Sectors of Circles - Wikispaces · Sectors of Circles MARS Shell Center ... 4 arc length of a...
Transcript of Sectors of Circles - Wikispaces · Sectors of Circles MARS Shell Center ... 4 arc length of a...

Lesson #38
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham
Mathematics Assessment Project
Formative Assessment Lesson Materials
Sectors of Circles
MARS Shell Center University of Nottingham & UC Berkeley
Alpha Version
Please Note: These materials are still at the “alpha” stage and are not expected to be perfect. The revision process concentrated on addressing any major issues that came to light during the first round of school trials of these early attempts to introduce this style of lesson to US classrooms. In many cases, there have been very substantial changes from the first drafts and new, untried, material has been added. We suggest that you check with the Nottingham team before releasing any of this material outside of the core project team.
If you encounter errors or other issues in this version, please send details to the MAP team c/o [email protected].

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 1
Sectors of Circles 1
Mathematical goals 2
This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to solve problems involving area and 3 arc length of a sector of a circle using radians, and in particular, to help you identify and assist students who 4 have difficulties in: 5
• Computing perimeters, areas, and arc lengths of sectors using formulas. 6 • Finding the relationships between arc lengths, and areas of sectors after scaling. 7
Common Core Standards 8
This lesson relates to the following Standards for Mathematical Content in the Common Core State Standards 9 for Mathematics: 10
A-SSE: Interpret the structure of expressions. 11 G-C: Find arc lengths and areas of sectors of circles. 12
This lesson also relates to the following Standards for Mathematical Practice in the CCSS: 13
1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 14 7. Look for and make use of structure. 15
Introduction 16
The lesson unit is structured in the following way: 17
• Before the lesson, students work individually on an assessment task that is designed to reveal their 18 current understanding and difficulties. You then review their solutions and create questions for students 19 to consider, in order to improve their work. 20
• During the lesson, small groups work on a collaborative task, in which they match cards according to 21 the length, area or perimeter of the sectors. 22
• After considering in the same small groups the general results of changing the radius and/or sector 23 angle of a sector, there is a whole-class discussion. 24
• Finally, in a follow-up lesson students return to their original task, consider their own responses, and 25 then use what they have learned to complete a similar task. 26
Materials required 27
• Each student will need a copy of the assessment tasks, Sectors of Circles and Sectors of Circles 28 (revisited), the sheet Circles, a mini-whiteboard, a pen, and an eraser. 29
• Each small group of students will need a mini-whiteboard, a pen, and an eraser, a glue stick, an 30 enlarged copy of Arc Lengths and Areas of Sectors, and the cut-up cards Dominos 1, Dominos 2, 31 Changing the Angle and Radius of a Sector. 32
• There are some projector resources to support whole-class discussions. 33 You may want to copy the Card Sets onto transparencies to be used on an overhead projector to support 34 whole-class discussions. 35
Time needed 36
Approximately 20 minutes before the lesson, an eighty-minute lesson (or two forty-minute lessons), and 20 37 minutes in a follow-up lesson. Exact timings will depend on the needs of the class. 38
39

