shear strain(due to shear stress&torsional stress)
-
Upload
mehedi-hasan -
Category
Business
-
view
1.219 -
download
5
Transcript of shear strain(due to shear stress&torsional stress)

1
AHSANULLAH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Name : MD.Mehedi hasanStudent ID: 10.01.03.094Course No: CE-416Course Title: Prestress Concrete Lab
11/24/2013

2
Shear Strain(Due to Shear & Torsional Stress)
11/24/2013

3
Stress
This is a measure of the internal resistance in a material to an externally applied load. Stress is designated and is defined as:
stress = load W
area A
11/24/2013

4
When a body is subjected to some external force, there is some change of dimension of the body. The ratio of change of dimension of the body to its original dimension is known as strain.Strain may be:- a) Tensile strain b) Compressive strain c) Volumetric strain d) Shear strainTensile strain- Ratio of increase in length to original length of the body when it is subjected to a pull forceCompressive strain- Ratio of decrease in length to original length of the body when it is subjected to a push forceVolumetric strain- Ratio of change of volume of the body to the original volumeShear strain-Strain due to shear stress`
STRAIN
11/24/2013

5
Concept of strain
11/24/2013

6
Sign convention for strain:
• Tensile strains are positive whereas compressive strains are negative.
• The strain defined earlier was known as linear strain or normal strain or the longitudinal strain.
11/24/2013

7
Shear Stress
Similarly in shear the shear stress is a measure of the internal resistance of a material to an externally applied shear load.
shear stress = load W
area resisting shear A
11/24/2013

8
Concept of Shear Stress
• Shear stress is defined a the component of force that acts parallel to a surface area.
• Shear stress is a stress state where the shape of a material tends to change (usually by "sliding" forces – torque by transversely-acting forces) without particular volume change.
11/24/2013

9
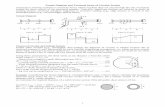
Shear stress and strain
Shear force
Shear Force
Area resisting shear Shear displacement (x)
Shear strain is angle L
11/24/2013

10
Shear Stress
Shear stress tends to change the shape of a body without changing its volume
Note: we apply shear force and shear stresses develop in the interior of the material11/24/2013

11
Sign convention of shear stress
The sign convention for shear force and stress is based on how it shears the materials as shown below.
11/24/2013

12
Hooke’s Law for ShearBy conducting a similar material testing to normal stress (Section 2.4), there is a linearrelationship (for most engineering materials) between the shear stress and shear strain
Fig : Relationship of shear stress τ – shear strain γ for linear elastic material
11/24/2013

1311/24/2013

14
Torsion
Torsion occurs when an external torque is applied and an internal torque, shear stress, and deformation .
11/24/2013

15
Torsion and Shearing Stress
• There is also an internal shear stress which develops inside the shaft.
• This shearing stress on the cross sectional area varies from zero at the center of the shaft linearly to a maximum at the outer edge.
• This may be thought of as being due to the adjacent cross sectional areas of the shaft trying to twist passed each other.
11/24/2013

1611/24/2013

17
THANK YOU
11/24/2013