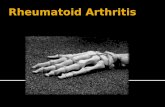
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition Progressive, systemic, inflammatory disorder...
-
Upload
beatrix-melton -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
4
Transcript of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition Progressive, systemic, inflammatory disorder...

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition Progressive, systemic, inflammatory disorder Unknown etiology Characterized by
u Symmetric synovitisu Joint erosionsu Multisystem extra-articular manifestations

RA - Epidemiology * RA has a worldwide
distribution with an estimated prevalence of 1-2%.
Prevalence increases with age, including 5% in women over age 55.
The average annual incidence in the US is about 70 per 100,000 annually.
Both incidence and prevalence of RA are two to three times greater in women than in men.
Although rheumatoid arthritis may present at any age, patients most commonly are first affected between the ages of 30 and 60 years.

RA – Epidemiology Continue RA is among the
oldest diseases. Arthritis and
osteoarthritis are the most prevalent conditions.
RA affects all races. Older age and
overweight are risk factors for arthritis.
Patients with RA have a shortened life span.
For women over 45 years, arthritis is the leading cause of activity limitation.
The most frequent cause of death is cardiovascular disease.
Other mortality conditions result from septicemia, pneumonia, etc.

Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pathologic finding: chronic synovitis with pannus formation. The pannus erodes cartilage, bone, ligament and tendons. In the acute phase effusion and other manifestations of inflammation are evident; in the later stages ankylosis of the joint may set in. In both the acute and chronic phase, there may be widespread inflammation of the tissues around the joint that can lead to significant joint destruction.

RA – Immunologic Manifestations continue
Pannus is an organized mass of cells that grows into the joint space and invades the cartilage.

Pathology
Normal jointu synovial
membrane (macrophage and fibroblast-like cells)
u fibrous joint capsule
u synovial fluidu cartilage covers
articular surface
RA jointu SM hyperaemic, congestedu synovial cell proliferation and villous
hypertrophyu SM infiltration by lymphocytes,
macrophagesu Vascular pannus at cartilage-synovium
junctionu increased volume and cellularity of SFu atrophy of supporting musclesu osteopaenia of surrounding bone

Immunopathology
Aggregates of T-cells, macrophages and plasma cells in SMu Activated phenotype
SF contains mainly neutrophils Pro (TNF, IL1, IL6) and anti-inflammatory (IL10,
TGF) cytokines within joint Interplay between immune cells and cytokines
generates inflammation and joint damage
What initiates the process and why doesn’t it resolve?
Nobody knows the answer.

Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
B cell
T cell
Antigen-presenting
cells
B cell ormacrophage Synoviocytes
Pannus
Articularcartilage
Chondrocytes
Macrophage
HLA -DRother cytokines
IFN- &
Production of collagenase and otherneutral proteases
Osteoclast
TNFIL-1
RheumatoidFactors, anti-CCP
Immune complexes
Bone
Complement
Neutrophil
Mast cell
Adapted from Arend WP, Dayer JM. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:305–15
Current Treatment Targets

Chronic Inflammation: Imbalance Between Mediators
Proinflammatory
Anti-inflammatory
TNFIL-1
IL-8IL-6
IFNIL-4/IL-13
IL-1RaTGF
IL-10

RA – Signs and Symptoms It is a highly
variable disease that ranges from a mild illness of brief duration to a progressive destructive polyarthritis associated with a systemic vasculitis.

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont. The joints involved
most often are the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints of the hands, the wrists, shoulders, elbows, knees, ankles, and metatarsophalangeal joints. The spine except in late disease is usually not affected.

Rheumatoid Arthritis: PIP Swelling Swelling is confined to
the area of the joint Synovial thickening
feels like a firm sponge

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont.
Morning stiffness, persisting more than one hour but often lasting several hours is especially characteristic of RA.
Its duration is a useful gauge of the inflammatory activity of the disease.

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Ulnar Deviation and MCP Swelling
An across-the-room diagnosis
Prominent ulnar deviation in the right hand
MCP and PIP swelling in both hands
Synovitis of left wrist

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont. Nonspecific systemic
symptoms primarily fatigue, malaise, and depression , may commonly precede other symptoms of the disease by weeks to months.
Patients have complained of severe fatigue 4-6 hours after wakening.
Fever occasionally occurs and is almost always low grade.
It is typical of patients with RA that their symptoms vary, often making diagnosis and treatment difficult.

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont.
Erosions, seen on x-ray, occur within the first 2 years. These changes result in limitation in range of motion.

