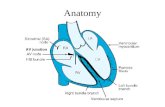
The ECG and Toxicology Adam Davidson June 4, 2009.
-
Upload
audra-gaines -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of The ECG and Toxicology Adam Davidson June 4, 2009.

The ECG and Toxicology
Adam DavidsonJune 4, 2009

Toxicologic Window While many toxic ECG changes are non-
specific, it can be helpful with the diagnosis in certain cases
The ECG often our first clue to a “toxic” patient
Easy to get and available before blood work, urine, etc
Can be used to guide and monitor therapy

Objectives
Review cases highlighting ECG changes for some specific overdoses
Discuss the ECG as a guide predicting toxicity with TCA overdose
Discuss the ECG as a guide for therapy in the TCA overdose

Case 1
74 yo M presents with altered mental status
Vitals: HR 38, BP 110/55, Afeb, SaO2 97%
PMHx: HTN, CHF, Oteoarthritis Meds: Unknown

ECG 1:

ECG 2:

Digoxin ECG changes when “therapeutic” and
toxic Classic Toxicity:
Increased automaticity with AV block Bi-directional V tach (rare)
Dig Effect: T Wave flattening/inversion/biphasic ST scooping (Salvador Dali) QT shortening PR prolongation

Dig Toxicity Ectopic Rythms
Atrial tach with block Junctional Tach V tach (Uni and bi-directional)
Conducction AV blocks
Automaticity PVS’s, PAC’s

Case 2:
74 yo M presents with collapse and altered mental status
Vitals: Afeb, HR 34, BP 84/40, SaO2 97%
PMHx: Atrial fibrillation

ECG 1:

ECG 2:

Beta-Blockers ECG Findings
Sinus Brady AV blockade
Special Cases Propanolol: -Na Channel Blockade (Wide QRS) Sotalol: -K Channel Blockade (Prolonged QT and risk
for Torsades)

CCB’s
At toxic levels the selectivity of the drugs is lost
All types will have both cardiac and vascular effects at high doses
ECG abnormalities can be delayed b/c of sustained-release tabs

CCB’s vs BB’s
CCB assoc with hyperglycemia BB assoc with euglycemia or mild
hypoglycemia Mental status is often preserved w/
CCB’s

Case #2 cont’d
What if case #2 had a PMHx of chronic kidney disease instead of A fib?

ECG:

DDx Hypotension and Bradycardia
The Big 4: BB’s CCB’s MI Hyper K

Case #3
44 yo F presents confused and tremulous
Vitals: Afeb, HR 53, BP 110/65, SaO2 100%
REDIS History: mulitple psych visits NeuroExam: hyper-reflexia, clonus,
mild ataxia

ECG:

Lithium Toxicity Acute toxicity associated with GI, Neuro
and Cardiac findings ECG:
T wave flattening/inversion- present in many patients at “therapeutic levels”
Diffuse TWI suggests severe toxicity U Waves Sinus Node Dysfunction- bradycardia and
junctional escape rythms Ventricular dysrhythmias are rare

Case #4
38 yo M presents after witnessed seizure
Vitals: Afeb, HR 112, BP 143/94, SaO2: 99%
PMHx: Depression, Insomnia

ECG:

TCA Overdose
Amitriptyline increasing in use for insomnia, migraines, chronic pain
Toxic effects are neurologic and cardiac
ECG is the #1 test to predict toxicity, guide, and monitor therapy

Rick Morris Pimp Question
SEVEN!!!! Re-uptake inhibition of Serotonin Re-uptake inhibition of Norepinephrine Na Channel Blockade Alpha blockade Anti-cholinergic Anti-histaminic Anti-GABA
How many different receptors/neurotransmitters are affected by TCA’s? Can you name them?

ECG Effects of TCA’s Sinus tachycardia Widening of QRS Rightward deviation of terminal
40msec: seen as R wave in AVR and S waves in I and AVL Not specific for toxicity in children
QT prolongation RBBB

Predicting Toxicity QRS > 120- high risk for seizures QRS > 160- high risk for dysrythmia QRS > 100- generally considered
the threshold to start HCO3 therapy AVR R wave >3mm
81% sens, 73% sp for szr or dysrythmia AVR R wave >5mm
50% sens, 97% sp for szr or dysrythmia

Sodium Bicarbonate
Initial Treatment? How do you prepare a drip? Why does it work? What are your end points of
therapy?

Thank YOU!!!

References
ECG in Emergency Medicine and Critical Care
Chan, Brady, Harrigan, Ornato, Rosen
2005