Session no. 3.1. energy transformation atp – adp cycle and photosynthesis
-
Upload
anonymous143 -
Category
Environment
-
view
355 -
download
3
Transcript of Session no. 3.1. energy transformation atp – adp cycle and photosynthesis

Energy Transformation:
ATP – ADP Cycle and Photosynthesis
Leila A. Ombat, PhDBiology Department
College of Arts and SciencesCaraga State University, Butuan City

Learning ObjectivesThe learners should be able to:1.explain coupled reaction processes and describe the role of ATP in energy coupling and transfer (STEM_BIO11/12-IIa-j-1).2.describe the major features and chemical events in photosynthesis (STEM_BIO11/12-IIa-J-2).3.explain the importance of chlorophyll and other pigments (STEM_BIO11/12-IIa-J-3).

4.describe the patterns of electron flow through light reaction events (STEM_BIO11/12-IIa-j-4).
5.describe the significant events of the Calvin Cycle (STEM_BIO11/12-IIa-j-5).

Activity• Match the fruit to its leaves
1 2 3 4
dcba

Those plants starts from a tiny seed.
•How does it happen?
•Where does mass of tree come from?
•Where do they get their energy?

Activity: Role of chlorophyll in photosynthesisExtraction of chlorophyll variegated leaf was collected placed in test tube with 70% ethyl alcohol boiled in a water bath until the leaf became pale the leaf was rinsed with water it’s ready for the test of presence of starch using a drop(s) of iodine solution. a blue black color indicates the presence of starch.








Analysis
1.Why do we have to use alcohol in the removal of chlorophyll?
2.Which portion of the leaves turn blue-black? What does it indicates?
3.Why is it that some portion of the leaves are not green?
4.What is the main function of the chlorophyll in photosynthesis?

ATP-ADP Cycle

The Flow of Energy
•All life on earth depends on the flow of energy through ecosystems
•All energy on the earth ultimately comes from the sun

Organisms are classified according to their energy source
These are the:
AUTOTROPHS
HETEROTROPHS

Autotrophs• organisms capable of making their own food.• plants are photoautotrophs• they use light energy from the sun to produce glucose (sugar)

Heterotrophs• organisms not capable of making their own food• they are consumers of the biosphere• they must eat plants, or other animals who eat plants to acquire indirectly the energy from the sun

Pyramid of Energy

What is the energy currency of the cells of autotrophs and
heterotrophs?

Adenosine Triphosphate
The common energy currency of
cells.
With one big molecule that is
made of 5 smaller molecules bonded
together. Adenosine Tri-phosphate

How energy is released from ATP?
• ATP transfer energy from the breakdown of food molecules to cell function.
• Energy is released when phosphate group (P) is removed
• ADP is charge into ATP when phosphate group (P) is added.

Key concepts of ATP/ADP Cycle
1.ATP contains MORE energy than ADP because it has more bonds.
2.When a phosphate is REMOVED energy is RELEASED.
3.When a phosphate is ADDED energy is NEEDED.

ATP-ADP Cycle: Carbohydrates• Energy: up to 36 ATP molecules (1 glucose)•Details:•Most commonly broken down to make ATP•Not stored in large amounts

• Energy: about 146 ATP molecules (triglyceride)•Details:• Lipids store the most energy• 80% of the enrgy in our body
ATP-ADP Cycle: Fats/Lipids

• Energy: about 36 ATP molecules BUT…•Details:•Proteins are least likely to be broken down to make ATP,•Amino acids not usually needed for energy
ATP-ADP Cycle: Proteins

Energy Content of BiomoleculesMOLECULES ENERGY
Carbohydrates 4 calories per mg
Lipid 9 calories per mg
Protein 4 calories per mg

Learning Check
1.Where does plants get energy to produce its own food?
2.Consumers are also termed as ___________.3.When does ATP release its stored energy?4.What molecule will be formed if 1 molecule of
phosphate will be released?5.Which of the biomolecules possessed greater
amount of energy?

Answer
1.Sun2.Heterotrophs3.When 1 of the phosphorus is
broken and released4.ADP 5.Lipids/Fats

PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Converts light energy to the chemical energy of food

• Occurs in plants, algae, certain other protists, and some prokaryotes (cyanobacteria and purple sulfur bacteria
PHOTOSYNTHESIS

1.Inorganic molecules (carbon dioxide and water)
2.Light energy 3.Chlorophyll inside the
chloroplast
What are the requirements for photosynthesis to take place?

