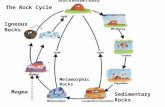
Rocks & Minerals Review Regents Earth Science Miss Wojdan.
54
Rocks & Minerals Review Regents Earth Science Miss Wojdan
-
Upload
bethany-pitman -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
3
Transcript of Rocks & Minerals Review Regents Earth Science Miss Wojdan.
- Slide 1
- Rocks & Minerals Review Regents Earth Science Miss Wojdan
- Slide 2
- 1. Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of: A. White Quartz B. Aluminum C. Pink Feldspar D. Iron
- Slide 3
- 1. Compared to felsic igneous rocks, mafic igneous rocks contain greater amounts of: A. White Quartz B. Aluminum C. Pink Feldspar D. Iron
- Slide 4
- 2. What are the two most abundant elements by mass found in the Earths crust? A. Aluminum and Iron B. Sodium and Chlorine C. Oxygen and Silicon D. Calcium and Carbon
- Slide 5
- 2. What are the two most abundant elements by mass found in the Earths crust? A. Aluminum and Iron B. Sodium and Chlorine C. Oxygen and Silicon D. Calcium and Carbon
- Slide 6
- 3. The graph below shows the relationship between mass and volume between three samples, A, B, and C, of a given material. What is the density of the material? A. 1.0 g/cm cubed B. 5.0 g/cm cubed C. 10 g/cm cubed D. 15.0 g/cm cubed
- Slide 7
- 3. The graph below shows the relationship between mass and volume between three samples, A, B, and C, of a given material. What is the density of the material? A. 1.0 g/cm cubed B. 5.0 g/cm cubed C. 10 g/cm cubed D. 15.0 g/cm cubed
- Slide 8
- 4. Which sample best shows the physical properties normally associated with regional metamorphism? A. Sample A B. Sample B C. Sample C D. Sample D
- Slide 9
- 4. Which sample best shows the physical properties normally associated with regional metamorphism? A. Sample A B. Sample B C. Sample C D. Sample D
- Slide 10
- 5. The graph below shows the concentration (percentage) of copper at various depths in the bedrock at a mine in Arizona. Between which depths should the bedrock be mined in order to contain rock with the greatest percentage of copper? A. 100 130 ft. B. 230 260 ft. C. 330 360 ft. D. 650 680 ft.
- Slide 11
- 5. The graph below shows the concentration (percentage) of copper at various depths in the bedrock at a mine in Arizona. Between which depths should the bedrock be mined in order to contain rock with the greatest percentage of copper? A. 100 130 ft. B. 230 260 ft. C. 330 360 ft. D. 650 680 ft.
- Slide 12
- 6. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? A. Calcite B. Halite C. Pyrite D. Mica
- Slide 13
- 6. Which mineral is white or colorless, has a hardness of 2.5, and splits with cubic cleavage? A. Calcite B. Halite C. Pyrite D. Mica
- Slide 14
- 7. Compared to dull and rough rock surfaces, shiny and smooth rock surfaces are most likely to cause sunlight to be: A. Reflected B. Refracted C. Scattered D. Absorbed
- Slide 15
- 7. Compared to dull and rough rock surfaces, shiny and smooth rock surfaces are most likely to cause sunlight to be: A. Reflected B. Refracted C. Scattered D. Absorbed
- Slide 16
- 8. The diagrams below show the crystals of four different rocks viewed through the same hand lens. Which crystals most likely formed from molten material that cooled and solidified most rapidly? A B C D
- Slide 17
- 8. The diagrams below show the crystals of four different rocks viewed through the same hand lens. Which crystals most likely formed from molten material that cooled and solidified most rapidly? A B C D
- Slide 18
- 9. Which sedimentary rock is most likely to be changed to slate during regional metamorphism? A. Breccia B. Conglomerate C. Dolostone D. Shale
- Slide 19
- 9. Which sedimentary rock is most likely to be changed to slate during regional metamorphism? A. Breccia B. Conglomerate C. Dolostone D. Shale
- Slide 20
- 10. Which rock is metamorphic and shows evidence of foliation? A. Rock 1 B. Rock 2 C. Rock 3 D. Rock 4
- Slide 21
- 10. Which rock is metamorphic and shows evidence of foliation? A. Rock 1 B. Rock 2 C. Rock 3 D. Rock 4
- Slide 22
- 11. What do all four rocks have in common? A. They show cleavage B. They contain minerals. C. They are organically formed D. They formed on Earths surface
- Slide 23
- 11. What do all four rocks have in common? A. They show cleavage B. They contain minerals. C. They are organically formed D. They formed on Earths surface
- Slide 24
- 12. Which of the following choices is not a characteristic of metamorphic rocks? A. Banding B. Distorted structure C. Fossils D. Contact metamorphism
- Slide 25
- 12. Which of the following choices is not a characteristic of metamorphic rocks? A. Banding B. Distorted structure C. Fossils D. Contact metamorphism
- Slide 26
- 13. Which two processes result in the formation of igneous rocks? A. Solidification and Evaporation B. Melting and Cementation C. Crystallization and Solidification D. Compression and Precipitation
- Slide 27
- 13. Which two processes result in the formation of igneous rocks? A. Solidification and Evaporation B. Melting and Cementation C. Crystallization and Solidification D. Compression and Precipitation
- Slide 28
- 14. Which rock is formed by the compression and cementation of sediments with particle sizes ranging from 0.08 to 0.1 centimeters? A. Basalt B. Conglomerate C. Granite D. Sandstone
- Slide 29
- 14. Which rock is formed by the compression and cementation of sediments with particle sizes ranging from 0.08 to 0.1 centimeters? A. Basalt B. Conglomerate C. Granite D. Sandstone
- Slide 30
- 15. Which statement about the formation of a rock is best supported by the rock cycle? A. Magma must be weathered before it can change to metamorphic rock. B. Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to a sedimentary rock. C. Sedimentary rock must melt before it can change to metamorphic rock. D. Metamorphic rock must melt before it can change to sedimentary rock.