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont.
Typical visible changes in the joints.

Rheumatoid Arthritis:Key Features
• Symptoms >6 weeks’ duration• Often lasts the remainder of the patient’s life
• Inflammatory synovitis• Palpable synovial swelling• Morning stiffness >1 hour, fatigue
• Symmetrical and polyarticular (>3 joints)• Typically involves wrists, MCP, and PIP joints • Typically spares certain joints
• Thoracolumbar spine • DIPs of the fingers and IPs of the toes

Rheumatoid Arthritis:Key Features (cont’d)
• May have nodules: subcutaneous or periosteal at pressure points
• Rheumatoid factor• 45% positive in first 6 months• 85% positive with established disease
• Marginal erosions and joint space narrowing on x-ray
Adapted from Arnett, et al. Arth Rheum. 1988;31:315–324.

Clinical Course of RA
Type 1 = Self-limited—5% to 20%Type 2 = Minimally progressive—5% to 20%Type 3 = Progressive—60% to 90%
0
1
2
3
4
0 0.5 1 2 3 4 6 8 16
Type 1Type 2Type 3
Years
Sev
erity
of
Art
hriti
s
Pincus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1995;21:619.

Pincus, et al. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993;19:123–151.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Typical Course
• Damage occurs early in most patients • 50% show joint space narrowing or erosions in
the first 2 years• By 10 years, 50% of young working patients
are disabled• Death comes early
• Multiple causes• Compared to general population
• Women lose 10 years, men lose 4 years

Investigations
Haematologyu Hb, wcc, plts, ESR
Biochemistryu CRP
Microbiologyu viral titres
Immunologyu RhF, ANA, SSP
Radiologyu XR, bone scan, MRI

possible features
clinical
• arthritis / arthralgia• vasculitis• fever• Raynaud's phenomenon• fatigue• various renal diseases
laboratory
• increased ESR, CRP• anaemia • leukopenia•ANA• trombopenia
systemic autoimmune diseases
not specific
for
one single disease
not specific
for
one single disease

people
how do you recognize them ?
each person
has a face

each autoimmune disease
has its own "face"
how do you recognize it?
RA

Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody
Specificity Sensitivity
RF + 75% 60%
Anti-CCP + 96% 75%
Anti-CCP + RF +
99% 80%
* High titer anti-CCP may predict aggressive erosive disease.
Linn-Rasker SP, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65:366-71

Rheumatoid factor (RF or RhF) is an autoantibody (antibody directed against an organism's own tissues) most relevant in rheumatoid arthritis. It is an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG, which is itself an antibody. RF and IgG join to form immune complexes which contribute to the disease process

Citrulline is a non-standard amino acid, created by de-imination of arginine residues in several proteins by the action of peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD). There are several isotypes of this enzyme; in the inflammatory RA synovium, PAD 2 and PAD 4 are abundant These enzymes cause the local citrullination of synovial proteins, such as fibrin. Citrullinated extracellular fibrin in the RA synovium may be one of the major autoantigens driving the local immune response, suggested by the discovery of local production of anti-CCP and anti-citrullinated filaggrin antibodies in the joint. Also, functional haplotypes of PADI4 may be associated with RA.

Stage I Early – no destruction
Stage II Moderate – no joint deformity, osteoporosis with bone and cartilage destruction
Stage III Severe – cartilage and bone destruction with osteoporosis, joint deformity
Stage IV Terminal – fibrous or bony ankylosis





Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis

Disease Activity Score
Frequent Assessments of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Disease
Activities are:
DAS28 (Disease Activity Score)
DAS28=(0.56*TJC1/2)+(0.28*SJC1/2)+(0.7*ln[ESR])+(0.014* VAS, [in mm])

ІІ. Степень активности.1 Степень активности:Боль, ВАШ
(см)0до 3утренняя скованность (минуты)30-
60СОЕ (мм/час)менше 152 степень – ВАШ 4-6
утренняя скованность до 12 часов , СОЕ 31-45 мм/час;
3 степень: ВАШ больше 6, утренняя скованность на
протяженидня, СОЄбольше 45


Differential diagnosis Post viral condition Reactive arthritis SLE Polyarticular Gout Polyarticular OA

Factors Suggesting Poor Prognosis
>20 swollen joints High RF titer Elevated anti-
CCPs Elevated Sed Rate Elevated CRP Late
implementation of treatment
Joint erosions Presence of
rheumatoid nodules Socioeconomic
characteristics Smoking Poor functional status

