CHAPTER 12 SEX-LINKED TRAITS Karyotype: a picture of chromosomes.
Sex-Linked Traits
description
Transcript of Sex-Linked Traits

Sex-Linked Traits

Genetic Counseling
Sometimes it’s a good idea to know the odds . . . . Especially when dealing with sex-linked traits.

It’s all about the SEX!
• Sex-linked genes are located on the 23rd chromosome (sex chromosome).
• Sex chromosomes are X and Y.• XY = Boy• XX = Girl• Sex-linked genes are shown as SUPERSCRIPTS
on the X chromosome.

Sex-Linked Traits• Sex-linked traits can be Dominant or Recessive.
• A = dominant a = recessive
• What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sex-linked Dominant trait and do not express (have) the trait?
• Expresses Trait: Male - XA Y Female - XA XA or XA Xa
• No Expression: Male - Xa Y Female - Xa Xa
• What would be the genotypes of a male and female that have a Sex-linked Recessive trait and do not express the trait?
• Expresses Trait: Male - Xa Y Female - Xa Xa
• No Expression: Male - XA Y Female - XA XA or XA Xa (Carrier)
• Most Sex-linked traits are Recessive!

Sex-Linked Recessive Traits• More males are affected than females.• An affected son can have parents who have the
normal phenotype. (XAY, dad) x (XAXa, mom)• For a daughter to have the trait, her father must also
have it. Her mother must have it or be a carrier. (XaY, dad) (XaXa or XAXa, mom)
• The trait often skips a generation from the grandfather to the grandson.
• If a woman has the trait (XaXa), ALL of her sons will be affected.
• Pedigrees show only female carriers--no male carriers.

Examples of Sex-Linked Recessive Disorders
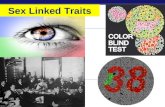
• Red/Green Colorblindness – Difficulty perceiving differences between colors (red or green, blue or yellow).
• Hemophilia – Absence of one or more proteins necessary for normal blood clotting.
• Deafness• Cataracts – opacity in the lens that can lead to blindness• Night blindness – (Nyctalopia) rods do not work so that can not see in the
dark• Glaucoma – pressure in the eye that can lead to optic nerve damage and
blindness• Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy – progressive weakness and degeneration
of skeletal muscles that control movement due to absence of dystrophin (protein that maintains muscle integrity). Mainly in boys, onset 3-5 yrs, by 12 years can’t walk, and later needs respirator.

To See or Not To See
Color-Blind-- cannot see the numbers or designs in the circles.
-- What do you see?

Color Blind: Recessive SL Trait

Color-Blind Pedigrees
• Draw a pedigree showing a cross between a man with normal vision and a woman who carriers the color-blind trait.
• Color-blind is a recessive trait.• Genotypes of Parents:• Male = XR Y Female = XR Xr

Does yours look like this?• Pedigree of color-blind trait.
• Genotypes of Parents:• Male = XR Y Female = XR Xr
XRY XRXr
XRY XrY XRXR XRXr

Can a female be color-blind?
• Think about it.
• If so, how? Why?

YES—she can!
• If dad (XrY) is color-blind and mom (XRXr) is a carrier =
50% chance XrXr
• She’s color-blind.

Hemophilia•It is a rare blood disorder.•The blood does not clot.• A hemophiliac will bleed “freely”, while a normal person will eventually stop bleeding because a scab forms.•Hemophiliacs require medical intervention to stop the flow of blood. •Usually they are given clotting factors, which help them form scabs.•Hemophilia is inherited. •About 1 out of 5,000 males are born with hemophilia each year.

Pedigree Royale: Hemophilia