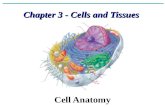
SNC2D Animal Cells and Tissues
description
Transcript of SNC2D Animal Cells and Tissues

SNC2D Animal Cells and Tissues

What factors influence cell specialization in Animals?
• Take a look on p85 and take a couple of minutes to read the page
• The contents of the cell’s cytoplasm
• Environmental conditions (like temperature)
• The influence of neighbouring cells

The Effect of Cytoplasm on Cell Specialization
• After cytokinesis, the contents of the cytoplasm may differ in each daughter cell
• This helps determine what type of cell it will become

The Effect of Environmental Conditions on Cell Specialization
• For example, in siamese cats, only cells that develop at cool temperatures produce dark hair colour (this usually occurs at the tips of cat’s feet, tail, ears, and nose)

The Effect of Neighbouring Cells on Cell Specialization
• When cells are close to each other, substances can diffuse through the cell membrane
• These substances change which genes in DNA gets expressed
• For example, in the embryo of a chick, neighbouring cells influence eye development in a specific location in the embryo
• 16 days embryo

Chick Development
6 Days 10 Days
16 Days

Abnormal Development• Chemicals (contaminants
like heavy metals) in the environment can affect an animal’s development
• In humans, 90% of developmental issues can be traced to environmental factors!

Structural Organization of Multicellular Organisms
atoms↓
molecules↓
organelles ↓
cells ↓
tissues ↓
organ ↓
organ system↓
organism

ReviewChemical – atoms combine to form moleculesCellular – molecules interact to make up cellsTissue – cells are grouped into tissueOrgan – tissues compose organsOrgan system – organs function together to form
organ systemsOrganism (individual) – made up of the organ
systems

Levels of Structural OrganizationAtoms
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ System
Organism

Necessary Life Functions• Ideas?• Maintaining boundaries
– Cellular level – accomplished by plasma membranes
– Organism level – accomplished by the skin)
• Movement • Responsiveness• Digestion• Metabolism• Excretion• Reproduction • Growth

Cells that have the same Function form Tissues
• Despite there being millions of different organisms, there are only a few different types of tissues!

What are the different tissues?• Find out for yourself! Fill in your chart of Animal Tissues
using the hand out• For homework, answer questions p76 #2-5 (on the
Nelson Textbook Handout)