Endocrine system.pdf · The Adrenal glands: The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands)...
Transcript of Endocrine system.pdf · The Adrenal glands: The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands)...
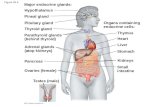
The endocrine system is a chemical messenger system comprising of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system.
The pituitary gland
▪ The pituitary gland, in humans, is a pea-sized gland(weighing 0.5 grams)
▪ that sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica.
▪ It is composed of three lobes: anterior, intermediate, and posterior.
The pituitary gland
▪ The anterior lobe :
S.No. Type of cell Hormone secretedPercentage of
type of cell
1. Somatotropes human growth hormone (hGH) 30-40%
2. Corticotropes adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) 20%
3. Thyrotropes thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) 3–5%
4. Gonadotropes
gonadotropic hormone i.e., both luteinizing
hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone
(FSH)
3–5%
5. Lactotropes prolactin (PRL) 3–5%
The pituitary gland
▪ The posterior lobe:
▪ The posterior pituitary stores and secretes (but does not synthesize) the following important endocrine hormones:
▪ Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, also known as vasopressin and arginine vasopressin AVP)
▪ Oxytocin
The Thyroid :
The Thyroid :
▪ The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ composed of two lobes.
▪ It weighs 25 grams in adults.
▪ with each lobe being about 5 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 2 cm thick.
▪ The thyroid is near the front of the neck, lying against and around the front of the larynx and trachea .
Hypothyroidism :
Symptoms: Fatigue
Increased sensitivity to
cold
Muscle aches and
weakness
Constipation Pain, stiffness or swelling
in your joints
Heavier than normal or
irregular menstrual
periods
Signs : Dry skin
Weight gain Slowed heart rate
carpal tunnel
syndrome
Slowed heart rate
Hoarseness Impaired memory
Elevated blood
cholesterol level
Enlarged thyroid
gland (goiter)
Thinning hair myxedema
Hyperthyroidism :
Symptoms:
Increased sweating and
heat intolerance
palpitations
lethargy Increased bowel
frequency
Breathlessness Muscle weakness
Signs: Tachycardia
Warm extremities Goitre
Arrhythmias Proximal myopathy
Increased irritability Loss of weight
The Adrenal glands:
▪ The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones.
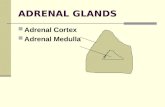
▪ They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla.
▪ The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones:
1. the zona glomerulosa.
2. the zona fasciculata.
3. the zona reticularis.
The Adrenal cortex:
▪ Zona glomerulosa:( المنطقة الكبية)
▪ Is The outermost zone of the adrenal cortex It lies immediately under the fibrous capsule of the gland
▪ This layer is the main site for production of aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid
▪ Zona fasciculata : (المنطقة الحزمية)
▪ it is situated between the zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis.[
▪ It is the largest of the three layers, accounting for nearly 80% of the volume of the cortex.
▪ This layer is the main site for production of glucocorticosteroids (cortisol)
▪ Zona reticularis ( :المنطقة الشبكية)
▪ The innermost cortical layer
▪ . It produces androgens, mainly dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione (the precursor to testosterone) in humans.
Cushing’s syndrome:
Symptoms:
oligomenorrhea
Decreased sex drive
Hirsutism(females)
fatigue
Muscle weakness
Signs: Central obesity
Moon face Acne
bruising Purple strains
Osteoporosis Secondary diabetes
Poor wound healing Pigmentations(ACTH related)
High levels of free fatty acids Arterial hypertension
Addison’s disease :
Symptoms:
Weakness
Lethargy
Salt craving
anorexia
amenorrhea
Decreased sex drive
signs
Hyperpigmentation of the skin
Hypotension
Weight loss
Vitiligo(البهاق يتظاهر عند مرضى داء اديسون المناعي الذاتي )
The pancreas :
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates.
In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland.
The pancreas has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function.
As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin,
glucagon, somatostatin
Diabetes Mellitus:
Symptoms:
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Extreme hunger
Sudden vision changes
Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
Feeling very tired much of the time
Signs:
Unexplained weight loss
Very dry skin
Sores that are slow to heal
More infections than usual
Sheehan syndrome:
Symptoms:
•irregular menstrual
periods (oligomenorrhea)
or no periods
(amenorrhea)
•fatigue or weakness
•difficulty breastfeeding
or an inability to
breastfeed
•intolerance to cold
•decreased sex drive
• joints pain
Signs: •weight gain
•loss of pubic and
underarm hair
•slowed mental
function
•breast shrinkage •fine wrinkles
around the eyes
and lips
•low blood sugar •low blood
pressure
•irregular
heartbeat
Diabetes
Insipidus( نادربشكل)
تسلسل ظهور األعراض و العالمات في متالزمة شيهان
فشل أو نقص في اض انخف)الدرةالحليبية
(البروالكتين
انقطاع الطمث الثانوي
قصور درق ثانوي قصور كظر ثانوي
Pituitary Gland Tumor:
Symtptoms:
Headaches
Vision problems
Unexplained tiredness
Changes in menstrual cycles in women
Erectile dysfunction
Inappropriate breast growth or production of
breast milk
Signs:
Mood changes
Irritability
Infertility, which is the inability to have
children
Cushing’s syndrome
Acromegaly