- Slide 31
- 15. Which statement about the formation of a rock is best supported by the rock cycle? A. Magma must be weathered before it can change to metamorphic rock. B. Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to a sedimentary rock. C. Sedimentary rock must melt before it can change to metamorphic rock. D. Metamorphic rock must melt before it can change to sedimentary rock.
- Slide 32
- 16. According to the Earth Science Reference Table, which is a sedimentary rock that forms from the result of evaporation of seawater? A. Conglomerate B. Gypsum C. Basalt D. Shale
- Slide 33
- 16. According to the Earth Science Reference Table, which is a sedimentary rock that forms from the result of evaporation of seawater? A. Conglomerate B. Gypsum C. Basalt D. Shale
- Slide 34
- 17. When various minerals are split by a wedge, some break evenly along a flat surface, while others fracture unevenly. Which property of a mineral is reponsible for the way it splits? A. Hardness B. Density C. Chemical Composition D. Atomic Arrangement
- Slide 35
- 17. When various minerals are split by a wedge, some break evenly along a flat surface, while others fracture unevenly. Which property of a mineral is reponsible for the way it splits? A. Hardness B. Density C. Chemical Composition D. Atomic Arrangement
- Slide 36
- 18. Which property best describes a rock which formed from sediments? A. Fragmental particles arranged in layers B. Distorted structure C. Crystalline structure D. Banding or foliation
- Slide 37
- 18. Which property best describes a rock which formed from sediments? A. Fragmental particles arranged in layers B. Distorted structure C. Crystalline structure D. Banding or foliation
- Slide 38
- 19. The igneous rock pictured looks most likely like which rock name? A. Gabbro B. Obsidian C. Granite D. Dunite
- Slide 39
- 19. The igneous rock pictured looks most likely like which rock name? A. Gabbro B. Obsidian C. Granite D. Dunite
- Slide 40
- 20. Which statement correctly describes the distribution of sedimentary rocks on the Earth? A. Sedimentary rock layers are the thickest in the middle of the ocean B. Sedimentary rocks extend all the way from the Earths crust to the inner core C. Sedimentary rocks are usually located in volcanic regions D. Sedimentary rocks form a thin layer over large areas of the continents
- Slide 41
- 20. Which statement correctly describes the distribution of sedimentary rocks on the Earth? A. Sedimentary rock layers are the thickest in the middle of the ocean B. Sedimentary rocks extend all the way from the Earths crust to the inner core C. Sedimentary rocks are usually located in volcanic regions D. Sedimentary rocks form a thin layer over large areas of the continents
- Slide 42
- 20. Which process is responsible for turning a pile of sediments into a sedimentary rock, such as in the diagram? A. Heat and/or pressure B. Melting and solidification C. Recrystallization D. Compaction and cementation
- Slide 43
- 20. Which process is responsible for turning a pile of sediments into a sedimentary rock, such as in the diagram? A. Heat and/or pressure B. Melting and solidification C. Recrystallization D. Compaction and cementation
- Slide 44
- 21. Which of the following minerals would be able to scratch the other three? A. Quartz B. Gypsum C. Pyrite D. Dolomite
- Slide 45
- 21. Which of the following minerals would be able to scratch the other three? A. Quartz B. Gypsum C. Pyrite D. Dolomite
- Slide 46
- 22. Why do both calcite and dolomite bubble when placed in acid? A. Both are silicate minerals B. Both are carbonates C. Both are metamorphic rocks D. Both are colorless and of similar hardness
- Slide 47
- 22. Why do both calcite and dolomite bubble when placed in acid? A. Both are silicate minerals B. Both are carbonates C. Both are metamorphic rocks D. Both are colorless and of similar hardness
- Slide 48
- 23. Which process would form a sedimentary rock? A. Cooling of molten magma within Earths crust B. Recrystallization of unmelted material within Earths crust C. Adding heat and pressure to a rock D. Precipitation of minerals as seawater evaporates
- Slide 49
- 23. Which process would form a sedimentary rock? A. Cooling of molten magma within Earths crust B. Recrystallization of unmelted material within Earths crust C. Adding heat and pressure to a rock D. Precipitation of minerals as seawater evaporates
- Slide 50
- 24. Which property of minerals is being tested in the diagram below? A. Color B. Luster C. Streak D. Cleavage/Fracture
- Slide 51
- 24. Which property of minerals is being tested in the diagram below? A. Color B. Luster C. Streak D. Cleavage/Fracture
- Slide 52
- 25. Which of the following below is most likely a non-sedimentary rock? A. A rock containing fossils B. A rock composed of layers of gravel cemented together C. A rock consisting of large, intergrown crystals D. A rock showing ripple marks and mud cracks
- Slide 53
- 25. Which of the following below is most likely a non-sedimentary rock? A. A rock containing fossils B. A rock composed of layers of gravel cemented together C. A rock consisting of large, intergrown crystals D. A rock showing ripple marks and mud cracks
- Slide 54
- Good Job! Please tally up the number of questions you answered correctly.