RA – Signs and Symptoms cont.The American
Rheumatism Association’s criteria for diagnosis of RA.
1. Morning stiffness in and around the joints that lasts for at least 1 hour.
2. Arthritis of 3 or more joint areas; at least 3 joints have soft tissue swelling or fluid.
3. Arthritis of wrist, MPC, or PIP joint.
4. Symmetric involvement of joints
5. Rheumatoid nodules over bony prominences, or extensor surfaces, or in juxtaarticular regions
6. Positive serum RA factor 7. Radiographic changes,
including erosions or bony decalcification to the involved joints

2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis

2010 ACR/EULARClassification Criteria for RA
JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
≥6 = definite RA
What if the score is <6?
Patient might fulfill the criteria…
Prospectively over time (cumulatively)
Retrospectively if data on all four domains have been adequately recorded in the past

Algorithm to Classification of RA Including Radiographs
Longstanding inactive disease
suspected?
Longstanding inactive disease
suspected?
≥6/10 on the scoring system?
≥6/10 on the scoring system?
Not RA
RA
NoNo
Radiographsalready available
Radiographsalready available
Perform radiographic assessment
Perform radiographic assessment
YesYes Erosions typical forRA present?
Erosions typical forRA present?
YesYes≥1 swollen joint,
which is not best explained by another disease?
≥1 swollen joint, which is not best explained by
another disease?
NoNo
NoNo
NoNo
YesYes
Document result of the scoring system
Document result of the scoring system
YesYes
YesYes
NoNo

The 2010 Tree Algorithm for classifying definite RA (green circles) or for excluding its presence (red circles) among those who are eligible to be
assessed by the 2010 ACR-EULAR RA Classification Criteria
APR = acute-phase response. Serology: + = low-positive for rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti–citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA); serology: ++ = high-positive for RF or ACPA; serology: +/++ = serology either + or ++. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman A, Funovits J, Felson D, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology / European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569-81.

Definitions
≥6 = definite RA
JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
Definition of “JOINT INVOLVEMENT”
- Any swollen or tender joint (excluding DIP of hand and feet, 1st MTP, 1st CMC)
- Additional evidence from MRI / US may be used for confirmation of the clinical findings

DefinitionsJOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted)
2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted)
3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
≥6 = definite RA
Definition of “SMALL JOINT”
MCP, PIP, MTP 2-5, thumb IP, wrist
NOT: DIP, 1st CMC, 1st MTP

Definitions
≥6 = definite RA
JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
Definition of “LARGE JOINT”
Shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, ankles

JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
≥6 = definite RA
Definition of “>10 JOINTS”
- At least one small joint
- Additional joints include: temporomandibular, sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, and others (reasonably expected in RA)
Definitions

Definitions
≥6 = definite RA
JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
Definition of “SEROLOGY”
Negative: ≤ULN (for the respective lab)
Low positive: >ULN but ≤3xULN
High positive: >3xULN

Definitions
≥6 = definite RA
JOINT DISTRIBUTION (0-5)
1 large joint 0
2-10 large joints 1
1-3 small joints (large joints not counted) 2
4-10 small joints (large joints not counted) 3
>10 joints (at least one small joint) 5
SEROLOGY (0-3)
Negative RF AND negative ACPA 0
Low positive RF OR low positive ACPA 2
High positive RF OR high positive ACPA 3
SYMPTOM DURATION (0-1)
<6 weeks 0
≥6 weeks 1
ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS (0-1)
Normal CRP AND normal ESR 0
Abnormal CRP OR abnormal ESR 1
Definition of “SYMPTOM DURATION”
Refers to the patient’s self-report on the maximum duration of signs and symptoms of any joint that is clinically involved at the time of assessment.

Evolving RA Treatment Paradigm
Initial
treatment:
traditional DMARDs
• Early aggressive treatment
• Biologics• Combination therapy
Current Approach Evolving Paradigm

Rheumatoid Arthritis:Treatment Principles
Confirm the diagnosis Determine where the patient stands in the
spectrum of disease When damage begins early, start aggressive
treatment early Use the safest treatment plan that matches the
aggressiveness of the disease Monitor treatment for adverse effects Monitor disease activity, revise Rx as needed

Critical Elements of a Treatment Plan: Assessment
• Assess current activity • Morning stiffness, synovitis, fatigue, ESR
• Document the degree of damage • deformities• Joint space narrowing and erosions on x-ray• Functional status
• Document extra-articular manifestations • Nodules, pulmonary fibrosis, vasculitis
• Assess prior Rx responses and side effects