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 2
Before the lesson 39
Pre-Assessment task: Sectors of Circles (20 minutes) 40
Have the students complete this task, in class or for 41 homework, a few days before the formative assessment 42 lesson. This will give you an opportunity to assess the 43 work, and to find out the kinds of difficulties students 44 have with it. You will then be able to target your help 45 more effectively in the follow-up lesson. 46
Give each student a copy of the task Sectors of Circles. 47
Read through the questions and try to answer 48 them as carefully as you can. 49
It is important that students are allowed to answer the 50 questions without your assistance, as far as possible. 51
Students should not worry too much if they cannot 52 understand or do everything, because in the next lesson 53 they will engage in a similar task, which should help 54 them. Explain to students that by the end of the next 55 lesson, they should expect to answer questions such as 56 these confidently. This is their goal. 57
Assessing students’ responses 58
Collect students’ responses to the task, and note down 59 what their work reveals about their current levels of 60 understanding and their different approaches. 61
We suggest that you do not score students’ work. The 62 research shows that this will be counterproductive, as it 63 will encourage students to compare their scores, and will 64 distract their attention from what they can do to improve 65 their mathematics. 66
Instead, help students to make further progress by 67 summarizing their difficulties as a series of questions. 68 Some suggestions for these are given on the next page. 69 These have been drawn from common difficulties 70 observed in trials of this unit. 71
We strongly recommend that you write questions on each 72 piece of student work. If you do not have time, select a 73 few questions that will be of help to the majority of 74 students. These can be written on the board in the follow-up lesson. 75
76
77
78
79
80
Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-1
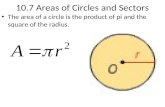
Sectors Of Circles You may find the following formulas useful:
Arc length: r!
Area: 12r2!
1. The diagram shows three concentric circles. The radii of the inner, middle, and outer circles are 2cm, 4cm and 8cm respectively. The circles are divided into twelve equal angles at the center. A sector of the middle circle is shaded.
(i) Find the angle, in radians, of the shaded sector.
Sector A
Sector B has the same arc length as Sector A, but has a different radius and sector angle. (ii) Shade in Sector B. Explain how you know it has the same arc length as Sector A.
Sector B
Sector C has the same area as Sector A, but a different radius and sector angle. (iii) Shade in Sector C. Explain how you know it has the same area as Sector A.
Sector C
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!! !
Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-2
2. The radius of Sector D is half the radius of Sector E.
The area of Sector D is half the area of Sector E.
Shade in possible sectors for D and E. Show all your work.
Sector D
Sector E

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 3
Common issues: Suggested questions and prompts:
Student has difficulty working in radians.
For example: The student figures out the size of the sector in degrees, but is unable to convert this angle to radians (Q1(i)).
Or: The student incorrectly draws the angle.
Or: Calculates the arc length and area using degrees.
• What is the definition of a radian? • How many radians are there at the center of a
circle? • Now use the formula for arc length and area
where the angle is measured in radians.
Student provides an angle bigger than 2π.
• Does your answer make sense? • How many radians are there in one full turn of
360°?
Student makes a technical error when substituting values into the formula for arc length or area of sector
• Check your work.
Student does not provide answers given as multiples of π
• Have you rounded your answers? How can you write your answer more accurately?
Student assumes that because the sector radius is doubled, the angle must remain the same (Q2)
• The radius of Sector D is half the radius of Sector E. Does this mean the area of Sector D will be double the area of Sector E? How do you know?
Student uses guess and check to figure out the size of the sector
• Can you use a more efficient method? • How can the formulas help you solve this
problem more efficiently?
Student provides little or no explanation • Can you use a formula to explain your answer?
81
82
For example:To obtain a sector with an area of 16!3
the student provides a radius of 2cm and an angle
of 8!3
radians (Q1(iii))

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 4
Suggested lesson outline 82
Whole-class interactive introduction (25 minutes) 83
This lesson assumes that students are familiar with radians, and should not be regarded as an introduction to 84 them. 85
Give each student a mini-whiteboard, a pen and an eraser. Give each student a copy of the Circles handout. 86 Students are to draw their sectors on these circles. 87
Throughout the introduction, encourage students to first tackle a problem individually, and only then discuss it 88 with a neighbor. In that way students will have something to talk about. Maximize participation in the whole-89 class discussion by asking all students to show you solutions on their mini-whiteboards. Select a few students 90 with interesting or contrasting answers to justify them to the class. Encourage the rest of the class to challenge 91 these explanations. 92
Introducing the idea of a radian. 93
Show Slide 1 of the projector resource. 94
95
What do these sectors have in common? 96
Most students will reply that for all the sectors, the radius is equal to the arc length. 97
What else do they have in common? [Angles a, b, c are equal.] 98
What fraction of a complete circle is each sector? How do you know? 99 [Arc length of each sector = r, total circumference of circle = 2πr, 100
so fraction of the complete circle is ] 101
What is the size of each angle? How do you know? 102
[ ] 103
Students may notice that the sectors are all similar, and that angles a, b, and c are all equal. 104
Each of these angles is equivalent to one radian. 105 Today you are going to work with sectors of circles, using radians rather than degrees to describe the 106 angles. 107
108
© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Sectors of Circles
1
!"
!
!
!# "
"
#
$$#!$ !$
a, b and c are all sector angles (in degrees.)
!
r2"r
= 12"
.
!
360 " 12#
= 3602#
= 57.3°.

