The Cell Ch. 7. Cell History Hooke - is the scientist who 1st coined the term “cell” – in the...
-
Upload
ariel-mood -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
3
Transcript of The Cell Ch. 7. Cell History Hooke - is the scientist who 1st coined the term “cell” – in the...

The Cell
Ch. 7

Cell History• Hooke - is the scientist who 1st coined the
term “cell” – in the 1660’s he observed cork from a tree stem (they reminded him of the rooms monks lived in)
Schleiden looked at plant cells & Schwann looked at animal cells. They both observed that cells make up all parts of an organism. Along with Virchow they formulated the Cell Theory.

• Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow

The Cell Theory
• It has 3 components.1. All living things are made of cells.
• 2. Cells are the basic units of structure & function.
• 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells.

Variety in Cells • Cells come in a great variety of shapes & sizes. The
smallest cells are mycoplasmas & the largest cells are ostrich eggs. The size & shape of the nerve cell are related to its function.
• Sketch of a skin cell:
• Sketch of a nerve cell:

Cell Size• The surface area of the cell does not
increase at the same rate as the volume. Because of this, cells typically stay small & will divide rather than getting larger.

Differences in Cells•
1. Prokaryotes - have no true nucleus – DNA is not arranged into chromosomes – ex. = bacteria – they have no membrane-bound organelles.

• 2. Eukaryotes - have a nucleus - & cellular organelles.

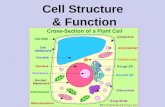
Parts of the Cell
• 1. Nucleus - control center of the cell – controls most of the activities of the cell ; also transmits hereditary information & contains DNA. The nucleus holds chromosomes (threadlike) that are seen only when the cell is dividing & chromatin (granular) when the cell isn’t dividing.

• 2. Nucleoli - these are found in the nucleus – where the assembly of ribosomes begins.

• 3. Nuclear envelope - double membrane - this surrounds the nucleus & acts as a boundary between the nucleus & the cytoplasm – it contains pores that allow substances to pass

• 4. Cell membrane - this acts as the outer boundary of the cell & contains phospholipids & proteins - it is very important because it regulates what enters & leaves the cell

• 5. Cell wall - this is found in plants, algae, fungi, & bacteria- it protects & supports the cell – it lies outside of the cell membrane & allows water & gases to pass through – plant cell walls are made of cellulose

• 6. Cytoplasm - is the jellylike layer of the cell – it contains the organelles & moves materials throughout the cell in a process called cytoplasmic streaming

• 7. Endoplasmic reticulum - this is a series of canals or channels that winds through the cytoplasm – it acts as the cell’s internal transport & connects with the nuclear envelope; there are 2 types – (1) smooth ER- this builds lipids for the plasma membrane, (2) Rough ER - has ribosomes attached - Protein synthesis

• 8. Ribosomes- the sites of protein synthesis; 2 types (1) Free - makes protein to be used in the cell, (2) Bound - make protein to be transported out of the cell

• 9. Golgi Bodies - these pinch off from the ER – they are stacks of membranes that look like tiny flattened balloons – they are areas for storage & packaging of chemicals – enzymes in this apparatus attach carbohydrates & lipids to proteins

• 10. Mitochondria - the cell’s powerhouse – they produce the energy for the cell – they have many folds on the inside called cristae that increase surface area for more energy

• 11. Plastids - are found only in plants – some store food, others have pigments – 3 types: (1) Leucoplasts - colorless – store starches in roots & stems (2) Chromoplasts - they are orange & yellow – beta carotene (3) Chloroplasts - these are green & the sites for photosynthesis

• 12. Vacuoles - bubblelike storage structures that store water, liquids, wastes, & foods – these hold plants erect & firm

• 13. Lysosomes - these are membrane-bound organelles that are formed in Golgi bodies – they are loaded with enzymes that digest large particles found in the cell – also break down old organelles

• 14. Microtubules - hollow cylinders of protein that support & shape the cell – found in the cytoskeleton, spindle fibers, centrioles, basal bodies , cilia, & flagella

• 15. Spindle fibers - appear during cell division & move chromosomes through the cytoplasm

• 16. Centrioles - small dark bodies located outside the nucleus – they are active during cell division

• 17. Cilia - short, threadlike structures used for movement – they are numerous & hairlike

• 18. Flagella - long, whiplike structures used for movement – usually only 1 per cell

• 19. Cytoskeleton - network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape – also involved in cell movement - these are made of:a) microtubules - hollow tubes of protein – maintain cell shape & serve as “tracks” along which organelles are moved (used to make cilia & flagella)b) microfilaments - long, thin fibers that function in the movement & support of the cell – tough, flexible framework that supports the cell

THE CELL – PART 2
• CELL TRANSPORTCells must get nutrients in & wastes out of the cell in order to stay alive. They have several methods of doing this. Some methods expend energy. Some do not. The cell membrane regulates what enters & leaves the cell & also provides protection & support. The cell membrane is a double-layered sheet called a phospholipid bilayer. The cell membrane is like a fluid-mosaic.




PASSIVE MECHANISMS
• – no cellular energy is required1. Diffusion - molecules or ions spread from higher concentrations to lower concentrations – this continues until equilibrium is reached

• 2. Facilitated diffusion - glucose combines with a special protein carrier that helps pass it across the membrane (still from higher concentration to lower concentration)

• 3. Osmosis - water molecules diffuse from a higher to a lower concentration (water tends to diffuse toward the area of higher osmotic pressure)

Tonicity• Drawing 1: • Drawing 2: • Drawing 3:
Cell is _______________ Cell is _________________ Cell is ________Solution is _______________ Solution is ________________ Solution is _____Cell will _________________ Cell will __________________ Cell will ______

• 4. Filtration - molecules are forced through membranes by the hydrostatic pressure that is greater on one side of the membrane than on the other (this usually happens with blood vessels)

ACTIVE MECHANISMS – cellular energy is required
• 1. Active transport - using carrier proteins to move substances from lower concentrations to higher concentrations (sugars, a.a.’s, ions)

• 2. Endocytosis - molecules that are too large to enter a cell by diffusion enter by the formation of a vesicle - 2 Types:a) phagocytosis - “cellular eating” – takes in solids (common in white blood cells) b) pinocytosis - “cellular drinking ” – takes in liquids (water)


• 3. Exocytosis - sends materials out of the cell

• Organisms with only one cell are called unicellular while organisms with many cells are called multicellular.

LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
•1. Cells - basic functional unit of life2. Tissues - group of similar cells that perform a particular function 3. Organs - groups of tissues working together4. Systems - group of organs working together (11 in the body)


















![CELL THEORY A Brief History. Robert Hooke named the cell [1665] based on observations of the cell walls of cork tissue.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649f265503460f94c3dff5/cell-theory-a-brief-history-robert-hooke-named-the-cell-1665-based-on-observations.jpg)
