DNA & RNA Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis. DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid RNA Ribonucleic Acid.
Ribonucleic Acid RNA. The structure of ribonucleic acid Learning Objectives: Describe the structure...
-
Upload
dulcie-booth -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
1
Transcript of Ribonucleic Acid RNA. The structure of ribonucleic acid Learning Objectives: Describe the structure...

Ribonucleic Acid
RNA

The structure of ribonucleic acid
Learning Objectives: Describe the structure of ribonucleic acid (RNA) Describe the structure and role of messenger
RNA (mRNA) Describe the structure and role of transfer RNA
(tRNA)

RNA
RNA = ribonucleic acid RNA is a single -stranded polymer Each RNA nucleotide consists of:
A pentose sugar (ribose) A phosphate group A base – adenine, cytosine, guanine,
uracil (instead of thymine) RNA used in protein synthesis is
messenger RNA (mRNA) or transfer RNA (tRNA).

RNA contains the pentose sugar ribose.
DNA contains the pentose sugar deoxyribose.

The Genetic Code (recap of unit 2)
3 nucleotide bases on mRNA (a codon) codes for each amino acid in a protein (DNA = triplet code).
A few amino acids have a single codon. The code is degenerate – most amino acids have
more than one codon. 3 codons code for no amino acids – they are stop
codons and mark the end of the polypeptide chain. Non-overlapping – each nucleotide is read only
once. Universal – same codon codes for the same amino
acid in all organisms (few minor exceptions).

mRNA (m = messenger)

tRNA (t = transfer)Amino acid joins here
Anticodon

Complete the worksheet…

Messenger RNA (mRNA) Used to transfer the DNA code from the nucleus
to the cytoplasm, 1 gene at a time.
Complementary to the DNA code.
Small enough to leave the nuclear pores.
Once in the cytoplasm, mRNA associates with the ribosomes.
Easily broken down and only exists whilst it is needed to manufacture a protein.

Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Small molecule (~80 nucleotides). Single stranded and folded into a clover leaf shape
with one end of the chain slightly longer. This longer section is attached to an amino acid. Each tRNA carries a different amino acid. 3 bases at the opposite end of the tRNA are called
an anticodon. Each amino acid has a different anticodon. The anticodon pairs with the complementary codon
on the mRNA.

Go to boardworks ppt…

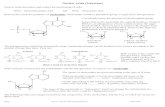
Polypeptide synthesis – transcription and splicing
Learning Objectives: How is pre-mRNA produced from DNA in the
process called transcription?
How is pre-mRNA modified to form mRNA?

Transcription Helicase (enzyme) acts on a region
of DNA to break the hydrogen bonds between the bases.
RNA polymerase moves along one of the two DNA strands – template strand
RNA polymerase matches up complementary RNA nucleotides.
C matches G and G matches CU matches A and A matches T
As the RNA nucleotides join together the pre-mRNA is formed.
The DNA behind the RNA polymerase rejoins into a double helix.
When the RNA polymerase reaches a “stop” codon, the chain is terminated and the pre-mRNA detaches.

Splicing of mRNA to form mRNA
Once the introns (non-functional DNA) have been removed, the remaining exon sections join together.

RNA Splicing
snRNPs
Spliceosome

Transcription Animation
http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranscription.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::525::530::/sites/dl/free/0072464631/291136/mRNA_synthesis.swf::mRNA_synthesis.swf
mRNA splicinghttp://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?
it=swf::525::530::/sites/dl/free/0072464631/291136/spliceosomes.swf::spliceosomes.swf

Polypeptide synthesis – translation
Learning Objectives: How is a polypeptide synthesised during the
process of translation?
What are the roles of mRNA and tRNA in translation?

Translation (Protein Synthesis)
mRNA
tRNAAmino acids

Synthesising the polypeptide (translation) mRNA attaches to the ribosome at the “start” codon
– AUG. tRNA with a complementary anticodon attaches to
the mRNA – UAC. This tRNA is attached to an amino acid – methionine The ribosome moves along the mRNA bringing in 2
tRNA molecules at any one time. An enzyme and ATP are used to join the amino
acids with a peptide bond. The first tRNA is released and can collect another
amino acid. The process is repeated until a “stop” codon is
reached. Many ribosomes can travel along the mRNA at the
same time – polysome.


Translation Animation
http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::525::530::/sites/dl/free/0072464631/291136/protein_synthesis.swf::protein_synthesis.swf