrate on one aspect, and improve on itReversibility- Know that if you stop training, your muscles will go into atrophy, and your fitness levels will decreaseTedium- Ensure the training you are doing is mentally and physically stimulating
F.I.D.Frequency- How often do you train?Intensity- How hard do you train?Duration- How long do you train for?
The Human Body
Soft Tissues
Antagonistic EffectorsMuscles work in opposition, ie, one contracts, the other relaxes. -Contractor = Agonist -Relaxer = AntagonistEg. During a bicep curlThe bicep is the agonist, while the tricep is the antagonist
Fast Twitch fibres- Muscles work powerfully, in short ‘explosions’ anaerobically for short periods, they fatigue easily. Eg’s, Sprinting, fast bowlingSlow Twitch fibres- Produce less powerful, slower contractions, can work for long periods of time. Eg’s, marathon running, long distance cycling
TrainingPrinciples of Training
Q1: If I wanted to increase my bicep size, which principle would I use?
Q2: How is atrophy part of the reversibility principle?
Q3: Without turning over, name the five principles, and what they involve
Q4: If I ran 2km in one session, what could I change, to ensure I progress in the next session?
A: Q1Overload Q2atrophy is the decrease in muscle size, when training decreases Q3see overleaf Q4run further, ie 3km
Front Back
Training
Speed- The ability to perform quickly and efficiently -Timed 100m sprint
Stamina- The ability to perform aerobically for long periods of time
-Bleep testStrength- To be able to move an object of resistance
-Hand grip dynameter Suppleness- The range of mobility around all joints is good
-Sit and Reach test Somatotype- Body shape, ie, endomorph –d for dumpy, ectomorph –t for thin, mesomorph –m for muscles
-fat callipers
The 5S’s
(Tests in italics)
Training
Agility- the ability to change the body’s position fast and effectively [Compass Run]Balance- the ability to maintain the body’s centre of gravity, with minimal ‘postural sway’ [Stork Stand]Coordination- the ability to make different parts of the body work together, efficiently [Ball Bounce]Power- speed x strength [sergeant jump]Reaction Time- the time taken from the presentation of a stimulus, to the onset of a response [ruler drop]Timing- the ability to combine all of the above, to produce an effective response [hitting a cricket ball]
Skill Related Fitness
[test’s in brackets]
Training
State which man is: mesomorphic, ectomorphic, endomorphic
The 5S’s
Training
Skill Related Fitness
Q1: Name an event in which optimum balance is required
Q2: Which components of skill related fitness would a rugby player need, to be at the top of his game?
Q3: Which component(s) does a sprinter use, as she hears the starting gun?
A: Q1eg, the beam Q2all of them! Q3reaction time, power, balance
Front Back
Training
Interval- Involves alternating between fixed periods of exercise and fixed periods of rest. Eg, run 10m, walk 5m, run 10m etc.
Fartlek- The intensity and type of exercise is varied (ie, through changes in pace, terrain, style…) eg. Walk 10m, Jog 5m, Sprint 15m…
Continuous- Long, slow, distance exercises, at a constant rate, without rest
Weight- Each exercise focuses on a specific muscle group, using machine or free weights.
Circuit- Involves a series of exercises, each taking place at a different station, alternating the muscle groups worked
Training Methods
Training
Effects of Training Short TermSweating Redness (Blood rises to skin to cool)Dehydration Heavy/Faster BreathingFatigue Lactic acid build up/Cramp‘Stitch’ Tightness/Soreness in muscles
Long TermWeight loss ~ Muscle:Fat ratio increases ~ Aerobic/Anaerobic fitness improves ~ Speed, Stamina, Strength, Suppleness improve ~ Somatatype Changes
Training
Training Methods
Needs specialist, expensive equipment
Improves strength, tone, posture
Weight
Tedious
Non-specific
Improves aerobic fitness
Decreases body fat
Little specialist equipment needed
Continuous
Tedious
Non-specific
Improves aerobic & anaerobic fitness
Increases metabolic rate
Fartlek & Interval
DisadvantagesAdvantagesMethod
Training
Effects of Training
Q1: What effect(s) will lifting weights increase?
Q2: If a runner sweats a lot, what must he do in order for him to counteract the sweating?
Q3: To increase aerobic fitness, how much effort should you be expiring (in terms of the percentage of your maximum workrate)?
A: Q1Sweating, hotness, muscle size/strength Q2Drink lots of water/fluid Q3 60-80%
Front Back
Issues in Sport
Types of Sponsorship-Shirt Sponsors (Adidas, Nike, Fly Emirates)-Stadium Sponsors (Reebok, Emirates)-Event Sponsors (Bupa, Flora, McDonalds)-Sport Sponsor (Amateur Swimming)-Series Sponsor (RBS, Norwich Union)-An Individual (Adidas, Gillette, Police)
Sponsorship
Issues in Sport
Amateurs/Professionals
Professional players keep fit to take part
are paid to take part
compete for a career
Amateur players take part to keep fit
receive no financial rewards
compete for pleasure
Issues in Sport
Q1: Name three advantages of sponsorship for; a team/performerthe company
Q2: Name three disadvantages of sponsorship for:a team/performera company
Q3: Give 5 examples of sponsors in sport
Sponsorship
A: Q1equipment, travel, scholarships, money/publicity, advertising, reputation Q2over dependence on sponsor, exploitation, minority sports decline/risk (success isn’t guaranteed), media coverage may reduce, wrong image presented Q3see overleaf
Issues in Sport
Amateurs/Professionals
Add these labels to the diagram: Few fulltime professionals, some part time semi-pro’s, many amateurs performing at various levels
Front Back
Issues in SportMedia
TV
Radio
Books/Magazines
Newspapers
CD’s/DVD’s
Internet
Media
Issues in Sport
Etiquette A set of unwritten rules, concerning a participants ability to respect and honour their opponent and the game. Eg’s. Acknowledging opponents
good play, shaking hands after a game, replacing divots on the golf course
Gamesmanship‘Winding up’ an opponent. Through comments in the media (Eg. Ferguson vs. Wenger), diving, timewasting, employing other tactics, eg, war dances (the Haka)
Sporting Behaviour
Issues in Sport
Q1: How can the internet be helpful to a team wanting to know more about their opposition?Q2: How can media coverage be detrimental to a sport? Give an exampleQ3: How can the media influence more children to uptake a sport?
