Skeletal Tissues. Compact vs. Spongy Compact bone is dense and solid in appearance. Compact bone is...
-
Upload
thomasine-wood -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
3
Transcript of Skeletal Tissues. Compact vs. Spongy Compact bone is dense and solid in appearance. Compact bone is...
Compact vs. Spongy Compact vs. Spongy
CompactCompact bone is dense and bone is dense and solid in appearance. solid in appearance.
CancellousCancellous, or spongy, bone , or spongy, bone is characterized by open is characterized by open space partially filled by an space partially filled by an assemblage of needle-like assemblage of needle-like structures.structures.
Four Bone TypesFour Bone Types Long bones – extended Long bones – extended
longitudinal axis and expanded longitudinal axis and expanded and often uniquely shaped and often uniquely shaped articular ends.articular ends. Examples are the femur and humerusExamples are the femur and humerus
Short Bones – cube- or box-shaped Short Bones – cube- or box-shaped structure, which are about as structure, which are about as broad as they are long.broad as they are long. Examples include the wrist (carpals) Examples include the wrist (carpals)
and ankle (tarsal) bonesand ankle (tarsal) bones
Flat bones – generally broad Flat bones – generally broad and thin with a flattened and and thin with a flattened and often curved surface.often curved surface. Examples include some skull bones, Examples include some skull bones,
scapulae, ribs, and sternum scapulae, ribs, and sternum
Irregular Bones – often Irregular Bones – often clustered in groups and come clustered in groups and come in various shapes and sizes.in various shapes and sizes. Examples include the vertebral Examples include the vertebral
bones that form the spine and facial bones that form the spine and facial bonesbones
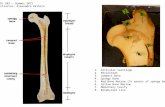
Parts of a Long Bone Parts of a Long Bone
DiaphysisDiaphysis – main shaftlike portion – main shaftlike portion
EpiphysesEpiphyses – both ends of a long bone – both ends of a long bone have a bulbous shape that provides have a bulbous shape that provides generous space near the joints for generous space near the joints for stability and muscle attachment. stability and muscle attachment.
Articular CartilageArticular Cartilage – thin layer of – thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers joint hyaline cartilage that covers joint epiphyses and acts as a cushion.epiphyses and acts as a cushion.
PeriosteumPeriosteum – Dense, white fibrous – Dense, white fibrous membrane that covers bone except at membrane that covers bone except at joint surfacesjoint surfaces
Medullary (marrow) cavityMedullary (marrow) cavity – tubelike – tubelike hollow space in the diaphysis of a long hollow space in the diaphysis of a long bone. In adults it is filled with fatty bone. In adults it is filled with fatty yellow marrow.yellow marrow.
EndosteumEndosteum – thin epithelial membrane – thin epithelial membrane that lines the medullary cavity of long that lines the medullary cavity of long bones. bones.
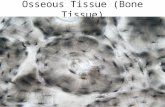
Bone (Osseous) TissueBone (Osseous) Tissue
Connective tissueConnective tissue
Consists of cells, fibers, and extracellular Consists of cells, fibers, and extracellular matrix matrix
Extracellular components are hard and Extracellular components are hard and calcifiedcalcified
Matrix is more abundant that the bone cells Matrix is more abundant that the bone cells
Composition of Bone Composition of Bone Matrix Matrix
Inorganic Salt are responsible for the Inorganic Salt are responsible for the hardness of bone. hardness of bone.
Hydroxyapatite – composed of calcium Hydroxyapatite – composed of calcium and phosphateand phosphate
Organic Matrix – composite of Organic Matrix – composite of collagenous fibers and a mixture of collagenous fibers and a mixture of protein and polysaccharides called protein and polysaccharides called ground substance.ground substance.
OsteoporosisOsteoporosis
Age related skeletal disease that is Age related skeletal disease that is characterized by loss of bone mineral characterized by loss of bone mineral density, increased bone fragility, and density, increased bone fragility, and susceptibility to fracturessusceptibility to fractures
More common in womenMore common in women
May lose 4% - 8% of their bone density May lose 4% - 8% of their bone density on a yearly basison a yearly basis
Microscopic Structure of Microscopic Structure of BoneBone
Compact bone contains many Compact bone contains many cylinder-shaped structural units cylinder-shaped structural units called osteons, or Haversian called osteons, or Haversian systems. systems.
Each osteon surrounds a canal that Each osteon surrounds a canal that runs lengthwise through the bone. runs lengthwise through the bone.
Main Structures of the Main Structures of the OsteonOsteon
Lamellae – concentric, cylinder Lamellae – concentric, cylinder shaped layers of calcified matrix. shaped layers of calcified matrix.
Lacunae – small spaces containing Lacunae – small spaces containing fluid and bone cells fluid and bone cells
Canaliculi – ultrasmall canals Canaliculi – ultrasmall canals radiating in all directions from the radiating in all directions from the lacunae that connects them to each lacunae that connects them to each other and the Haversian canal other and the Haversian canal
Haversian canal – Extends Haversian canal – Extends lengthwise through the center of lengthwise through the center of each Haversian system; contains each Haversian system; contains blood vessels, lymph vessels and blood vessels, lymph vessels and nervesnerves
Volkmann’s canals – run Volkmann’s canals – run perpendicular to Haversian canalsperpendicular to Haversian canals
Cancellous BoneCancellous Bone There are no osteons in cancellous There are no osteons in cancellous
bonebone
Consists of needle-like bony spicules Consists of needle-like bony spicules called called trabeculaetrabeculae. .