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 5
108
Spend a few minutes checking that students understand the relationship between radius, arc length, and sector 109 angle: 110 On your mini whiteboard, show me another sector with an angle of one radian. 111 Write down the radius and arc length of your sector. 112 Now show me a sector with an angle of 2 radians, 3 radians, 1.5 radians …. 113
Introduce the formula for arc length. 114
First, verify that all students remember how to calculate the circumference and area of a full circle. 115
Show Slide 2 of the projector resource. 116
117
Then ask: 118
How many radians are there in a full turn of 360°? [2π = circumference ÷ r] 119
On the Circles handout, shade in a sector with an angle of π radians. 120
Now repeat for 2π, π/2, π/6, 5π/6 ……. radians. 121
Depending on your class, you may want to ask students to shade in more than these five examples of sector 122 angles. 123
What did you make the radii of your circles? Did this matter? 124 [No. The radii can be any length, as they are unrelated to the angles.] 125
What fraction of the circumference of the full circle is each arc length? How do you know? 126
Suppose your circle has a radius of r. What is the arc length of each sector? 127
Project slides 3, 4 and 5 which show the table below (partially filled) and complete the cells with the class: 128
Sector angle
!
"
Fraction of circle 1
Arc length ?
Challenge students to generalize the results in the last column. 129
What is the formula for figuring out the arc length of this sector? 130 How do you know? 131
What do you multiply the angle by to obtain the arc length? 132
© 2011 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Sector of a Circle
2
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!!"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
!
12
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 6
This is a challenging question so allow students sufficient time to think about it on their own and then discuss it 133 with a partner. Encourage students to use the arc lengths they have already calculated. 134
The arc length is of the circumference of the circle, so the arc length = 135
136 Introducing the formula for area. 137 138 Now move your questioning on to deriving a formula for the area of a sector. 139 Project the slides 6, 7 and 8 as the following discussion unfolds: 140
What is the area of your sectors? 141
Sector angle
!
"
Fraction of circle 1
Area of sector
!
12"r2
?
142 How can we figure out the general formula for a sector of a circle, of radius r, and sector angle θ? 143 What expression do you multiply the angle by to obtain the sector area? 144
Again this is a challenging problem so allow students sufficient time. 145
Area of sector =
146
147
Check that students understand through questioning.
Now draw on the board a sector with radius 12 and sector angle of
To establish that students understand the difference between perimeter and arc length, you may want to ask:
What is the perimeter of this sector? [24+2π] Is the perimeter always bigger than the arc length? Why? [Yes because you add the radius twice]
Ask the following questions in turn. Students draw their sector on their mini whiteboards. 148
Show me a sector that has the same arc length as this one, but with a different radius and sector angle. 149 Show me a sector with double the perimeter. How do you know? 150 Show me a sector with double the area. How do you know? 151
If students provide decimal answers (e.g. 6.283185), you could ask: 152
Which is the more accurate answer 2π or 6.283185? 153
In this lesson some measurements will be provided as multiples of π and you can leave your answers as 154
multiples of π. 155
156
!
"2#
!2"
!2"r = r!
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
!
12
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12
!
"2#
$ #r2 =12"r2
!
"6
.
© 2011 MARS, University of Nottingham Draft Version February 2011 Projector resources:
A Sector of a Circle
2
!!"#$%#&'
()
*

