Target VII Identify and describe the functions of the component structures of the plasma membrane:...
-
Upload
ariana-freeman -
Category
Documents
-
view
266 -
download
0
Transcript of Target VII Identify and describe the functions of the component structures of the plasma membrane:...

Target VII
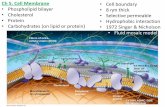
Identify and describe the functions of the component structures of the plasma membrane: phospholipid, integral protein, peripheral protein, cholesterol, hydrophilic head (polar), hydrophobic tails (non-polar), glycolipids, and glycoproteins.

The Cell Membrane
• Composed of macromolecules: phospholipids,
proteins, and carbohydrates
• Is selectively permeable . . .
• Phospholipid bilayer is amphipathic
– Hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails
– Hydrophilic phosphate heads
• Structure and movement of cell membrane is
described as the FLUID MOSAIC MODEL

I. FLUIDITY of MembraneA. Lipids and proteins move laterally within the membrane
B. Fluidity depends upon a variety of factors:1. Type of hydrocarbon tails2. Temperature3. Presence of cholesterol4. Composition of lipids and proteins within the
membrane (dynamic)5. Whether membrane components are attached to ECM
or cytoskeleton

I. FLUIDITY of MembraneC. Proper functioning of membrane depends upon
membrane fluidity
D. Fluidity can be altered by changing composition and quantity of proteins and/or lipids within membrane
-->Adaptations of plants and smaller vertebrates to cold temperatures in winter

II. Mosaic:assortment of various proteins w/in membrane
A. PROTEINS determine function(s) of membrane1. Integral Proteins
*transmembrane protein*describe the domain (portion) of the protein that
is embedded within the membrane
2. Peripheral Proteins*If inside cell, held in place by cytoskeleton*If outside cell, held in place by Extracellular
matrix (ECM)3. One protein may have multiple functions OR
several different proteins are required in a membrane to accomplish cellular tasks

Hydrophobic/philic Domains

II. Mosaic:assortment of various proteins w/in membrane
B. Carbohydrates are located on the exterior surface of plasma membrane
1. Cells communicate with and recognize each other by the types of CHO on their exterior plasma membrane surface (ex: A, B, O blood types)
2. Oligosaccharides may be bound to lipids or proteins (oligo- = Few; ~15 monosaccharides)
a. Glycolipid b. Glycoprotein


Target VIII
Use representations, models, and/or data to analyze situations in which molecules move passively by diffusion, osmosis, or facilitated diffusion.

III. Movement Across MembranesA. Membrane is selectively permeable
1. What does selectively permeable mean?
2. Name examples of molecules that CAN pass thru cell membrane… WHY can they pass thru?
3. Name examples of molecules that CANNOT pass thru c.m WHY can’t they?
B. Functions of membrane proteins
1. Transport: water, ions, glucose
2. Enzyme Activity: cellular respiration, photosynthesis
3. Signal Transduction: bind protein hormone
4. Intercellular joining: tight &/or gap junctions, desmsomes
5. Cell to Cell Recognition: glycoproteins
6. Attach cell to ECM and/or cytoskeleton
1. All transport proteins must be ________, because….

Membrane Protein Functions

IV. Passive TransportA. Movement of molecules down concentration gradient; from
high [ ] to low [ ]
B. Membrane must be permeable for molecules to diffuse
C. Once equilibrium is reached, NET molecular movement is
EQUAL both into and out of cell
**molecules DO NOT stop moving**
D. Diffusion HAPPENS (no energy required!)
E. Diffusion of one type of molecule occurs independent of
another molecule if they’re both permeable; direction of
diffusion for each molecule depends upon [ ] of a particular
molecule across membrane
F. Can be: Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis

V. Facilitated Diffusion A. ‘Help’ polar and charged molecules across membrane
thru transport (integral) proteins1. Recall transport proteins are specific to molecules they move (like enzyme/substrate specificity)2. Transport proteins can be saturated therefore, they have a maximum rate of moving stuff due to limited # of proteins within membrane3. Transport proteins can be inhibited4. ‘Catalyze’ physical movement of stuff that would not be able to cross membrane
B. Molecules move down concentration gradientC. AQUAPORINS: transport protein for waterD. GATED CHANNELS: stimulus (electrical or chemical),
cause opening & closing--> stimulus causes change of protein shape

V. Facilitated Diffusion E. Examples of gated channels:
Ligand-gated Voltage-gated Mechanically-gated

VI. Osmosis (a type of passive transport)A. Movement of WATER from high [water] to low [water]B. Water follows solutes… water moves from area of low
[solute] to area of high [solutes]C. Direction of water movement depends upon [ ] of water and
solutes across a membrane between a cell and solution (environment)
D. Osmosis and Cells
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Plant & Animal Cell Osmosis ReviewA. hypotonic solution
-->low [solute] in solution compared to cell
animal cell: lysed plant cell: turgid
B. HYPERTONIC solution:
-->high [solute] in solutionn compared to cell
animal cell: crenate plant cell: plasmolysed
C. ISOTONIC solution: =[solute] in solution & cell
animal cell: normal plant cell: flaccid

Osmosis

VI. Osmosis Water balance for Osmoregulators
1. In cells WITHOUT cell walls (animals, protists)•MUST control amount of water entering and leaving cell
if not in an environment that is isotonic to cell = osmoregulate
•Osmoregulators use ENERGY to maintain internal osmotic balance different from the surrounding environment
•example: Paramecium contractile vacuole
-->The pond in which the Paramecium lives is ______
to the cell, so water moves ______ and cell has to use energy to pump water ______ the cell

Paramecium Contractile Vacuole

VI. Osmosis Water balance for Osmoregulators
2. In cells WITH cell walls (plants, fungi, bacteria)
•Cells prefer to be in a HYPOTONIC solution because water enters cells and pressure of extra water in vacuole pushes against cell walls.
•The water pressure in the vacuole is exterted onto and by nearby cells which makes cells TURGID - very firm so plant structures (stems, leaves) stand upright :)
•In isotonic solution cells lack adequate ‘push’ from water in nearby cells…FLACCID-plants wilt, droop:|
•In hypertonic solution, cell wall NOT an advantage, cell shrinks and plasma membrane pulls away from cell wall…PLASMOLYSIS - lethal to cell :(

Target IX
Use representations, models, and/or data to analyze situations in which molecules move actively to establish concentration gradients across a membrane or move large molecules into or out of a cell (endocytosis and exocytosis).

Co-Transport

VII. CO-TRANSPORT (active transport)
SYMPORT (Active, Indirect) ANTIPORT (Active, Direct)
Hyperlink to Animation

How do macromolecules enter or exit cells?
How do large quantities of substances enter or exit cells?
There are FOUR ways!

IIX. EXOCYTOSIS
A. Secrete large molecules out of cell
B. Cellular vesicles fuse with plasma membrane
C. Process of fusion repairs / replaces cell membrane
D. Process deposits proteins from inside surface of vessicle membrane to outer surface of cell
membrane b/c vesicle turned inside out as it becomes part of plasma membrane
E. Therefore, exocytosis ensures the plasma membrane will display its characteristic CELL SURFACE
proteins which dictate membrane function

IX. ENDOCYTOSIS
A. Phagocytosis: cell eating
More animations
B. Pinocytosis: cell drinking
Another animation of pinocytosis
X. Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
-->Intake of specific molecules, regardless of their concentration, due to specificity and affinity of ligand (binding molecule) to it’s ligand-receptor protein on cell surface
-->Example Animation: Cholesterol Metabolism

X. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis