Skeletal & Muscular Systems
-
Upload
hilel-harrison -
Category
Documents
-
view
29 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Skeletal & Muscular Systems
Engage Deboned
What would happen if humans did not have bones? Your body would be limp like a rag doll. Could you stand up? Could you walk?
Without bones in your body, you would be like the blob.
As a class we will observe two bones that were soaked in two different solutions.
Explore The Calcium Test Students will test various types of
materials to determine the presence or absence of calcium.
Explore Computer Lab http://www.medtropolis.com/VBody.asp You will visit the above website and
answer questions while navigating through the narrated skeletal system section
Explain What are the 5 Main Functions of the
Skeleton
1. provide structure and support for body
2. protect internal organs
3. make blood cells
4. store minerals
5. attachment for muscles for movement
Exoskeleton external skeleton Arthropods and Mollusks Arthropod’s skeleton is made of a
material called chitin and must be shed to permit growth.
Mollusk’s skeleton is made by the mantle from calcium carbonate.
Endoskeleton Internal skeleton Grows with the organism Made of cartilage or a combination of cartilage and
bone. Ossification – replacing cartilage with bone around 7
months before birth Osteoclasts – break down bone Osteoblasts – form bone tissue Contains 2 parts : axial and appendicular areas.
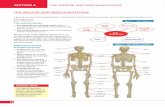
Skull
Sternum
Ribs
Vertebral column
Metatarsals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
Clavicle
Scapula
Humerus
RadiusPelvis
Ulna
Carpals
Femur
Patella
Fibula
Tibia
Tarsals
Phalanges
Axial Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
Structure of Bone
Spongy bone
Compact bone
Periosteum
Bone marrow
Haversian canalCompact
bone
Spongy bone
Osteocyte
Artery
VeinPeriosteum
Part of Bone
1. Marrow Yellow – fat cells Red – RBC, WBC, Platelets
2. Periosteum - Outer connective tissue – tough 3. Compact bone
Haversian Canals Tubes carrying blood vessels and nerves
4. Spongy bone Less dense; inside compact bone; ends of long bones and
middle of short, flat
Structure of Bone
Spongy bone
Compact bone
Periosteum
Bone marrow
Haversian canalCompact
bone
Spongy bone
Osteocyte
Artery
VeinPeriosteum
Freely Moveable Joints
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Hinge Joint
Pivot Joint
Saddle Joint
Clavicle
Ball-and-socket joint
ScapulaHumerus
Femur
Patella
Hinge joint
Tibia
Fibula
Humerus
Radius
Pivot joint
Ulna
Metacarpals
CarpalsSaddle joint
Joint Structure Tendon – Muscle to Bone Ligament – Bone to Bone Synovial Fluid – lubricating film
Bursa – small sac of synovial fluid Bursitis – inflammation of a bursa