Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
-
Upload
raphaela-travassos -
Category
Documents
-
view
248 -
download
0
Transcript of Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
1/52
ASSOC PROF DR BAHARUDIN ABDULLAHDept of Otorhinolaryngology-Head Neck
Surgery
School Of Medical Sciences
Universiti Sains Malaysia
ENT Head and Neck Radiology Seminar 16-17 July 2010
Hospital Ampang
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
2/52
! Thin, flat muscles which areconnected to the dermis byfasciocutaneous ligamentsand osteocutaneousligaments (zygoma andmandible)
! Innervated by the facial nerve! These muscles may often
blend into each other! Relaxed skin tension lines
run perpendicular to thedirection of muscle fibers
! During tumor extirpation,significant loss is requiredbefore a functional deficit isappreciated.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
3/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
4/52
The face is supplied by branches of the externalcarotid and the internal carotid artery
Two main branches of the external carotid:Facial
artery and superficial temporal artery
Main branches of the internal carotid that suppliesthe medial upper face and scalp is theophthalmic artery
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
5/52
• Most veins in the face run parallel with theircorresponding arteries
! These veins lack valves and therefore allowbidirectional blood flow
! The facial vein can communicate with thecavernous sinus through the ophthalmic vein orthe pterygoid plexus (which drain the paranasalarea and the upper lip)
! Wound infections in this area have thepotential to gain access to the cavernous sinus
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
6/52
! Innervates muscles of facial expression! Exits stylomastoid foramen and travels
through through parotid gland where itdivides into its five majorbranches:Temporal, Zygomatic, Buccal,Marginal Mandibular, Cervical
! Posterior auricular branch arises proximalto parotid
!
There is significant variability in thecourse and arborization of this nerve frompatient to patient.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
7/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
8/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
9/52
! The marginal mandibular branch exits theparotid and runs along the mandiblewhere it is covered by the platysma.
! At the anterior border of the masseter itpasses superficial to the facial artery andvein and runs along the mandible.
! At a point 2 cm from the oral commissureit takes a more superficial position, but isstill protects as long as the underlyingmuscles have not been violated.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
10/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
11/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
12/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
13/52
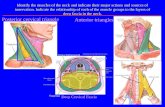
Sternocleidomastoid
TrapeziusDeep Cervical Fascia
Investing layer of deep cervical fascia
Prevertebral fascia
Pretracheal fascia(visceral part)Carotid sheath
Buccopharyngeal fasciaAlar fascia
Pretrachealfascia
(muscular part )
T
E
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
14/52
! deep fascia of neck condenses to formfour layers:
1) investing2)pretracheal3)prevertebral4)carotid sheath
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
15/52
! surrounds neck like collar! splits to enclose two muscles (trapezius &
sternocleidomastoid), two salivary glands(parotid & submandibular) and two spaces
(suprasternal & supraclavicular)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
16/52
! between angle of mandible and mastoidprocess, it splits into two laminae toenclose parotid gland, superficial lamina(parotid fascia) extends to zygomatic arch
! deeper lamina (between angle of mandible and styloid process) formsstylomandibular ligament
! forms roof of anterior and posteriortriangles of neck
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
17/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
18/52
! situated in front of prevertebral musclesof neck (surrounds cervical vertebrae andassociated muscles)
! forms floor of post. triangle of neck! cervical and prox. brachial plexuses are
deep to this fascia! axillary sheath is extension of this fascia
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
19/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
20/52
! triangular area in neck enclosed betweensternocleidomastoid and trapezius
! Boundaries:base: mid 1/3 of clavicle
apex: lies on sup. nuchal lineant: post border of sternocleidomastoidpost: ant border of trapeziusroof: investing layer of cervical fasciafloor: prevertebral fascia fascia covering splenius
capitus, levator scapulae, scalenus medius, andscalenus posterior
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
21/52
! spinal accessory, cervical plexus,phrenic,brachial plexus
! accessory n. (CN XI) divides post triangle
into sup and inf parts, runs betweensternocleidomastoid and trapezius(supplying both), enters at 1/3 way downsternocleidomastoid
! lesser occipital n. (C2) ascends shortdistance along sternocleidomastoid before itdivides to supply skin of neck and scalp postto auricle, and sup auricle
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
22/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
23/52
! supraclavicular nn. (C3-4) arise as singletrunk, which divides into med,intermediate and lat branches
! phrenic n. (C3-5) curves around latborder of scalenus ant, descendsobliquely across ant surface, deep totransverse cervical and suprascapularart, enters thorax by crossing origin of internal thoracic between subclavianart and vein
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
24/52
! Innervates trapezius andsternocleidomastoid muscles
! Most vulnerable when it enters posteriortriangle of the neck at Erb ’s point
! Other nerves at risk near Erb ’s point:-Greater Auricular-Transverse Cervical-Lesser Occipital-Supraclaviular
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
25/52
! Draw a horizontal line from the thyroidnotch across the neck
! Nerve exit SCM 2 cm superior to the lineand enters trapezius 2 cm inferior to theline (King and Mott, 1983)
! Draw a line from the Mastoid process tothe angle of the mandible. Then drop aperpendicular line at the mid point. Thisline will intersect the posterior border of the SCM.
