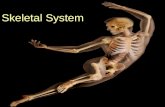
Skeletal system
-
Upload
ihmcbiology1213 -
Category
Documents
-
view
275 -
download
1
Transcript of Skeletal system


• Support- framework that supports body and cradles its soft organs
• Protection- for delicate organs, heart, lungs, brain
• Movement- bones act as levers for muscles
• Mineral storage- calcium & phosphate
• Blood cell formation- hematopoiesis

• Long Bones- legs and arms
• Short Bones- hands and feet
• Flat Bones- rib, pelvis, scapula, skull, sternum
• Irregular Bones- vertebrae, some facial bones, carpals, tarsals
• Sesamoid- patella


Distal
epiphysis
Proximal
epiphysis
diaphysis
yellow marrow
epiphyseal line
periosteum
compact bone
spongy bone
Endosteum
hyaline cartilage
Sharpey’s fibers




Cervical Vertebrae (7)
Thoracic Vertebrae (12)
Lumbar Vertberae (5)
SacrumCoccyx
Cervical Vertebrae (7)
Thoracic Vertebrae (12)
Lumbar Vertberae (5)
SacrumCoccyx
The Vertebral ColumnThe Vertebral Column

Sternum
True Ribs (7)
False Ribs (3)
Floating Ribs (2)
Sternum
True Ribs (7)
False Ribs (3)
Floating Ribs (2)
The Thoracic CageThe Thoracic Cage

Bones of the Pectoral GirdleBones of the Pectoral Girdle

Humerus
Ulna
Radius
8 Carpals
14 Phalanges
5 Metacarpals




Ischium
Ilium
Acetabulum
Pubis
Ischium
Obturator foramen
Pelvis (lateral view)

Male Pelvic Girdle
Female Pelvic Girdle


Patella
The Lower Limb (Legs)
The Lower Limb (Legs)
Femur
TibiaFibula
5 Metatarsals14 Phalanges
7 Tarsals




metatarsals
phalanges
tarsals
metatarsals
phalanges
tarsals


Immovable Joints (synarthrosis)
suturesuture
pubis symphisispubis symphisis

Slightly Movable Joint (ampharthrosis)

femur
ligaments
pelvis
(diarthrosis)- freely moveable

femur
pelvis
hyaline cartilage synovial
cavity
joint capsule


Abduction
Extension
RotationFlexion
Adduction
Synovial Joint Movement

275 bones12 weeks (6-9 inches
long)

cartilagecalcified cartilage
bone
epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal line
Endochondral Ossification
2o ossification
center
Fetus: 1st 2 months
AdultChildhood
Just before birth


hematomacallus bony callus
bone remodeling

Diseases of the Skeletal System:
Osteoporosis- bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposit; bones become lighter and fracture easier
Factors: • age, gender (more in women)• estrogen and testosterone decrease• insufficient exercise (or too much)• diet poor in Ca++ and protein• abnormal vitamin D receptors• smoking

Spinal Curvatures

Rickets- vitamin D deficiency
Osteomalacia- soft bones, inadequate mineralization in bones, lack of vitamin D
Pagets Disease- spotty weakening in the bones, excessive and abnormal bone remodeling
Rheumatoid arthritis- autoimmune reaction
Diseases of the Skeletal System: