The Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle Department of Animal Science & Technology...
-
Upload
sophia-parker -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
3
Transcript of The Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle Department of Animal Science & Technology...

The Excitation-contraction The Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal musclecoupling in skeletal muscle
Department of Animal Science & TechnologyDepartment of Animal Science & Technology
National Taiwan UniversityNational Taiwan University
De-Shien JongDe-Shien Jong

OutlineOutline
Excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal Excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal musclemuscle
Charge movement & Calcium releaseCharge movement & Calcium release Poor man’s fura-2Poor man’s fura-2 Model of Ca releaseModel of Ca release Effects of Ca on kinetics of charge movementEffects of Ca on kinetics of charge movement Model of charge movementModel of charge movement

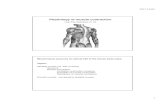
Peachey, 1965
Schematic drawing of skeletal muscle

Excitation-Contraction couplingExcitation-Contraction coupling
Skeletal muscleSkeletal muscle Action potentialAction potential → Motor neuron → Neuromu → Motor neuron → Neuromu
scular junction → muscle surface → Transversscular junction → muscle surface → Transverse tubular system (T-system) → Triad → Dihyde tubular system (T-system) → Triad → Dihydropyridine Receptors (DHPR) → Ryanodine Rropyridine Receptors (DHPR) → Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) → eceptors (RyR) → CaCa2+2+ release release from SR → bin from SR → bind to troponin → induce muscle contractiond to troponin → induce muscle contraction
How does DHPR and RyR talk to each other?How does DHPR and RyR talk to each other?

Excitation-Contraction couplingExcitation-Contraction coupling
Cardiac muscleCardiac muscle Action potential → Triad (or Diad) → DHPR Action potential → Triad (or Diad) → DHPR
→ Ca→ Ca2+2+ entry → Ca entry → Ca2+2+ bind to RyR → Ca bind to RyR → Ca2+2+ indu induce Cace Ca2+2+ Release → Ca Release → Ca2+2+ bind to contractile prot bind to contractile protein → muscle contractionein → muscle contraction
DHPR is L-type voltage-gated CaDHPR is L-type voltage-gated Ca2+2+ channel w channel which has two isoforms : Skeletal type & Cardiahich has two isoforms : Skeletal type & Cardiac typec type


Tanabe et al. 1988

Tanabe et al. 1990

Ryanodine ReceptorRyanodine Receptor
RyR has two isoforms in amphibian muscle : RyR has two isoforms in amphibian muscle : & &
RyR has three isoforms in mammalian muscle RyR has three isoforms in mammalian muscle : RyR1, RyR2, and RyR3: RyR1, RyR2, and RyR3 RyR1 mainly in skeletal muscleRyR1 mainly in skeletal muscle RyR2 in cardiac muscleRyR2 in cardiac muscle RyR3 in most other cells (i.e. brain)RyR3 in most other cells (i.e. brain)

Felder & Franzini-Armstrong, 2002
Ferguson et al. 1984

Franzini-Armstrong, 2004

Charge movement & CalciuCharge movement & Calcium releasem release
Dr. W. Knox Chandler
Dr. Paul C. Pape
Dr. Steve M. Baylor

Miledi et al. 1977, Caputo et al. 1984 Chandler et al. 1976


Effects of increased [CaEffects of increased [Ca2+2+]]ii
Bind to contractile protein troponinBind to contractile protein troponin Bind to various intrinsic Ca buffersBind to various intrinsic Ca buffers Activate additional release of Ca from the SR Activate additional release of Ca from the SR
(Ca induced Ca release)(Ca induced Ca release) Reduce additional Ca release from the SR (Ca Reduce additional Ca release from the SR (Ca
inactivation of Ca release)inactivation of Ca release) Bind to Ca indicatorsBind to Ca indicators

Irving et al. 1987

Poor man’s fura-2Poor man’s fura-2

Experimental methodsExperimental methods
A cut frog muscle fiber was mounted on a douA cut frog muscle fiber was mounted on a double Vaseline-gap chamberble Vaseline-gap chamber
Extracellular and intracellular solutions contaiExtracellular and intracellular solutions contain ion replacement to eliminate ionic currentsn ion replacement to eliminate ionic currents
Internal solution contained 20 mM EGTA plus Internal solution contained 20 mM EGTA plus 1.76 mM Ca1.76 mM Ca2+2+, which expecting to catch all the , which expecting to catch all the Ca released from the SRCa released from the SR


Fractional phenol red in the nonprotonated form f
f = (r - rmin) / (rmax - rmin)
where
r = Aind(570) / Aind(480)
pH = pk + log (f / (1 – f))
480 nm : isobestic wavelenth of phenol red
570 nm : a wavelength at which phenol red is sensitive to pH
690 nm : a wavelength not absorbed by phenol red

Estimation of Ca buffering power of muscle fiber




Advantages of Advantages of EGTA-phenol red methodEGTA-phenol red method
The EGTA-phenol red method estimates SR CThe EGTA-phenol red method estimates SR Ca release reliably (~ 96%) and Rapidly (<0.1 ma release reliably (~ 96%) and Rapidly (<0.1 ms).s).
The change in pH does not alter physiological The change in pH does not alter physiological condition and the buffering power condition and the buffering power is stable. is stable.
The dissociatin rate of Ca and EGTA, kThe dissociatin rate of Ca and EGTA, k -1-1, is s, is s
mall (~ 1 small (~ 1 s-1-1) compared to that of Ca and fura-) compared to that of Ca and fura-2 (~10-30 s2 (~10-30 s-1-1).).

k1[EGTA]-1 = 22 s
So the [Ca] signal estimated from pH would be the same amplitude as the measurement with PDAA

Model of Model of [Ca] near a single [Ca] near a single SR Ca channelSR Ca channel

[Ca] = / (4 DCa r) * exp ( -r / Ca)
Where CaDCak1[EGTA]R}1/2 = 81 nm

Time course of [Ca] after a step change in from a single point source in an isotropic infinite medium.

e-fold increase in d[CaT]/dt every 3.73 mV

Effects of released Ca on chaEffects of released Ca on charge movementrge movement




= Icm / (Qoo – Qcm)









Model of charge movementModel of charge movement

0/0 = exp[(v - v0)/k]

n = f n 0, n = f n 0 n = f n 0, n = f -n 0
Case 1 Case 2

n = f’f n 0, n = f’f -n 0
Case 3 Exp. Data

Calcium sparkCalcium spark

Thank youThank you