! The nerve emerges within a shortdistance above this point (Salasche andBernstein, 1988).
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
26/52
Arteries! subclavian (3rd part), transverse cervical,
suprascapular, occipitalVeins! external jugular! lymph nodes! muscles
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
27/52
! anterior triangle - triangular area in frontof neck
! Boundaries:
ant: midlinepost: ant border of sternocleidomastoidbase: lower border of mandible, line
drawn from angle of mandible to mastoid
processapex: jugular notch
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
28/52
! muscles:1)suprahyoid muscles: mylohyoid (floor
of mouth), geniohyoid (reinforce floorof mouth), stylohyoid, digastric(straplike, two bellies, intermediatetendon joined to hyoid)
2)infrahyoid muscles: omohyoid (twobellies), sternohyoid, sternothyroid(deep to sternohyoid), thyrohyoid (supcontinuation of sternothyroid)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
29/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
30/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
31/52
! Common Carotid Arteries-begins at bifurcation of brachiocephalic- arises from arch of aorta(post to sternoclavicular joints)-ascends within carotid sheath to level of
sup border of thyroid cartilage where itterminates by dividing into int & extcarotid art.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
32/52
! Internal Carotid Artery-has no branches in neck, but are
two of four major art. thatsupply blood to brain
-each passes vertically upwardsfrom common to enter carotidcanal in petrous part of temporal bone, accompaniedby plexus of sympathetic fibres
-during course through neck, liesdeep to sternocleidomastoidm and parotid gland
-enters middle cranial fossathrough the superior part of
foramen lacerum-supplies pituitary, orbit and
most of supratentorial part of brain
! External Carotid Artery-extends between C3/C4
vertebra to the neck of themandible
-runs midway betweenmastoid process and angleof mandible within theparotid gland
-terminates by dividing intotwo branches, maxillary a.and superficial temporal a.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
33/52
Common carotid
Omohyoid
Digastric
Ling ual
Sup. thyroidSup. laryngeal
Int. carotid
Ext. carotid
Ascending phary ngeal
Superficial temporal
Maxil lar y
Faci al
Pos t.auricular
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
34/52
! Internal Jugular Vein-largest vein in neck (usually larger on right side than
left)-drains blood from brain and superf part of face and
neck-course corresponds to line drawn from external
acoustic meatus to med end of clavicle-commences at jugular foramen in post cranial fossa,
as direct continuation of sigmoid sinus, fromdilation at origin (sup bulb of int jugular v.)
-it runs in carotid sheath, leaves ant triangle bypassing deep to sternocleidomastoid and unites withsubclavian post to med clavicle
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
35/52
Level Lymph Node Group
I Submental andsubmandibular nodes
II Upper jugular nodes (skullbase to level of carotidbifurcation/hyoid bone)
III Middle jugular nodes(carotid bifurcation toomohyoid muscle)
IV Lower jugular nodes(omohyoid muscle toclavicle)
V Posterior triangle nodes
VI Anterior compartmentlymph nodes(paratracheal/perithyroidal)
Lymph Node Groups of the Neck
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
36/52
! funnel-shaped fibromuscular tube! located post to nasal cavity, mouth and larynx! divided into three parts: nasopharynx,
oropharynx, and laryngopharynx!