Bone cells are found within the Bone cells are found within the trabaculaetrabaculae
Nutrients are delivered and wastes Nutrients are delivered and wastes removed by diffusionremoved by diffusion
Types of Bone Cells Types of Bone Cells
Osteoblasts – synthesize and secrete a Osteoblasts – synthesize and secrete a specialized organic matrix called osteoid, specialized organic matrix called osteoid, that is an important part of the ground that is an important part of the ground substance of bone. (bone forming cells)substance of bone. (bone forming cells)
Osteoclasts – giant multinucleate cells Osteoclasts – giant multinucleate cells that are responsible for the active that are responsible for the active erosion of bone minerals. (bone erosion of bone minerals. (bone reabsorbing cells) reabsorbing cells)
Osteocytes – mature, non-dividing Osteocytes – mature, non-dividing osteoblasts that have become osteoblasts that have become surrounded by matrix and now surrounded by matrix and now within a lacunae. within a lacunae.
Bone MarrowBone Marrow
Soft, diffuse connective tissue called Soft, diffuse connective tissue called myeloid tissue. myeloid tissue.
Site of blood cell production Site of blood cell production
Found in medullary cavities of Found in medullary cavities of certain long bones and in the spaces certain long bones and in the spaces of some spongy bones. of some spongy bones.
Red Marrow & Yellow Red Marrow & Yellow MarrowMarrow
In a child’s body, virtually all of the In a child’s body, virtually all of the bones contain red marrow. bones contain red marrow.
Red marrow produces red blood cells.Red marrow produces red blood cells.
As an individual ages red marrow is As an individual ages red marrow is replaced by yellow marrow. replaced by yellow marrow.
Yellow marrow has become saturated Yellow marrow has become saturated with fat and is no longer active in blood with fat and is no longer active in blood cell production. cell production.
Functions of BoneFunctions of Bone Support – Support –
supporting supporting framework of body framework of body
Protection – protect Protection – protect delicate structures delicate structures such as the brain such as the brain
Movement – joints Movement – joints act as levers and act as levers and allow movement in allow movement in conjuction with conjuction with muscular systemmuscular system
Mineral Storage – Mineral Storage – major reservoir for major reservoir for calcium, calcium, phosphorus, and phosphorus, and certain other certain other mineralsminerals
Hematopoiesis – Hematopoiesis – blood cell blood cell formation formation
Regulation of Blood Regulation of Blood Calcium LevelsCalcium Levels
98% of body calcium is stored in bone98% of body calcium is stored in bone
Osteoblasts remove calcium from blood Osteoblasts remove calcium from blood
Osteoclasts break down bone and Osteoclasts break down bone and calcium levels in the blood increasescalcium levels in the blood increases
Calcium is important for normal blood Calcium is important for normal blood clotting, nerve impulses, and muscle clotting, nerve impulses, and muscle contractioncontraction
Calcium in the Body Calcium in the Body Calcium that is Calcium that is
consumed is absorbed consumed is absorbed through the intestinesthrough the intestines
Calcium is stored and Calcium is stored and released from bone released from bone tissue tissue
The kidneys eliminate The kidneys eliminate extra calcium and extra calcium and absorb calcium from absorb calcium from urine if blood calcium urine if blood calcium levels get too low. levels get too low.
Parathyroid HormoneParathyroid Hormone
When calcium levels fall below their When calcium levels fall below their “set point,” osteoclasts are “set point,” osteoclasts are stimulated to increase the rate of stimulated to increase the rate of bone matrix breakdown. bone matrix breakdown.
Calcium is released into the blood Calcium is released into the blood until the level returns to normal.until the level returns to normal.
Vitamin D (Calcitriol)Vitamin D (Calcitriol)
Acts to increase blood calcium levelsActs to increase blood calcium levels
Facilitates the absorption of calcium Facilitates the absorption of calcium in the small intestinesin the small intestines
Calcitonin Calcitonin
Functions to reduce blood calcium Functions to reduce blood calcium levelslevels
Enhances excretion of calcium in Enhances excretion of calcium in urineurine
Inhibits osteoclastsInhibits osteoclasts
Development of BoneDevelopment of Bone
Before birth, the skeleton consists of Before birth, the skeleton consists of cartilage and fibrous structures shaped like cartilage and fibrous structures shaped like bones. bones.
Cartilage is replaced with calcified bone Cartilage is replaced with calcified bone matrix matrix
The combined action of osteoblast and The combined action of osteoblast and osteoclasts to make bone is known as osteoclasts to make bone is known as osteogenesisosteogenesis
Intramembranous Intramembranous OssificationOssification
Takes place within a connective Takes place within a connective tissue membranetissue membrane
Endochondral Endochondral Ossification Ossification
Bone forms from cartilage modelsBone forms from cartilage models
Forms from the center to the endsForms from the center to the ends
Bone Growth and Bone Growth and Resorption Resorption
Bone growth is from the combined Bone growth is from the combined action of osteoclasts and osteoblastsaction of osteoclasts and osteoblasts Osteoclasts break down bone to enlarge Osteoclasts break down bone to enlarge
the diameter of the medullary cavity.the diameter of the medullary cavity.
Osteoblasts from the periosteum build Osteoblasts from the periosteum build new bone around the outside of the new bone around the outside of the bonebone