The Adrenal Glands
description
Transcript of The Adrenal Glands

The Adrenal Glands
By: Jenny Desplat, Stephen Solinas, and Emila Danilowicz
Per. 1

Hormone control Growth Keeping blood normal Stress response Maintaining homeostasis Metabolism Sleep Mood Tissue function
Endocrine System

Adrenal Glands

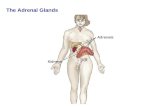
Sits over the kidney
Location

Hormone release
Stress response Regulating the osmolality of blood
plasma
Functions

Stress response
Cortisol, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine
Regulating the osmolality of blood plasma Aldosterone
Hormones Released

Steroid Hormone
Glucocorticoid Responds to stress Responds to low levels of
glucocorticoid in blood Immune system
suppressant Aids in Fat, Protein, and
Carbohydrate metabolism Synthetics can be used to
treat diseases
Cortisol

Hormone and
Neurotransmitter Regulating heart
rate, blood vessel and air passage diameters, and metabolic shifts
Triggers Fight-or-Flight response Central nervous
system response to stressful situations
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)

Neurotransmitter Increases heart
rate Norepinephrine
also underlies the fight-or-flight response
Triggers release of glucose
Increases brain’s oxygen supply
Norepinephrine

Controls sodium secretion of potassium
Increases amounts of water held in blood
Raises blood pressure
Increase water absorption into kidney
Aldosterone

Hyperaldosteronis
m
Causes: problems with adrenal glands causes them to release too much aldosterone
Symptoms: fatigue, headache, muscle weakness, numbness, paralysis (that comes and goes)
Causes: chromaffin cells found in core of adrenal glands cause tumors
Symptoms: high blood pressure, sweating, abdominal pain, headaches, anxiety, pale skin, weight loss
Pheochromocytoma

Hyperaldosteronis
m Pheochromocytoma

Each weigh 4 grams
Necessary for life
Made up of two regions Cortex Medulla
Interesting stuff

Mayo Clinic. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Apr. 2011.
<http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/ pheochromocytoma/DS00569/DSECTION=symptoms>.
Medline Plus. N.p., n.d. Web. 26 July 2011. <http://www.nlm.nih.gov/ medlineplus/ency/article/000330.htm>.
Encyclopedia.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 7 Mar. 2013. <http://www.encyclopedia.com/ topic/adrenal_gland.aspx>.
Bibliography

1) Which one is not a function of the Endocrine
System?a) Growth b) Keeping blood normalc) Protection d) Sleep
C
Concept Check Questions
2) Which hormone is not associated with the Adrenal Glands?
a) Prolactin b) Cortisolc) Epinephrine d) Aldosterone
A

3) Where are the adrenal glands located?
a) In the brain b) Above the kidneysc) In the pancreas d) In the Ovaries
B
Concept Check Questions
4) Explain what the hormone norepinephrine does.
Increases heart rate, underlies the fight-or-flight response, triggers release of glucose, increases brain’s oxygen supply.