it is about 15 cm in length, extends from base of skull to inf border of cricoid cartilage! widest (~5cm) opposite hyoid bone, narrowest
(~1.5cm) at inf end! post wall lies against prevertral fascia, with
potential retropharyngeal space in between
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
37/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
38/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
39/52
! membranes and ligaments:1)extrinsic: thyrohyoid membrane,
cricotracheal membrane2)intrinsic: quadrangular membrane
(extends between epiglottis andvestibular folds)
3)cricovocal membrane (extends between
vocal ligament and upper border of cricoid cartilage)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
40/52
! Cavity divided into three parts:-upper (vestibular) part-middle (ventricular) part: between
vestibular and vocal folds-lower (infraglottic/subglottic) part! rima glottidis: is the aperture
between the two vocal folds.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
41/52
! extrinsic muscles that move the larynxup and down during deglutition:
1)elevators of larynx : digastric,stylohyoid, mylohyoid, and geniohyoidmuscles
2)depressors of larynx : sternohyoid,sternothyroid, and omohyoid muscles
! instrinsic muscles: alterations in thelength and tension of vocal folds in theproduction of voice, and in changing thesize of rima glottidis
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
42/52
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
43/52
! largest of endocrine glands! consists of two lateral lobes, isthmus and
occasionally pyramidal lobe! isthmus overlies 2nd, 3rd and 4th tracheal rings!
med lat lobe overlies larynx, trachea,oesophagus, inf. constrictor of pharynx andcricothyroid muscles
! post surface of lat lobe extends over carotidsheath
! infrahyoid muscles cover gland anteriorly! levator glandulae thyroideae attaches pyramidal
lobe to hyoid bone, embryological remnant of thyroglossal duct
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
44/52
! Parathyroids are situated are situated on postborder, along line of sup and inf thyroid artanastomoses
! arteries:sup thyroid a. (from ext carotid a.); inf thyroid a.
(from thyrocervical trunk); and occasionallythyroid ima a.(from arch of aorta).
! Veins:sup and middle thyroid vv.(empty into int jug v);
inf thyroid vv (empty into brachiocephal v)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
45/52
! lies between body of mandible and hyoidbone
! superficial part includes submental anddigastric triangles
! deeper parts include root of tongue andfloor of mouth
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
46/52
! Structures1)muscles: digastric, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, hyoglossus2)submandibular gland-mixture of serous and mucous acini-two parts: superficial and deep
-superficial: in digastric triangle, reaching upward undercover of mandible, separated post from parotid gland bystylomandibular lig
-deep: extends forwards in interval between mylohyoid andhyoglossus, post end continuous with superf part of gland,while ant end reaches as far as sublingual gland
-coverings: inner ct capsule and outer fibrous capsule(derived from deep cervical fascia)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
47/52
! submandibular duct: runs from ant deepsubmandibular gland, forward betweenmylohyoid and hyglossus
! blood supply: branches of lingual and
facial, veins follow aa.! nerve supply: derived from
submandibular ganglion (receivesparasympathetic fibres from chordatympani, lingual and sympathetic trunk)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
48/52
! largest of salivary glands(serous acini)
! covered by a capsule and a
dense fibrous tissue sheath(parotid fascia) formed by deepcervical fascia
! divided into two (superficialand deep) parts by facial n.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
49/52
! lies in fossa post to ramus of mandible! extends from external acoustic meatus to upper
part of carotid triangle! med, extends to styloid process and around
neck of mandible! post, overlaps sternocleidomastoid and extends
ant over masseter! portion of facial part often detached and called
accessory parotid gland! wedge-shaped (base above, apex behind angle
of mandible)! sup: extends upward behind TM joint into post
mandibular fossa, called glenoid process! ant: extends forwards superf to masseter
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
50/52
! Parotid Duct! 5 cm long, 5mm wide! passes horizontally from ant edge, turns
med at ant masseter and piercesbuccinator, and enters oral cavityopposite crown of 2nd upper molar tooth
! Structures within the Glandfacial n (superf)
retromandibular vexternal carotid a. (deep)
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
51/52
! Nerve and blood Supply! supplied by branches of external carotid
a., drains by tributaries of retromandibular v.
! secretomotor (parasympathetic): fromglossopharyngeal n. (IX), via otic ganglion
! sensory: branches from greater auricularand auriculo-temporal nn.
-
8/15/2019 Surgical Anatomy of Head & Neck
52/52
ENT Head and Neck Radiology Seminar16-17 July 2010
Hospital Ampang