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 7
Collaborative activity 1: Domino Cards (20 minutes) 156
Organize the class into groups of two or three students. Give each group the cards Dominos 1 and Dominos 2. 157
Explain to the class that they are about to link cards together so that they will eventually create a closed loop. 158
If students are unsure what to do, explain as follows: 159
In front of you are six dominos. 160 Drawn on each domino is a diagram with three concentric circles. 161 The circles are divided into eight equal angles at the center. 162 The radius of the biggest circle is double the radius of the middle one. 163 The radius of the middle circle is double the radius of the smallest one. 164 We don’t know how big these radii are. You will need to work them out. 165
Choose a domino. 166
167
168 You must find the missing lengths and areas and draw any missing sectors. 169 Can you work out any of the missing answers? If not choose another domino! 170
Next to the diagram is an arrow with an instruction. 171 Your must connect the dominos by following the instructions. 172
Show Slide 9 of the projector resource, and ask students to read it carefully. 173
Work together to connect all the dominos. 174 As you do this, discuss with your partner how you came to your decision. 175 Both of you need to agree on, and explain all the connections. 176 Start by finding cards that give you plenty of information about the circles and the sectors. 177
The purpose of this structured group work is to help students engage with each other’s explanations, and take 178 responsibility for each other’s understanding. 179
If students assume the radii are the same size as the radii in the assessment (2 cm, 4 cm and 8 cm,) or if students 180 struggle to get started on the task: 181
Before connecting the dominos, what do you first need to know? [The radii of each circle.] 182 Are there any cards that will give you this information? 183
If students are still struggling direct them to Cards D or F. 184
What do you to know about this sector? 185 How can you use this information to help you to find the radius? 186
During small group work, you have two tasks, to notice students’ approaches to the task and to support student 187 reasoning: 188
Note different student approaches to the task 189
Notice how students make a start on the task, where they get stuck, and how they respond if they do come to a 190 halt. How do they approach the task? Do they first try to figure out the unknown measures on each card? Do they 191
Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2011 MARS University of Nottingham S-4
Cards: Dominos 1 A.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"
"
B.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:"
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"
!
9"2"
!
3"2
+ !!!!!!"
"
C.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
#$%"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!"&"$'"
""
"
""
Halve the perimeter of the sector.
Double the area of the sector.
................. the arc length of the sector.

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 8
try to work in degrees? Are they able to substitute values into formula correctly? You can use this information to 192 focus a whole-class discussion towards the end of the lesson. 193
Support student reasoning 194
Try not to make suggestions that move students towards a particular approach to the task. Instead, ask questions 195 that help students to clarify their thinking. Draw on the questions in the Common issues table to support your 196 own questioning. 197
If the whole class is struggling on the same issue, write relevant questions on the board and hold an interim 198 discussion. 199
Check that each member of the group understands and can explain each card placement. If you find a student in 200 any group is struggling to respond to your questions, return in a few minutes, to check the group has together 201 worked on understanding. 202
Which card(s) provides you with information about the radius of the sector? [Cards D, F and E] 203 What do you to know about this sector? How can you use this to figure out the radius? 204 What does the perimeter tell you about the radius/arc length? 205 Which cards provide you with the least information? How will you deal with these cards? 206 [Leave them to the end.] 207
If the perimeter is halved/doubled, what happens to the length of the radius? What happens to the arc 208 length? 209 If the arc length remains the same, does this mean the radius and the sector angle have to remain the 210 same? If the radius increases, how will the sector angle change? 211
Sharing work (10 minutes) 212
As students finish connecting the cards, ask them to share their solution with a neighboring group. 213
Check to see which connections are different from your own. 214
A member of each group needs to explain their reasoning for these connections. If anything is unclear, 215 ask for clarification. 216
Then together consider if you should change any of your answers. 217
It is important that everyone in both groups understands the math. You are responsible for each other's 218 learning. 219
Slide 4 of the projector resource summarizes this information. 220
When students are satisfied with their loop of dominos, give each small group a glue stick. They are to glue the 221 cards onto the poster. 222
223
224

