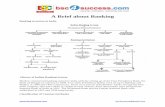
Structure of Indian Banking System
-
Upload
bulomine-regi -
Category
Education
-
view
340 -
download
0
Transcript of Structure of Indian Banking System


STRUCTURE OF BANKING SYSTEM





SCHEDULE BANK• Registered in the Second Schedule of RBI
Act, 1935.• Banks paid-up capital and reserves of an
aggregate value of not less than Rs. 5 Lakhs

NON-SCHEDULE BANK• Banking company as defined in clause
(c) of Section 5 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, which is not a scheduled bank.
• Bank with reserve capital of less than Rs. 5lakh
• These banks are not governed according to RBI Act.
• They don’t receive any benefits from RBI

COOPERATIVE BANKS• Cooperative banks are registered under
Cooperative Societies Act.• These banks are governed by the Banking
Regulations Act, 1949 and Banking Laws (Cooperative Societies) Act, 1955.
• People who come together to jointly serve their common interest often from a cooperative society under the Cooperative Societies Act.

• When a Cooperative Society engages itself in banking business it is called a Cooperative Bank.
• It gives credit facilities to small farmers, salaried employees, small-scale industries, etc.
• Cooperative Banks are available in rural as well as urban areas.


CENTRAL COOPERATIVE BANK

FUNDS OF THE BANKS

• These banks provide finance to member societies within the limits of borrowing capacity of societies.
• These banks also conduct all the business at a Joint Stock Bank

STATE COOPERATIVE BANK• State Cooperative Banks also known
as Apex banks.• Its funds are obtained from their• Own Share Capital• Deposits• Loans and• Overdraft from RBI• 50-90% of working capital of SCB are
contributed by the RBI

DISTRICT CENTRAL COOPERATIVE BANK
• The District Central cooperative Banks are federations of primary credit societies in a specific area, normally a District.
• Usually located in District Headquarters,• Some prominent town of the District.• These banks have a few private
individuals as shareholders, who provide both finance and management.

SOURCE OF FUND

INDIAN BANKS
• Indian Banks are those banks, which are
incorporated in India.

COMMERCIAL BANKS• Commercial banks are established with an
objective to help businessmen.• These banks collect money from general
public and give short term loans to businessmen by way of cash credits, overdrafts, etc.
• For the purpose of assessment of performance of banks, the RBI categorise them as Public Sector Banks, Old Private Sector Banks, New Private Sector Banks and Foreign Banks

Public Sector BanksPublic Sector Banks are banks, in which
the government has major holding.They can be further subdivided into SBI and its associate banks, other nationalised banks and regional rural banks.Public sector banks comprise 19
nationalised banks and SBI and its 7 associate banks.

Regional Rural BanksTo liquidate rural indebtedness by stages
and to dispense institutional credit facilities to framers and artisans in rural areas.
The government of India promulgated 26th September 1975, the regional rural banks ordinance 1975, to set-up Regional Rural Banks throughout the country.
RRB in India penetrated every corner of the country and extended a helping hand in the growth process of the country.

• SBI has 30 Regional Rural Banks in India known as RRBs.
• The rural banks of SBI are spread in 13 states extending from Kashmir to Karnataka and Himachal Pradesh to North East.
• Apart from SBI, there are other few banks, which functions for the development of the rural areas in India

• RRBs provide institutional credit to the weaker sections of the society at the concessional rate of interest, mobilise rural savings and channelise for supporting the productive
activities in the rural areas.

Private Sector Banks
• After the nationalisation of 14 larger banks in 1969.
• No banks were allowed to be set-up in the private sector.
• Global Trust bank was the first private bank after liberlisation; it was later amalgamated with Oriental Bank of Commerce (OBC).

• Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC) became the first to receive an “in principle” approval from the RBI to set up a bank in the private sector.
• Today, more than 30 private banks existing in India.

Foreign Banks• Foreign banks are those banks, which are
incorporated in a foreign country.• They have set-up their branches in India.• Now foreign banks in India are permitted to
set-up local subsidiaries.• The policy conveys that Foreign Banks in India
may not acquire Indian Ones (except for weak banks identified by the RBI, on its terms)
• Indian subsidiaries will not be able to open branches freely.