SIMECA: SDN-based IoT Mobile Edge Cloud Architecturebinh/archive/simeca-att-demo.pdfProposed mobile...
Transcript of SIMECA: SDN-based IoT Mobile Edge Cloud Architecturebinh/archive/simeca-att-demo.pdfProposed mobile...

SIMECA: SDN-based IoT Mobile Edge Cloud ArchitectureBinh Nguyen, Nakjung Choi, Marina Thottan, Jacobus Van der Merwe
Email : {binh, kobus}@cs.utah.edu {nakjung.choi, marina.thottan}@nokia.com
Limitations of current LTE/EPC architecture in supporting IoT
1. Inflexibility in deploying new IoT services:- The network is "closed" with a heavy weight standards process.
2. Centralized deployment of core network functions:- Specialized and hardware-based equipment (SPGW, MME, PCRF)
deployed in a limited physical locations. 3. Heavy-weight data and control plane for IoT traffic:
- GTP tunnels add data plane overhead and forwarding states.- Maintaining GTP tunnels incurs control plane signaling.
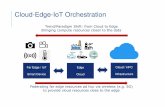
Proposed mobile edge cloud architecture for IoT services
1. Multiple IoT service providers share an infrastructure.• IoT network service abstraction (ISA) realized by NFV, SDN, and
cloud.2. More distributed architecture: mobile edge network and
cloud.• NFV mobility functions and cloud deployed close to the edge,
SDN-based forwarding.3. Light-weight data and control plane for IoT devices.
• Remove GTP tunnels, best-effort forwarding to local cloud.• SDN-based path implementation.
Demo set up
SIMECA vs. LTE/EPC: number of forwarding states
Infrastructure: mobile edge network and edge cloud
References
1. PhantomNet. https://www.phantomnet.org. 2. OpenAirInterface. http://openairinterface.eurecom.fr. 3. OpenEPC. http://www.openepc.com/.
IoT Service Abstraction, Control and Data plane
GTP tunnels in LTE/EPC core network
OpenEPC eNB* 1
OpenEPC eNB* 2
IoT device 1
IoT device 2
Attenuator
Mobility Function
SDN controller
OVS SDN edge network
Server OVS 1
Server OVS 2
Server 1
Server 2
SDN-enabled Base Stations SDN-based Edge cloud
Edge cloud
Service platform 1
Service platform 2
SDN-edge network
<1ms
<1ms
<1ms
OAI eNB*Nexus 5
Provider Control plane
S1AP/ NAS
OPF
OPF
REST
src: DI1 dst: DI2
D1
src: DI1 dst: DI2
D2
src: RI1 dst: RI2
src: DI3 dst: A
D3
src: RI3 dst: A
A
BS1
BS2BS3 BS4
Demo scenarios
1. C2S attach:- Nexus 5 attaches to edge cloud via OAI eNB*.
2. P2P attach:- Emulated client attaches and communicates with the Nexus 5 via
emulated OPENEPC eNB*.3. Mobility:
- Emulated client hands-over and maintains a continuous flow with the Nexus 5.
Region 1 Region 2
Edge Cloud
SDN edgeNetwork
S-BS
gatewayswitch
MC-1MC-2
MFIC
Dumb-core (SDN edge)
MC
eNB-1
eNB-2
MME
S-BS
SGW PGW Internet
S1AP
S11S5S8
OPF/S1AP
EPC-core
BS1
BS2
GTP-U tunnels
SDN rules
S1-U
SIMECA
LTE/EPC
GS
MF
UE1
UE2
REST
M1
M2
GTP/UDP/IP UDP/IP Payload
36 Bytes 28 Bytes
IP packet inside LTE/EPC core network
End-point sent IP packet
Identity mgnt
Connectivity Handover
NIBDevice tracking
Mobility interface
SDN
IoT service abstraction
Infrastructure
"Attach to server A"
MF MC
1
2
3
4
5