The General and Special Senses
description
Transcript of The General and Special Senses

1
THE GENERAL AND SPECIAL SENSES
Chapter 9

2
Overview I•The 4 general receptor classes are throughout the body and are:•Temperature•Pain•Touch, Pressure, Position•Chemical
•Your book lists about 6 different general receptors, then explains them in different categories.

3
Overview II•The 5 special senses are localized and are:•Smell (olfactory)•Taste (gustation)•Vision (optical)•Balance (equilibrium)•Hearing (auditory)

4
Overview III•Sensory receptor•Specialized cell, sends sensation to the CNS•The simplest are free nerve endings•The complex-est are specialized•Each monitors a specific receptor field

5
Overview IV•Sensory info•Relayed via action potentials in a sensory (Afferent) fiber•Larger the stimulus = greater frequency of action potentials•CNS interprets the nature of the arriving info on the basis of the area of the brain stimulated•SENSATION is arriving information•ADAPTATION is a reduction in sensitivity in the presence of a constant stimulus• Done via change in sensitivity or inhibition of sensory pathways

6
THE GENERAL SENSES 1/4PAIN
•NOCICEPTORS• Fast pain• Prickling
• Slow pain• Burning (not necessarily temperature-related) and aching
•Perception of pain in parts not actually hurting is called referred pain (Also, auxiliary pain)•This is because nociceptors have a large receptive field.•Sensitive to: temperature extremes, mechanical damage, dissolved chemicals (e.g. histamine from mast cells)

7
THE GENERAL SENSES 2/4TEMPERATURE
•THERMOCEPTORS•Respond to changes in temperature•Located in dermis, skeletal muscles, liver, hypothalamus•Cold thermoreceptors•Hot thermoreceptors• No known structural differences between these• 3-4 times as many cold to hot thermoreceptors

8
THE GENERAL SENSES 3/4MECHANORECEPTORS
•Sensitive to stimuli such as:•Stretching•Compression• twisting

9
THE GENERAL SENSES 3a/4TOUCH
•TACTILE RECEPTORS•Distinctions are not as precise• Free nerve endings: touch and pressure• Root hair plexus: distortions and movement on the body surface•Merkel (tactile) discs and Merkel cells: fine touch•Meissner’s (tactile) corpuscle: fine touch and pressure LF vibration• Lamellated (pacinian) corpuscle: pulsing, HF vibration, • Ruffini corpuscle: pressure and distortion of the skin

10
THE GENERAL SENSES 3b/4PRESSURE
•BARORECEPTORS•Sensitive to pressure•Provide info for the autonomic activities•Rapid response•Rapid adaptation

11
THE GENERAL SENSES 3c/4POSITION
•PROPRIOCEPTORS• Sensitive to position•Monitor position of joints, tension in tendons and ligaments, and the state of muscle contraction• Free nerve endings, Golgi tendon organs, muscle spindles
•Do not adapt• Primarily subconscious processing and only a minor amount of conscious awareness• Your sense of body position comes from these and the info from the inner ear

12
THE GENERAL SENSES 4/4CHEMICAL
•CHEMORECEPTORS•Respond only to these substances dissolved in the surrounding fluid:•Water-soluble• Lipid-soluble
•Primarily measure pH, CO2, and O2

13
THE SPECIAL SENSES – 1/5•SMELL (olfaction)•OLFACTORY RECEPTOR CELLS•Mucus is formed over the olfactory epithelium to help:• prevent the buildup of potentially dangerous/overpowering stimuli• Keeps the area moist• Keeps are free of debris•Only smell about 2% of inhaled air•Must be water or lipid soluble•Diffuses through mucous before they can stimulate olfactory receptor cells.

14
THE SPECIAL SENSES – 2/5•TASTE•GUSTATORY RECEPTORS (tastebuds)•Over tongue and adjacent parts of the pharynx and larynx (voicebox).•Cirvumvallate papillae: large clusters of tastebuds, come in contact with DISSOLVED food.•Primary taste sensations: sweet, sour, salty, bitter.•Tastebuds in all parts of the tongue can provide all taste sensations.•Technically, there is a 5th sensation: water.•Most sensitive to extremes of pH.

15
ANATOMY OF THE EAR – •Ear is divided into 3 parts:•External: collects and directs sound waves toward the middle ear.•Middle: collects and amplifies sound waves toward a portion of the inner ear.• Inner: contains the sensory organs for hearing and equilibrium.

16
ANATOMY OF THE EAR – 1/3•EXTERNAL EAR•Our regular “ear” or the auricle (also, pinna)•Cerumen (Earwax) is important:•Together with outward-facing hairs, helps prevent foreign stuff, including insects from entering.
•Tympanum/tympanic membrane (eardrum)•Separates external from middle ear

17
ANATOMY OF THE EAR – 2/3•MIDDLE EAR•The tympanic cavity, mechanically amplifies audio•Also connects to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian/pharyngotympanic tube.•Unfortunately, you can get an ear infection (otitis media) from microorganisms going up this passageway.•Auditory ossicles: hammer, anvil, stirrup•Muscles can control the amplification of the audio.

18
ANATOMY OF THE EAR – 3/3• INTERNAL EAR•3 primary parts:•Vestibule (equilibrium)•Semicircular canals (equilibrium)•Cochlea (hearing)

19
THE SPECIAL SENSES – 3/5•EQUILIBRIUM•2 types:•Dynamic•Static
•Semicircular ducts: rotational motion•The vestibule: gravity and linear acceleration

20
THE SPECIAL SENSES – 4/5•HEARING
•The ear senses FREQUENCIES•LF near center, HF at outside, where the cochlea is stiffer.•Movement of basilar membrane is amplified as it goes to the tectorial membrane.

21
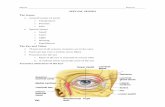
THE SPECIAL SENSES – 5/5•VISION

22
Accessory Structures - •Eyelids and associated exocrine glands•Superficial epithelium of the eye•Structures associated with the production, secretion, and removal of tears•The extrinsic eye muscles (muscles outside of the eye itself)

23
Accessory Structures –•Eyelids/palpebrae – act as lubricating windshield wipers•Connected to the canthuses•Associated diseases:•Sty•Conjuctivitis•Lacrimal apparatus