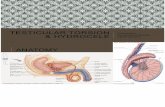
Testicular Torsion
-
Upload
fredys-arrechea-tartabull -
Category
Documents
-
view
300 -
download
7
description
Transcript of Testicular Torsion

March,2008March,2008Dept of Dept of surgerysurgery
SURGICAL EMERGENCY!!

Dr. Fidel Echevarria Fernandez Dr. Fidel Echevarria Fernandez First Degree Specialist in General Surgery First Degree Specialist in General Surgery Thoracic Surgeon Thoracic Surgeon Laparoscopic SurgeonsLaparoscopic Surgeons
Dr. Fredys Arrechea Tartabull Dr. Fredys Arrechea Tartabull First Degree Specialist in Anaesthesiology First Degree Specialist in Anaesthesiology and Resuscitation and Resuscitation Intensive Care Specialist Intensive Care Specialist Master in Clinical ToxicologyMaster in Clinical Toxicology

Epidemiology/Risk FactorsEpidemiology/Risk Factors1/4000 males <25 yrs annually1/4000 males <25 yrs annuallyCongenital malformation of processus Congenital malformation of processus vaginalis vaginalis (90% of cases)(90% of cases)
Covered testicle + epididymis + spermatic Covered testicle + epididymis + spermatic cord= free rotation of testis in tunica vaginalis cord= free rotation of testis in tunica vaginalis
BELL CLAPPER DEFORMITYBELL CLAPPER DEFORMITY
Trauma Trauma (4-8% of cases) (4-8% of cases) especially with especially with significant swelling significant swelling

Bell Clapper DeformityBell Clapper Deformity

Epidemiology/Risk Factors Epidemiology/Risk Factors (cont…)(cont…)
Other Other (2-6% of cases):(2-6% of cases):– Increase in testicular volume (puberty)Increase in testicular volume (puberty)– testicular tumortesticular tumor– testicles with horizontal lietesticles with horizontal lie– spermatic cord with long intrascrotal portionspermatic cord with long intrascrotal portion– Cryptorchidism (one or both testes)Cryptorchidism (one or both testes)– Strenuous exerciseStrenuous exercise

Diagnosis is Diagnosis is CRITICAL!!CRITICAL!!

Initially obstructs Initially obstructs venous returnvenous return
Equalization of venous and arterial pressures
Compromised arterial flow
TESTICULAR ISCHEMIA
As soon as 4 hours!!
Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion

ISCHEMIA vs Salvage RateISCHEMIA vs Salvage RateISCHEMIAISCHEMIA: as soon as 4 hrs: as soon as 4 hrs
almost CERTAIN in 24 hrsalmost CERTAIN in 24 hrs
Salvage Rate:Salvage Rate:90% success if < 6 hrs90% success if < 6 hrs50% success if <12 hrs 50% success if <12 hrs <10% success if >24 hrs<10% success if >24 hrs

Testicular Testicular PAIN!PAIN!
16-42%16-42% acute scrotal pain acute scrotal pain
TESTICULAR TORSIONTESTICULAR TORSION
NOT something you want to NOT something you want to miss!!!miss!!!

Differential Differential DiagnosisDiagnosis
Epididymitis/Orchitis
IncarceratedHernia
Idiopathic Scrotal Edema
Varicocele AppendixAppendix TestisTestis

NO DIFFERENCENO DIFFERENCE in in
PRESENTING PRESENTING SYMPTOMSSYMPTOMS

Clinical ExaminationClinical ExaminationEpididymitisEpididymitis: edematous , orange peel : edematous , orange peel (late),(late), possible pyuria possible pyuria
Appendix TestisAppendix Testis: hard, tender nodule : hard, tender nodule (2-3mm) (2-3mm) on upper pole of testicle, BLUE on upper pole of testicle, BLUE DOT sign, edema, epididymis remains DOT sign, edema, epididymis remains posteriorposterior
Scrotal EdemaScrotal Edema: develops rapidly : develops rapidly obscuring physical exam findingsobscuring physical exam findings
torsedappendage

Clinical Examination Clinical Examination (cont…)(cont…)
Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion: : – PAIN in scrotum: often described as PAIN in scrotum: often described as
“sharp and debilitating” “sharp and debilitating” – No necessary precipitant eventNo necessary precipitant event– Scrotal erythema and edemaScrotal erythema and edema- Possible Nausea/Vomiting- Possible Nausea/Vomiting– LightheadednessLightheadedness

Clinical Examination Clinical Examination (cont…)(cont…)
Testicular TorsionTesticular Torsion::– Epididymis: medially, laterally or anteriorly Epididymis: medially, laterally or anteriorly (depends on degree of torsion) (depends on degree of torsion) one side one side
– Spermatic cord shortens as it twists higher appearing testis
STRONG EVIDENCE OF TORSION

Clinical Examination Clinical Examination (cont…)(cont…)
Testicular Torsion: NO Cremasteric Reflex (most sensitive finding; 99%) if testicle moves ≥ 0.5 cm = +veTesticle:– Hard– Fixed to dartos & scrotal wall– Larger than unaffected side(due to congestion of blood)
Prehn’s sign negative

Diagnostic ModalitiesDiagnostic Modalities
Doppler UltrasoundDoppler Ultrasound Radionuclide Testing
Surgical Exploration
Imaging: ONLY IF
SUSPICION FOR TORSION =LOW
FasterMore available More sensitive

Evaluation of Acute Scrotal Evaluation of Acute Scrotal PainPain

TreatmentTreatmentRapid Rapid restoration of bloodrestoration of blood flow: flow: CRITICALCRITICALManual detorsionManual detorsion = = quick, noninvasive quick, noninvasive treatmenttreatment rotate testicle away from midline 180 degrees rotate testicle away from midline 180 degrees (done with IV sedation)(done with IV sedation) document return of blood flow document return of blood flow relieves problem acutely, however relieves problem acutely, however elective elective orchipexyorchipexy still recommended still recommended
DON’T DELAY SURGICAL CONSULT!!!DON’T DELAY SURGICAL CONSULT!!! only only definitive resolution of torsiondefinitive resolution of torsion
DON’T MISS THE DIAGNOSISDON’T MISS THE DIAGNOSIS
open book

Most Significant Most Significant ComplicationComplication
Loss of testisLoss of testis may lead to infertility may lead to infertilityCommon Causes of loss of testis:Common Causes of loss of testis:– 58%: DELAY in seeking medical 58%: DELAY in seeking medical
attentionattention– 29%: INCORRECT initial DIAGNOSIS29%: INCORRECT initial DIAGNOSIS– 13%: DELAY in TREATMENT at hospital!13%: DELAY in TREATMENT at hospital!

ConclusionConclusion
Surgical consult if necessarySurgical consult if necessary
DetorsionDetorsion
Exploration of scrotum if doughtful.Exploration of scrotum if doughtful.