Support and Locomotion The skeletal and muscular systems.
-
Upload
baldric-roberts -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Support and Locomotion The skeletal and muscular systems.

Support and Locomotion
The skeletal and muscular systems

Locomotion
• The ability to move from place to place• Motile
• Remember, organisms that can not move are stationary or sessile.

Why Move?
• Easier to obtain food• Easier to find a suitable place to live• Escape from predators• Reproduction and finding a mate

Locomotion generally requires…
• A muscular system and a skeletal system

2 types of skeletal systems
• Endoskeleton-– Bone and cartilage
inside body walls– Examples) vertebrates
like us
• Exoskeleton-– Hard outer material
made of calcium or chitin
– Examples) clams, oysters, insects, crabs, spiders

Endoskeleton Exoskeleton

Locomotion in Protist-a review
• Ameba
• Paramecium
• Euglena
• Pseudopods
• Cilia
• Flagella

Paramecium
Ameba Euglena

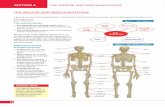
Human Skeletal System
• Made of :– Bone– Cartilage– Ligaments– Tendons

Bone-”osteo-”
• Connective tissue that is hard and inflexible• Site of attachment for muscles• Gives body shape and support• Protection• Storage for minerals (calcium, phosphorus)• Produces blood cells

Diagram of Human Skeletal System

Cartilage
• Connective tissue able to bend• Embryos have skeletons of cartilage
– Turns to bone by ossification after birth• Function: Cushions against impact or
pressure

Joints
• Points where bones meet

Ligaments
• Connective tissue holding bones of a joint together

Tendons
• Connective tissue attaching muscle to bone

The muscular system
• Three types of muscle– Skeletal– Smooth– Cardiac

Skeletal Muscle
• Used for voluntary movements
• Has a striated or striped appearance

Smooth Muscle
• Used for automatic, involuntary movements
• Ex) walls of alimentary canal, diaphragm

Cardiac Muscle
• Heart muscle• Involuntary• Striped appearance