The Color Wheel
description
Transcript of The Color Wheel


History of Color• Colors are often
symbolic.• Let’s talk about what
role color has played in different times in history.

In China…• Yellow has religious
significance and is still the Imperial color today!

In Greece and Rome…• Red was believed to
have protective powers.
• Purple was restricted to use by nobility.

The Egyptians• Adorned walls of
tombs and temples with brilliant colors of blue, tangerine, and green.

In the Italian Renaissance…• Colors were vibrant
reds, greens, golds and blues.

In the Rococo period…• Tastes became
very feminine, colors became less vibrant.

In 18th Century England…• There was great
elegance. Colors were rich, showing a strong Chinese influence in the use of red and gold.

During the Victorian era…• There was great
Eclecticism known for it’s abundance of “things”.
• Colors were mostly dull reds, greens, browns, and mauves.

In the Early 20th Century… • Colors were
Monochromatic. There were sleek surfaces and strong contrasts with black, gray, silver, brown, beige and white.

In the 1920’s…• All-white interiors
became popular which gave way to delicate pastels with bright accents.

In the 1950’s..• Light colors were
preferred.• However,
American interest turned to Mexico and a shift to bright colors with bright contrasts.

And in the 1990’s…• Regal gold, blue,
and red were used. Southwestern remained popular and Victorian was being revived.
• Ivy league also becomes popular with forest greens and cranberry reds.

Where does color come from?• A ray of light is the
source of all color.• Without light, color
does not exist.• Light is broken down
into colors of the spectrum. You can often see a variety of colors in a bright beam when you look at something like a rainbow.

Color• Color can alter the
appearance of form and space.
• Color can affect our performance abilities and change our moods.

Pigments• Pigments are substances that
can be ground into fine powder and used for adding color to dyes and paints.
• Pigments were originally derives from animal, mineral, and vegetable sources.
• Examples:– Purple from shellfish– Red dye from the dried bodies
of scale insects• To create our own color wheel,
we will be mixing different pigments together to create all the colors in the color wheel.

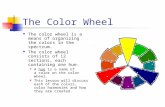
The Color Wheel• The color wheel is a basic tool we
use when working with colors. • It is based on the standard color
theory known as Brewster/Prang. • In addition to the traditional color
wheel, there are two color systems that are useful when more detailed colors are required.– The Munsell system:
• Has 5 principles hues and 5 intermediate hues. A numbering system helps designers identify the exact hue they need.
– The Ostwald system:• Made from pairs of complementary
colors. The color circle has twenty-four hues.

The Color Wheel
• There are 12 hues in the spectrum of color.
• They are divided into three categories…
Red-vio let
V io let
B lue-vio le tB lue
B lue-green
G reen
Yellow -green
Yellow
Yellow -orange O range
Red-orange
R ed

The Primary Colors• Red, Yellow, and
Blue• These colors
cannot be combined from mixing any colors together.
R ed-vio le t
V io let
B lue-v io le tB lue
Blue-green
G reen
Yellow -green
Yellow
Yellow -orange O range
R ed-orange
R ed

The Secondary Colors• Green, violet, and
orange• Made by
combining the Primary colors together.
R ed-vio le t
V io let
B lue-v io le tB lue
Blue-green
G reen
Yellow -green
Yellow
Yellow -orange O range
R ed-orange
R ed

The Tertiary Colors• Yellow-green, blue-
green, blue-violet, red-violet, red-orange, yellow-orange.
• Made by combining a primary and a secondary hue.
• Named by the Primary color first.
R ed-vio le t
V io let
B lue-v io le tB lue
Blue-green
G reen
Yellow -green
Yellow
Yellow -orange O range
R ed-orange
R ed

Color Wheel Assignment• Now it’s your turn to create
your own color wheel! • You decide whether you
want to earn full credit by completing the assignment as shown here…
• Or you can earn extra credit, by creating another picture with your color wheel…– A rainbow, a tire, a flower,
etc.• Make sure to label all twelve
colors correctly, and label your assignment in architectural writing with your name, assignment name and period.