Spinal Reflexes
-
Upload
scuffruff -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
10.290 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Spinal Reflexes

Spinal reflexes
The reflex arc

The reflex arc
An automatic, rapid response to an adverse stimulus.
Action is involuntary the brain is not involved in the event but may be informed of it
Many reflex actions are protective Some complex actions (swallowing, coughing
and blinking) are coordinated by reflexes.

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone
spinal cord of central nervous system

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone
spinal cord of central nervous system
relay neurone

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone
spinal cord of central nervous system
relay neurone
motor neurone

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone
spinal cord of central nervous system
relay neurone
motor neurone
effector

A simplified reflex arc
stimulus
receptor
sensory neurone
spinal cord of central nervous system
relay neurone
motor neurone
effectorresponse

A withdrawal reflex

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat from the hot object

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature, they are called thermoreceptors.

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory neurone.

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord
white matter (neurone axons)

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord
white matter (neurone axons)
The sensory neurone enters the spinal cord via the dorsal branch of the spinal nerve and forms a synapse with a relay neurone, inside the grey matter

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord
white matter (neurone axons)
The sensory neurone enters the spinal cord via the dorsal branch of the spinal nerve and forms a synapse with a relay neurone, inside the grey matter
The short relay neurone forms a synapse with a motor neurone that leaves the spinal cord via the ventral root of the spinal cord.

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord
white matter (neurone axons)
The sensory neurone enters the spinal cord via the dorsal branch of the spinal nerve and forms a synapse with a relay neurone, inside the grey matter
The short relay neurone forms a synapse with a motor neurone that leaves the spinal cord via the ventral root of the spinal cord.
The motor neurone carries the impulse to an effector, in this case muscles in the arm, which contract to withdraw the hand from the hot object. This action is known as the response.

A withdrawal reflex
The stimulus is the heat
from the hot object
The stimulus is detected by receptors in the dermis of the skin. Since these sensory cells respond to temperature they are called
thermoreceptors.
The thermoreceptors initiate nerve impulses that pass to the spinal cord along a sensory
neurone.
sensory neurone cell body
grey matter (neurone cell bodies)
spinal cord
white matter (neurone axons)
The sensory neurone enters the spinal cord via the dorsal branch of the spinal nerve and forms a synapse with a relay neurone, inside the grey matter
The short relay neurone forms a synapse with a motor neurone that leaves the spinal cord via the ventral root of the spinal cord.
The motor neurone carries the impulse to an effector, in this case muscles in the arm, which contract to withdraw the hand from the hot object. This action is known as the response.

A few reminders!
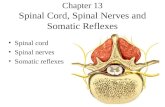
The central grey matter contains the cell bodies of relay and motor neurones.
The outer white matter contains myelinated axons, which run up and down the spinal cord to and from the brain.
In the centre of the grey matter is the spinal canal, through which the nutritive cerebrospinal fluid cirulates.

A few reminders!
Sensory neurones enter the spinal cord through the dorsal root and the concentration of their cell bodies forms a swelling called the dorsal root ganglion.
Motor neurones leave the spinal cord via the ventral root.