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 9
Collaborative activity 2: Changing Arc Lengths and Areas (15 minutes) 224
This activity provides students with an opportunity to summarize and generalize their work in the previous task. 225
Give each group the sheet Arc Lengths and Areas of Sectors, and the cards Changing the Angle and Radius of a 226 Sector. 227
You are to place two of the small instruction cards into one of the boxes on your sheet. 228
Students may find their domino connections help them with this task. Support the students as before. 229
When students are satisfied with their placements they are to glue the cards onto the sheet. 230
Encourage students who work through the task more quickly to think about how they can explain the scaling in 231 general terms. They may use algebra in their explanation, or simply highlight the properties of a formula that 232 determine the scaling. 233
Can you use algebra to show you are correct? If the radius is multiplied by n, what should happen to θ 234
in order to keep the arc length the same/to double the arc length? 235
If the radius is multiplied by n, what should happen to θ in order to keep the area the same/to double 236
the area? 237
Whole-class discussion (10 minutes) 238
Depending on how your class has progressed you may want to focus the discussion on the first or second 239 collaborative activity. 240
Organize a whole-class discussion about different strategies used to connect (or place) the cards. First select a 241 pair of cards that most groups connected (or placed) correctly. This approach may encourage good explanations. 242 Then select one or two cards that most groups found difficult to connect (or place). 243
Once one group has justified their choice for a particular connection (or placement), ask other students to 244 contribute ideas of alternative approaches, and their views on which reasoning method was easier to follow. The 245 intention is that you focus on getting students to understand and share their reasoning, not just checking that 246 everyone produced the right answers. Use your knowledge of the students’ individual and group work to call on 247 a wide range of students for contributions. You may want to draw on the questions in the Common issues table to 248 support your own questioning. 249
You may want to use a selection of these questions: 250
Johnny, do you agree with Maddie’s connection (or placement) of the cards? 251 Can you put her explanation into your own words? 252
Which was the easiest card to connect (or place)? Why? 253 Does anyone disagree with the connection (or placement)? 254
Which was the most difficult card to connect (or place)? Why? 255 Does anyone disagree with the connection (or placement)? 256
When sharing your work with another group, did any of you see anything to make you change your 257 mind? Why? 258
Can anyone think of another way of keeping the sector arc length/area the same? 259 How many ways are there of keeping the sector arc length/area the same? 260
Can anyone think of another way of doubling sector arc length/area? 261 How many ways are there of doubling the sector arc length/area? 262
263

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 10
Follow-up lesson: Sector of Circles (revisited) (20 minutes) 263
Return to the students their original assessment task, and a copy of Sectors of Circles (revisited). 264
If you have not added questions to individual pieces of work, then write your list of questions on the board. 265 Students should select from this list, only the questions they think are appropriate to their own work. 266
Look at your original responses and think about what you have learned this lesson. 267
Carefully read through the questions I have written. 268
Spend a few minutes thinking about how you could improve your work. 269
You may want to make notes on your mini-whiteboard. 270
Using what you have learned, try to answer the questions on the new task Sectors of Circles (revisited). 271
272
Solutions 273
Assessment Task: Sectors of Circles 274
1. i. Sector angle of 2!3
. 275
ii. Radius of sector: 4cm. Arc length: 8!3
. 276
The sector could have a radius of 2 cm and a sector angle of 4!3
radians. 277
OR a radius of 8 cm and a sector angle of !3
radians. 278
iii. Area of sector: 12!2!3! 42 = 16!
3cm2. 279
The sector could have a radius of 8 cm an a sector angle of !6
radians. 280
2. The sector angle of Sector E should be half the sector angle of Sector D.
281
282

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 11
Collaborative Activity 1: Domino Cards 282
Radii of circles are 3 cm, 6 cm and 12 cm. 283
D.
F.
A.
284
285
Arc length of sector: 3! ! radius = 6; " = ! 2
Area of sector : 12
" ! 2
" 62 = 9!
Perimeter of sector: 3! + 12
Perimeter of sector: 3! + 6 ! radius = 3Arc length of sector: 3! ! " = !
Area of sector : 12
" ! " 32 = 9!2
radius = 12; ! = " 4
Arc length of sector: 12 ! " 4
= 3"
Perimeter of sector: 3" + 24
Area of sector : 12
! " 4
! 122 = 18"
Keep just the arc length of the sector the same.
Quarter the angle of the sector. Multiply the radius of the sector by 4.
Halve the perimeter of the sector.

