SUPPY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
description
Transcript of SUPPY CHAIN MANAGEMENT

SUPPY CHAIN MANAGEMENT

Group Members
Manoj Jain 74Jigisha Patel 90Pinkesh Shah 101Niraj Singh 109Mansi Nagrecha 112Jitendra Solanki 113

Supply chain management is a set of approaches utilized to efficiently integrate suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and stores, so that merchandise is produced and distributed at the right quantities, to the right locations, and at the right time, in order to minimize system wide costs while satisfying service level requirements.
What is Supply Chain Management

Management beyond the borders of an organization
UpstreamThe upstream business partners are the external organizations
that supply products or services to an organization.
DownstreamThe downstream supply chain is the organizations external distribution channels, processes, and functions that the product passes through on its way to the end customer.

Evolution Of SCM.
The concept of SCM has only recently stepped into the marketing world. It rooted three decades back and has passed through three phases
Phase 1: Physical distribution management: This phase is better characterized as inventory push phase when manufacturing was handled in isolation and output was pushed down to the finished goods warehouses.

• Phase II : Integrated Logistics Management : This Phase Recognized The Importance Of Integrating Operations Within the Organization Like Sales, Procurement, Manufacturing, Warehousing, Distribution And Transportation To Achieve An Efficient And Effective Goods Distribution System.
• Phase III : SCM : The Graduation Of Logistics Management To Its Modern Day Avatar Is Better Known As ‘SCM’. SCM Extends The Scope To Link External Partners Like Suppliers, Vendors, Distributors And Customers With A View To Deliver Enhanced Customer And Economic Value Through Synchronized Management Of The Flow Of Physical Goods and associated Information from Source To Consumption.

What Drove Logistics To SCM?
One can identify a number of drivers for a paradigm shift from logistics to SCM The major ones are:
• First, the expectations of customer for increased value addition, response time sensitivity, need for reliability, cost consciousness and information sensitivity.
• Second, the nature of competition favouring firms that have been in a position to decrease lead times as well as operational costs.
• Third, the recent revolution taken place in the field of information technology has enabled and encouraged the firms to initiate newer means in the field of distribution management.

• Fourth, managers have realized and recognized the need for continuous improvement of process involved in marketing activity. The attitude of managers has changed in favor of integrating all activities in the chain from sourcing to consumption.

LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT
Logistics management Logistics management is that part of the Supply Chain
Management process that plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customers' requirements

Types Of LogisticsThird-party logistics:
Third-party logistics (3PL)involves using external organizations to execute logistics activities that have traditionally been performed within an organization itself

Fourth-party logistics:Fourth-party logistics (4PL) as an integrator thatassembles the resources, capabilities and technology of its own organization and other organizations to design, build, and run comprehensive supply chain solutions

• Why sudden interest ?
Demanding customers
Shrinking product life cycles
Proliferating product offerings

• Why sudden interest ?Growing retailer power in some cases
Doctrine of core competency
Emergence of specialized logistics providers
Globalization

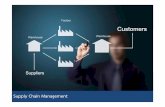
Supply Chain Structure
Information Flow
Raw Materials
RETAILERFACTORY DC RDC
SUPPLIER
Finished Goods

Supply chain Flow
Material/merchandise flows
Information flows
Financial flows
Supply chain management is the management of flows between and among supply chain stages to maximize total supply chain profitability

Merchandise Flow

Information Flow

Supply Chain Planning Processes
Demand PlanningMaterial Requirement PlanningDemand Forecasting
Supplier Plant Warehouse Logistics Retailer
ProductionPlan
Raw MaterialRequirement
Order Management

19
Benefits of SCM
Cost and Financial
Retailers
Manufacturers
Distributors
Streamlined inventories and reduced costs Reduced errors and redundant laborIncreased visibility of all business transactionImproved return on inventory investmentOptimized transportation costs, routes, and load timesIncrease cost savings from outsourcing for low cost materials
Improvements

20
Benefits of SCM
Processes
Improvements
Manufacturers
Improved forecast accuracy as well as resource and distribution planningImproved manufacturing and replenishment cycle timeEnhanced manufacturing schedulingIncreased effectiveness of planning and decision makingImproved overall efficiency in production

APPLICATIONS OF SCM
BLOOD BANK
IT INDUSTRY

RETAIL INDUSTRY
COURIER SERVICE INDUSTRY

Importance of Supply Chain Management
If it’s not in store you can’t show it. If you can’t show it you can’t sell it.

• Retailing – a set of business activities that adds value to the products and services sold to consumers for their personal or family use.
What is Retailing?

Basic elements of a retailing supply chain
ACTIVITY
Sourcing materials
Producing the product
Wholesale distribution
Retail distribution
INSTITUTION
Materials supplier
Producer
Wholesaler
Retailer
Consumer
OTHER ACTIVITIES
Warehousing, transport to producer
Design, warehousing, sellingthrough agents, transport towholesaler
Warehousing, transport toretailer, cash and carry
Regional and local distributioncentres, transport to store/home

WAL-MART
The US-based Wal-Mart ranked first in the global Fortune 500 list earning revenues of $219.81 billion Wal-Mart is the largest retailing company in the world.
Captain Vernon L. Beatty, aide-de-camp to the commander, Defense Supply Center, Columbus, Ohio said, "Supply chain management is moving the right items to the right customer at the right time by the most efficient means. No one does that better than Wal-Mart."

Retail Link system
More than 10,000 Wal-Mart suppliers use Retail Link to monitor sales of their goods at the store level and replenish inventories as needed.
Integrates into one of the largest data warehouses around, with more than 100 terabytes of information.
Make daily transactions details (more than 10 million daily) available to every Wal-Mart store by 4 a.m. the next day.

Wal-Mart's Best of practice on SCM
Relevant information is available to its partner.
The system is dynamic and adjust quantity of orders according to current situation
Wal-Mart must be able to get most up-to-date information out of the system to do be able to do proper prediction..

Thank You











![EC2004_ch08 Suppy Chain [Compatibility Mode]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/577d1e561a28ab4e1e8e4a68/ec2004ch08-suppy-chain-compatibility-mode.jpg)