The Human Body. MusclesCardiacVoluntary Muscle Involuntary Muscle Bone MarrowSkeletalCraniumCompact...
-
Upload
edwin-caldwell -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
6
Transcript of The Human Body. MusclesCardiacVoluntary Muscle Involuntary Muscle Bone MarrowSkeletalCraniumCompact...

The Human Body

Muscles Cardiac Voluntary Muscle
Involuntary Muscle
Bone Marrow
Skeletal Cranium Compact Bone
Spongy Bone
Ligaments Tendon Cartilage
Vertebrae Brain X Ray Interesting Facts

Muscles
• Many of these are attached to bones and help you to move.

Cardiac
• The heart is this kind of muscle.
• This muscle never gets tired or sore like your leg muscles do.
• It is an involuntary muscle that controls the heart.

Voluntary Muscles
• You can contract and relax this in order to move body parts.
• Another name for Skeletal Muscles
• Flexing your biceps, chewing, running, and jumping are examples of this.

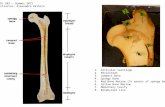
Skeletal
• This system is made up of over 22 bones!
• This system provides the framework for your body.
• We are born with 300 bones.

What is the Skeletal System?
• The Skeletal System is all of our bones
• It is the frame of our body
• Without bones, we would be floppy
• Some bones protect our fragile insides. Our skull protects our brain and our ribs protect our lungs, heart, and other insides

How Many Bones Do Humans Have?
• Humans are born with 300 bones
• As we grow our bones fuse, or grow together
• Adults have 206 bones

Are Bones Alive?
• Yes!
• Bones are made of hard stuff for strength and living cells to help them grow and repair themselves

How Do Bones Move?• Bones need muscles to help them move
• Joints are the place where two bones meet allowing them to move
• Our elbows, shoulders, knees, neck, and hips are joints

Cranium
• This is the part of the skull that protects your brain.
• It is the top part of your skull.

Bone Marrow
• This is where red blood cells are made.
• This is a soft jelly-like material that fills the inside of our bones.

Involuntary Muscles
• These are muscles that we do not control.
• Breathing
• This kind of muscle is also called a smooth muscle.

Compact Bone
• This is the hard outer part of the bone.

Spongy Bone
• The inner part of the bone

Ligaments
• These connect bones to other bones
• These connect one vertebrae to another

Tendon
• This connects muscles to bones
• This is the part that is named after Achilles

Cartilage• This is like a shock absorber for our bones
• This is what cushions the bones in your spinal column
• This is what the tip of your nose is made of

Vertebrae• There are 24
stacked on top of one another to make up the spinal column
• They are smaller in your neck than in your back
• There is one fused together in your spinal column called your tail bone

The Brain
• The brain is made up of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla.
• The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum.
• The medulla is connected to our spinal cord. It controls blood circulation and breathing.
• The cerebellum controls our balance and posture.

X-Rays
• X-rays are special pictures of our skeletal system.
• These pictures help us to see the inside frame of our bodies.

Did you know that…..
• Say cheese! When you smile, you use 17 muscles!
• Your stomach digest about 2, 190 quarts of food each year. That’s around 8,760 bowls of spaghetti!
• If you could line up all of your blood vessels, they would wrap around the world 4 times!
• When you sneeze, air comes out of your lungs at over 100 miles per hour!
• Your brain weighs only about 3 pounds, but it can store billions of bits of information!