The two ions that make up the action potential. The clamp half of the voltage clamp.
THE ACTION POTENTIAL · THE ACTION POTENTIAL Objectives: Understand the electrical underpinnings of...
Transcript of THE ACTION POTENTIAL · THE ACTION POTENTIAL Objectives: Understand the electrical underpinnings of...

THE ACTION POTENTIAL
Objectives:
Understand the electrical underpinnings of the action poten
Differentiate between voltage-time, current-time and currvoltage relations
Understand the electrical underpinnings of the action poten
Understand the general equation for macroscopic membrancurrent
Know the Nernst equation and the approximate concentratof Na+ and K+ ions inside and outside of cardiac cells


Superior
Vena CavaSA Node
Atrium
AV Node
Purkinje
Tricuspid Valve
Mitral Valve
Ventricle
ECGP
PR QRS
Q
R
S
T

Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley
&
Sir Alan Hodgkin
Cambridge University
Winners of the1963 Nobel Prize
for Physiology.

Axon Action Potential


IC = C dE/dt
Itot = IC + Iionic





Late = K+ curre
TEA sensitive
Early = Na+ cu
TTX sensitive

gK
gNa

gNagK


mV
30 ms
Na+
in
K+
out

IK = gK (Et - EK)
INa = gNa (Et - ENa)
gK = IK
(Et - EK)
gNa = INa
(Et - ENa)

+
+
+
Outside
Inside
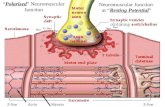
‘pore’
‘gate’
Voltage-gated Ion Channel

Outside
Inside
Sodium ionTetrodotoxin (TT
+
+
+

Outside
Inside
Potassium ionTetraethylammonium (TE
N
C2H5
C2H5
C2H5C2H5
+
+
+
+

Single-channel currents recorded from membra
of denervated frog muscle fibres.
Neher E, Sakmann B
Nature 260, 799-802, 1976
Nobel Prize 1991


pA = 10-12 A or 1/1,000,000,000,000th of an Amp
Or
1,000,000 ions per second per channel