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 12
Collaborative activity 1: Domino Cards (Continued) 285
B.
E.
C.
286
287
!
Arc length of sector : 3" 2
Area of sector : 9" 2
# Radius : 6; $ = " 4
Perimeter of sector : 3" 2
+ 12
Students may use simultaneous equations to figure out the missing measures :12$r2 = 9"
2
$r = 3" 2
# $ = 3" 2r
12%
3" 2r
% r2 = 9" 2
r = 6
$ = 3" 2%6
= " 4
Area of sector : 9! Radius:3; " = 2!Arc length of sector:6!Perimeter of sector: 6! + 6
Arc length of sector: 12!Perimeter of sector: 12! + 24! Radius:12; " = !
Area of sector : 12
" ! " 122 = 72!
Double the area of the sector.
Double the arc length of the sector.
.
Divide by 4 the arc length of the sector.

Sectors of Circles Teacher Guide Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham 13
Collaborative activity 2: Changing Arc Lengths and Areas 287
Another sector with the same arc length, can be
drawn by: doubling the angle θ, and
halving the radius, r.
multiplying the angle θ by 4, and dividing the radius, r by 4.
Another sector with the same area, can be drawn by:
multiplying the angle θ by 4, and halving the radius, r.
dividing the angle θ by 4, and doubling the radius, r.
Another sector with double the arc length, can be
drawn by:
keeping the angle, θ, the same, and doubling the radius, r.
doubling the angle θ, and keeping the radius the same.
Another sector with double the area, can be drawn by:
halving the angle θ, and doubling the radius, r.
doubling the angle θ, and keeping the radius the same.
Assessment Task: Sectors of Circles (revisited) 288
1. i. Sector angle of
ii. Arc length of sector:
Radius of sector: 1 cm. Sector angle:
Or: Radius of sector: 2cm. Sector angle:
iii. Area of sector:
The sector should have a radius of 2 cm and a sector angle of
2. The sector angle of Sector E should be half the sector angle of Sector D.
289
!!"#$%#&'
!
"! ! !!"#$%#&'
!
"! !
!!"#$%#&'
!
"! ! !!"#$%#&'
!
"! !
!
"3
radians.
!
4"3
cm.
!
4"3
radians.
!
2"3
radians.
!
8"3
cm2.
!
4"3
radians.

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-1
Sectors Of Circles You may find the following formulas useful:
1. The diagram shows three concentric circles. The radii of the inner, middle, and outer circles are 2cm, 4cm and 8cm respectively. The circles are divided into twelve equal angles at the center. A sector of the middle circle is shaded.
(i) Find the angle, in radians, of the shaded sector.
Sector A
Sector B has the same arc length as Sector A, but has a different radius and sector angle. (ii) Shade in Sector B. Explain how you know it has the same arc length as Sector A.
Sector B
Sector C has the same area as Sector A, but a different radius and sector angle. (iii) Shade in Sector C. Explain how you know it has the same area as Sector A.
Sector C
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!! !Arc length: r!
Area: 12r2!

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-2
2. The radius of Sector D is half the radius of Sector E.
The area of Sector D is half the area of Sector E.
Shade in possible sectors for D and E. Show all your work.
Sector D
Sector E

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-3
Circles Sector Angle =
Sector Angle =
Sector Angle =
Sector Angle =
Sector Angle =
Sector Angle =

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-4
Cards: Dominos 1 A.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
....................
....................
....................
B.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
....................
......
C.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
12π
.....................
........ + 24
!
9"2
!
3"2
+
Halve the perimeter of the sector.
Double the area of the sector.
................. the arc length of the sector.

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-5
Cards: Dominos 2 D.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
3π
....................
....................
E.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
.....................
9π
.....................
F.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
....................
....................
3π + 6
Keep just the arc length of the sector the same.
Quarter the angle of the sector. Multiply the radius
of the sector by 4.
Double the arc length of the sector.