Photosynthesis
• Video on photosynthesis

• CO2 from the atmosphere will enter into the leaves of the plants through the stomates
• H2O from the soil will enter into the roots through the root hairs
Carbon Dioxide and Water

Sun Light• When the white light from
the sun passes through a prism it produces the rainbow colors• Two colors are used for
photosynthesis, the blue and red that are trapped by chlorophyll a (P680 and P700) and b.• Most of the colors are
reflected to the environment.

Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants

• The leaves of plants are the major sites of photosynthesis

ChloroplastChloroplast is composed of:1.Outer membrane2.Inner membrane 3.Stroma that contains small circular DNA and ribosomes; its the area for dark reaction.4.Thylakoids are piled into granum (plural: grana)• The membrane of thylakoid consist of reaction centers, electron acceptors and enzymes needed for light reaction

Chloroplast: Chlorophyll• Thylakoid membrane consists of
photosystem I (P700) and photosystem II (680) for light reaction; electron acceptors and ATPase. This systems are found in the chlorophyll, responsible for trapping light energy

Chloroplast: Chlorophyll

Chloroplast: Chlorophyll

•Chloroplasts split water into Hydrogen and oxygen, incorporating the electrons of hydrogen into sugar molecules
Chloroplast: Chlorophyll

Chloroplast: Photosynthesis overview
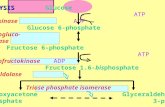
Two phases of photosynthesis
1.Light reaction – occurs in thylakoid membranes
2.Dark reaction or Calvin Cycle – happened in stroma

Electrons from chlorophyll travel through the carriers organized in the “Z scheme”

The transfer of electrons and protons is carried outby four protein complexes
6 CO2 + 18 ATP + 12 NADPH + 6 H2O = C6H12O6 + 18 ADP + 18 Pi + 12 NADP+ + 12 H+ + 6O2

How is ATP formed?Electron and proton transport form a proton motive force (PMF)
PMF is used to make ATP
Where are protons produced?1. Splitting of water2. PQ oxidationLight-dependent ATP synthesis: PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION
Peter Mitchell, 1960, photophosphorylation works via chemiosmotic mechanism

ATP synthase (ATPase)

1.Light Absorption: Electrons are “pulled” from water, and O2 is evolved (light reaction)
2. Electron Transport : NADPH is formed (light reaction)3. Generation of ATP: (light reaction)4. Conversion of CO2 into Carbohydrates (carbon reaction)
Light and Carbon reactions of Photosynthesis

Overview of the Calvin Cycle – 3 Stages6 CO2 + 18 ATP + 12 NADPH + 6 H2O = C6H12O6 + 18 ADP + 18 Pi + 12 NADP+ + 12 H+ + 6O2

The patterns of translocation of photosynthetic products: source to sink
Photosynthetic products or the metabolites move from source to sink.
SOURCE = area of supply- exporting organs: mature leaves- storage organs: seed endosperm, storage root of second growing season beet
SINK = areas of metabolism (or storage) - non-photosynthetic organs and organs that do not produce enough photosynthetic products to support their own growth or storage - Example: roots, tubers, developing fruits/seeds, immature leaves

Application of Photosynthesis.
•In-vitro culture of plant tissues- using florescent bulb•Farming

Thank you. Have a green day.

References
• Autotrophs images. http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-fk8X8x_kNt8/T3yor9fVd0I/AAAAAAAAFUg/Mdmkr45Tw3s/s1600/grow+plants.jpg• Ecosystem image. https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/564x/a9/b2/0a/a9b20a7da527d788912b016e66ef3fbe.jpg• ATP structure. https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/62/flashcards/2462062/jpg/atp-14A45523E763320B3A9.jpg• Carbohydrates. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/content/images/articles/161/161547/carbohydrate-foods.jpg

• Fats. http://pickyeaterblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/healthy-fats211.jpg• Chloroplast image.
https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/564x/db/cc/07/dbcc0711f792bbefee5be9d512a61f7a.jpg• Thylakoid membrane.
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/archive/d/de/20070405211312!Thylakoid_disc.png• Pyramid of Energy.
http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-j4WQijd8qOM/UyliDGgpIQI/AAAAAAAAC-4/chrLFjYnSG8/s1600/Energy+Pyramid.gif• Food chain. http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/consumers-in-
the-food-chain.jpg

• Campbell and Reece. 2009. Biology, 7th ed.• Taiz and Zeiger. 2009. Plant Physiology