Media
A: Q1find out past results, players, statistics, videos Q2decline in coverage, eg, hockey, netball Q3more sport coverage, coverage more suitable for children, more websites, games
Issues in Sport
Q1: Give two further examples of good etiquette in the sporting worldQ2: Give an example of poor sporting behaviour in football, and explain how officials clamp down on itQ3: What was the ‘Turner report’, and what changes did it suggest?
Sporting Behaviour
A: Q1cheering the opponent after a rugby game, swapping shirts, throwing rice into the ring before a sumo game Q2goalkeeper taking time over goal kick, yellow card; diving, yellow card Q3after Hillsborough/ Heysel disasters, the government produced an enquiry, it suggested all top league stadiums were all seater, clubs installed CCTV, segregation of fans, removal of perimeter fences
Front Back
GCSE Physical Education
Flash Cards
Contents
The Human Body [ x5 Cards]
Training [ x5 Cards]
Issues in Sport [ x4 Cards]
Aspects of Sport [ x4 Cards]
GCSE Physical Education
Aspects of Sport
Various RolesPlayer Referee/OfficialAdministrator/Organiser CoachMedia ChairmanCaretaker Medical Care
Factors affecting participationFamily GenderAge Peer GroupPopularity Race/CultureEducation Disability Environment
Participation In Sport
Q1: How are children living in the Alps more likely to take up a snowsport, rather than beach volleyball?Q2: How has communist Russia dictated as to how the county’s population participate in sport?Q3: What have the government done in the UK, to try and improve sports provision for the whole population?
Aspects of Sport
Participation In Sport
Opening Cards
Front Back
Aspects of Sport
Warm Up & Cool Down
Warm Up is essential to…-Prepare the body psychologically-To improve blood flow to the working muscles-To, literally, warm up; to avoid injury – muscles that are warm can flex and stretch rather than snap or tear.
Cool Down is essential to…-To bring the body’s systems (heart & respiration rates) gradually back to a resting rate-To rid the body of lactic acid-Help prevent soreness, and aid recovery
Aspects of Sport
Factors Affecting Performance
Opponent
Skill Level
Personality
Drugs
DisabilityDiet
Injury
Gender
Age
Crowd
AltitudePressure
Q1: How should a warm-up be carried out (structure)Q2: What type of stretching is more effective (and safer) to carry out at the start of a session; static or or dynamic?Q3: Suggest a simple and effective way of cooling down
Aspects of Sport
A: Q1cardio-vascular/aerobic, dynamic stretching, sport specific Q2dyamic- still keeps blood flow to working muscles up, whilst gradually stretching the muscles Q3Run 10m, walk 5m, Run 10m, Stretch, etc
Warm Up & Cool Down
Q1: How can altitude affect performance?Q2: Which factors do not affect a closed skill?Q3: Give another two factors which may affect performance
Aspects of Sport
Factors Affecting Performance
A: Q1the amount of oxygen in the air decreases as altitude increases Q2opposition, surface, weather Q3surface, body composition
Front Back
Alcohol-loss of coordination, lack of responsibilityAnabolic Steroids-Accelerate growth of musclesBeta Blockers-Help performers to relaxBlood Doping-red blood cells are removed, and then reinjected prior to a competition- increases the amount of oxyhaemoglobin in the bloodDiuretics-make a competitor lose water by urinationPeptide Hormones-increase muscle growth (Human Growth Hormone)Narcotics-Painkillers (Heroin, morphine)Stimulants-increase activity of the nervous and cardiovascular systemsTobacco-can help people relax
Aspects of Sport
Substance Abuse
Q1: In which sport would beta blockers be beneficial to the competitor?Q2: Human Growth Hormones can only be detected up to 24hours after use, how does this drug have an advantage over others will similar affects?Q3: Name two effects on the body caused by smoking
Aspects of Sport
A: Q1darts, snooker Q2 if a competitor takes the HGH more than 24hours before a drug test, it will go undetected Q3increased chance of heart disease- due to cholesterol in the coronary arteries; ‘smokers cough’ due to the hot air burning the trachea and lungs
Substance Abuse
Front Back
GCSE Physical Education Flash Cards Drew Harding 2008
Other Tips
-Constantly recap on things you’ve learnt – just simple things like naming the muscles, etc.
-Have confidence in yourself!
+Aim to be the best
-Revision = Relaxed, the more you revise, the more relaxed you will be come the exams
-talk to people, gain knowledge, and wisdom
End Cards
![Page 1: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/1.jpg)
![Page 2: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/2.jpg)
![Page 3: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/3.jpg)
![Page 4: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/4.jpg)
![Page 5: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/5.jpg)
![Page 6: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/6.jpg)
![Page 7: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/7.jpg)
![Page 8: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/8.jpg)
![Page 9: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/9.jpg)
![Page 10: The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://reader042.fdocuments.net/reader042/viewer/2022032701/56649c755503460f9492861a/html5/thumbnails/10.jpg)