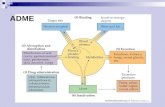
Route of drug administration-An overview
-
Upload
vinay-gupta -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
172 -
download
1
Transcript of Route of drug administration-An overview
ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
-vinay gupta
department of pharmacology
up rural institute of medical sciences & research
saifai, etawah, india
Definition:
A route of administration is the path by which a drug, fluid, poison or other substance is brought into contact with the body.
Route of administration
I) Oral
II) Topical
III) Rectal
IV) Parenteral
V) Vaginal
VI) Inhaled
VII) Ophthalmic
VIII) Otic
Factors determining Route of Administration
• 1) Drug Factors
• Physical Properties-
• Nature of Drug- certain drugs are destroyed by gastric acid or proteolytic enzymes eg. Insulin, oxytocin, vasopressin are peptides so degraded by proteolytic enzyme in gut.
• Absorption- certain drugs do not absorbed orally eg. Streptomycin is highly ionized at gut pH so not absorbed orally & given by parental route.
• Toxicity- admn topically eg. Neomycin.
• Bioavailability- poor bioavailability on oral admnof some drugs eg. Nitroglycerine, morphine have only 20% bioavailability, so ntg is admnsublingually while morphine by parenteraly(SC/IM/IV).
• Plasma t1/2- very short half life drugs are admn by parenteral route eg. Sod. Nitroprusside(vasodilator) half life 2-5 mts.
• Distribution- if a drug does not reach at site of action or does not cross BBB then it has to be given by such a route that reaches to the site of action.
• Metabolism- if drug undergoes extensive first paas metabolism it is avoided by oral route & preferably used by
parenteral route eg. Morphine
or Sublingual route eg. Nitroglycerine.
- The first pass effect is the term used for the hepatic metabolism of a pharmacological agent when it is absorbed from the gut and delivered to the liver via the portal circulation.
- The greater the first pass effect, the lower the bioavailability of the drug(the rate and extent of the drug reaching systemic circulation).
First pass effect :
• 2) Patient Factors
• Condition of patient
• Associated disease
• Convenience of patient
• Personality/ psychotic
• 3) Disease Factors
• Emergency situation
• Drug poisoning
• Local action
• A drug may produce different effects when given by different route eg. Magnisiumsulphate
• Orally - Laxative
• Topically - Boil, abscess
• Parenterally - Eclampsia
Routes of Administration
• 1) Enteral ( enteron = intestine)-
• Oral
• Sublingual
• Rectal
• 2) Parenteral ( par = beyond ,enteron = intestine)-
• Inhalation
• injections
injections
• Intravenous- (I.V. bolus or infusion) drug is given in superficial vein, 100% bioavailability.
• Intramuscular- in large muscles of arm
(deltoid) or leg (thigh, glutial muscle).
Advantages
1- suitable for injection of drug in aqueous
solution (rapid action) and drug in
Suspension or emulsion.
Disadvantages
1- Pain at injection sites for certain
drugs.
Injections cont…
Subcutaneous – in subcutaneous tissue under the skin. e.g. INSULIN
No more then 1.5 ml should be injected into the site
• Suspension, oily & colloids
Injections cont…
• Intradermal/intracutaneous (ID/IC)- drug is injected b/w the two layers of skin ie b/w epidermis & dermis with some times formation of bleb.
eg. Vaccines BCG, measles.
Injections cont…
• Intrathecal- drug is admn in subarrachnoidspace bypassing BBB & CSF.
in spinal anaesthesia.
• Epidural(extradural)- drug is injected b/w lining of spinal canal & duramater (extraduralspace) for purpose of anaesthesia & analgesia in different regions, used mainly in obstetrics.
Injections cont…
• Intramedullary- drug is injected in to bone marrow such as sternum or tibia. Mainly used for bone marrow transplantation & for blood transfusion in children where it is difficult to find a vein.
• Intraarterial- in this route inj is directly made in to artery, used in angiography.
Injections cont…
• Intra articular admn- drug is admn in the joint space in synovial fluid providing local effect & used for certain kinds of arrthritis. Eg steroids
• Intra cardiac- drug is injected directly into myocardium. Usually adrenaline is admn locally in case of cardiac arrest.
Injections cont…
• Intra ventricular- this route is useful for admn of drug in brain tumours in which drug is admn directly in to cerebral ventricles.
• Subconjectival- drug is injected just below conjunctiva eg. Amphotericin & miconazole that provides high & effective local c/n with less systemic toxicity.
Injections cont…