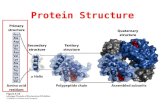
Four levels of protein structure Linear Sub-Structure 3D Structure Complex Structure.
Structure
-
Upload
abhishek-mewada -
Category
Documents
-
view
52 -
download
0
Transcript of Structure
Shear Force
•Shear force is unaligned force pushing one part of body in one direction and other in other direction.
•When forces are aligned in each other they are compression forces
•When forces are opposite to each other it is tension force.
•The cantilever method was derived to calculate and analyse shear forces and moments developed in different members like beams and columns of frame or structure due to lateral loads.
•The lateral loads includes wind load and earthquake load which must be taken into consideration while designing the building.
•The point assumed in this method are that the point of contraflexure is located at the mid point of vertical as well as horizontal members and that the direct stresses in the columns are proportional to distance from cental axis.
•Shear force is a force acting in a direction perpendicular to the extension of substance as for example pressure of air along the front of an airplane wing .
•Shear force often result in shear strain.
•Beam : Structural horizontal member resting on support to carry vertical loads .
•It carry tensile load.•Types of beam :•Cantilever beam.•Simply supported beam.•Overhanging beam.•Proped cantilever beam.•Fixed beam.•Continuous beam.
•Cantilever beam: This type of beam has fixed end on one end and free end on other.
Eg : Balcony.•Simply Supported beam: This type of
beam has support on both ends . This support are called hinge. Eg: classrooms, public places.•Overhanging beam : The supports are not
at the end but at some distance from end. Depth,design changes.
•Proped cantilever beam : This type of beam has fixed support on one end and support at other end is provided from downwards.
Eg : Mall , Public buildings elevation.•Fixed beam: has fixed supports on both
ends. Eg : Classrooms , Rooms of residence.•Continuous beam : Has continuous
supports. Supports are simply support. Reinforcement remains same. Depth , design remains same.
•Types of loading:•Point load or concentrated load : When a simple load is acted. When load is acted on point.•Uniformly distrubuted load: When is equally distrubuted on beam. Eg : slab .•Uniformly varying load : Load which uniformly varying on straight
line. Eg : 10 kN to 1 kN.
Bending moment
•A bending moment is a reaction in an structural element when an external force is induced on it causing an element to bend.
•The most common example of bending moment created in structural element is BEAM.
•The example shows a beam which is simply supported at both ends.
•Simply supported means each of beam can rotate therefore each end support has no bending moment.
•The ends can react to shear load.•The other ends have fixed support thus
they react to both shear force and bending moment.
•Beams also have on end fixed and other rotating.
•The simplest type of beam is cantilever.•The beam which has fixed support at one
end and free at other.• In reality beams are neither fixed nor
absolutely free.•The resultant internal couple is called
bending moment whereas internal force is called shear force.
•The bending moment at section through a structural element may be defined as “THE SUM OF MOMENTS ABOUT THAT SECTION OF ALL EXTERNAL FORCES ACTING ON ONE SIDE OF THAT SECTION.
•If clockwise bending moment is taken negative , than a bending moment will cause “SAGGING” and a positive moment will cause “HOGGING”.
•A point of zero bending moment is a point of COUTRAFLEXURE – point of transition from hogging to sagging and vice versa.
Calculation
•An important part of determining bending moment in practical moments of force .
•Let F be a force acting on point A in body .
•The moment of this force about a reference point is defined as M = r•F.
•Where M is moment and r is reference point to point of application (A) .