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-6
Arc Lengths and Areas of Sectors
Another sector with the same arc
length, can be drawn by: Another sector with the same
area, can be drawn by:
Another sector with double the arc
length, can be drawn by: Another sector with double the
area, can be drawn by:
!!"#$%#&'
!
"! ! !!"#$%#&'
!
"! !
!!"#$%#&'
!
"! ! !!"#$%#&'
!
"! !

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-7
Cards: Changing the Angle and Radius of a Sector
multiplying the angle θ by 4, and halving the radius, r.
doubling the angle θ, and keeping the radius the same.
multiplying the angle θ by 4, and dividing the radius, r by 4.
keeping the angle, θ, the same, and doubling the radius, r.
doubling the angle θ, and halving the radius, r.
dividing the angle θ by 4, and doubling the radius, r.
doubling the angle θ, and keeping the radius the same.
halving the angle θ, and doubling the radius, r.

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-8
Sectors Of Circles (revisited) You may find the following formulas useful.
1. The diagram shows three concentric circles. The radii of the inner, middle, and outer circles are 1cm, 2cm and 4cm respectively. The circles are divided into twelve equal angles at the center. A sector of the outer circle is shaded.
(i) Find the angle, in radians, of the shaded sector.
Sector A
Sector B has the same arc length as Sector A, but a different radius and sector angle. (ii) Shade in Sector B. Explain how you know it has the same arc length as Sector A.
Sector B
Sector C has the same area as Sector A, but a different radius and sector angle. (iii) Shade in Sector C. Explain how you know it has the same area as Sector A.
Sector C
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!! !Arc length: r!
Area: 12r2!

Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2012 MARS University of Nottingham S-9
2. The radius of Sector E is double the radius of Sector D.
The area of Sector E is double the area of Sector D.
Shade in possible sectors for D and E. Show all your work.
Sector D
Sector E

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Sectors of Circles
1
!"
!
!
!# "
"
#
$$#!$ !$
a, b and c are all sector angles (in degrees.)

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Sector of a Circle
2
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!!"

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
What fraction of a circle?
3
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!!"#$%#&'
!
(")!!"

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
What arc length?
4
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
What area of sector?
5
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
What area of sector?
6
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
rθ

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Generalize?
7
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
rθ

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Formulas for general case
8
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
!
12"r2
!
"r2
!
"r2
4
!
"r2
12
!
5"r2
12 ?
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
Area of sector
Sector angle
!
"
!
2"
!
"2
!
"6
!
5"6
!
"
Fraction of circle
!
12
1
!
14
!
112
!
512
!
"2#
Arc length
!
"r
!
2"r
!
"r2
!
"r6
!
5"r6
?
Area of sector
rθ
½r2θ

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Matching the Dominos
9
Moving out from the center, the radius of each circle is doubled. The radii are all integer lengths. All the center angles are equal.
Apply these instructions to the shaded sector on the domino. Then match the resultant sector to a sector on another domino.
Complete this information as you work through the task. Leave your answers as multiples of π.
Make sure every person in your group understands and can explain the placement of each domino.
Sectors of Circles Student Materials Alpha Version January 2012
© 2011 MARS University of Nottingham S-4
Cards: Dominos 1 A.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"
"
B.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:"
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"
!
9"2"
!
3"2
+ !!!!!!"
"
C.
Arc length of sector:
Area of sector:
Perimeter of sector:
#$%"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"!!!!!!!!"&"$'"
""
"
""
Halve the perimeter of the sector.
Double the area of the sector.
................. the arc length of the sector.

© 2012 MARS, University of Nottingham Alpha Version January 2012 Projector Resources:
Sharing work
10
1. Check to see which matches are different from your own.
2. A member of each group needs to explain their reasoning for these matches. If anything is unclear, ask for clarification.
3. Then together consider if you should change any of your answers.
It is important that everyone in both groups understands the math. You are responsible for each other's learning.











![Conversion of Radians and Degrees Degree Radian Radians Degrees Example 1Converting from Degrees to Radians [A] 60° [B] 30° Example 2Converting from Radians.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/56649f475503460f94c68e94/conversion-of-radians-and-degrees-degree-radian-radians-degrees-example-1converting.jpg)