Critical Elements of a Treatment Plan: Therapy
• Education • Exercise• Medications
• DMARDs : Immunosuppressive, cytotoxic, and biologic
• Analgesic and/or anti-inflammatory

Advantages of DMARDs Slow disease progression Improve functional disability Decrease pain Interfere with inflammatory processes Retard development of joint erosions

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatment Options
• Disease modifying drugs (DMARDs)• Sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine
• Moderate effect, low cost
Alarcon. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998;24:489–499.Paget. Primer on Rheum Dis. 11th edition. 1997:168.

Paget. Primer on Rheum Dis. 11th edition. 1997:168.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatment Options (cont’d)
• Immunosuppressive drugs• Methotrexate
• Most effective single DMARD• Good benefit-to-risk ratio
• Azathioprine • Slow onset, reasonably effective
• Cyclophosphamide• Effective for vasculitis, less so for arthritis
• Cyclosporine • Superior to placebo, renal toxicity

Selection of an Initial DMARD
Toxicities to monitorMyelosuppression, hepatotoxicity, lymphoproliferative Renal, hyperuricemiaMyelosuppression, rash,proteinuria, gastrointestinal
Myelosuppression, rashproteinuriaMacular damageHepatotoxicity, gastrointestinalHepatotoxicity, pulmonary, myelosuppressionMyelosuppression, proteinuriaMyelosuppression, gastrointestinal
Potential toxicityModerate
HighLow
Moderate
LowLow
Moderate
LowHigh
Low
Time to benefit2-3 months
4-8 weeks4-6 months
3-6 months
2-4 months4-8 weeks
1-3 months
3-6 months
1-3 months
AgentAzathioprine
CyclosporinGold, oral
Gold, parenteral
HydroxychloroquineLeflunomide
Methotrexate
D-Penicillamine
Sulfasalazine

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Monitoring Treatment With DMARDs
• These drugs need frequent monitoring• Blood, liver, lung, and kidney are frequent sites of
adverse effects• Interval of laboratory testing varies with the drug
• 4- to 8-week intervals are commonly needed • Most patients need to be seen 3 to 6 times a year

Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: DMARDs
*Physicians’ Desk Reference, 1998. Recommended doses are not necessarily those utilized in clinical practice.
AgentAzathioprineCyclosporinGold, oralGold, parenteral
HydroxychloroquineLeflunomideMethotrexateD-Penicillamine
Sulfasalazine
Recommended Dose *1.0-2.5 mg/kg/d2.5-4.0 mg/kg/d6-9 mg/d
25-50 mg every 2-4 weeks following initial weekly titration doses
200-400 mg/d
100 mg x 3 days loading; 20
mg/q.d.
7.5-20 mg/wk125-750 mg/d
2-3.0 g/d

Selection of an Initial DMARD: Methotrexate
Pros Long-term clinical
experience Favorable rate of
continuation of therapy
Proven efficacy in moderate to severe RA
Cons Laboratory monitoring
every 4-8 weeks
Toxicities: hepatotoxicity, myelosuppression, pulmonary

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unknown Case 3 52-year-old man with destructive RA treated with
NSAID and low-dose prednisone. MTX started 4 months ago, now 15 mg/wk
Presents with 3-week history of fever, dry cough, and increasing shortness of breath
Exam: Low-grade fever, fine rales in both lungs, normal CBC and liver enzymes, low albumin, diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest x-ray

RA: Unknown Case 3 (cont’d) What would you do?
A. Treat with antibiotic for bacterial pneumonia
B. Give cough suppressant for viral pneumonia and watch
C. Give oral steroid for hypersensitivity pneumonitis and stop methotrexate
D. Give a high-dose oral pulse of steroid and increase methotrexate for rheumatoid lung

DMARDs Have a Dark Side
Don’t Miss It
DMARDs have a dark sideMethotrexate may cause serious problems
LungLiverBone marrow
Be on the look out for toxicity with all the DMARDs

Methotrexate Lung
• Dry cough, shortness of breath, fever• Most often seen in the first 6 months of MTX
treatment• Diffuse interstitial pattern on x-ray
• Bronchoalveolar lavage may be needed to rule out infection
• Acute mortality = 17%; 50% to 60% recur with retreatment, which carries the same mortality
• Risk factors: older age, RA lung, prior use of DMARD, low albumin, diabetes
Kremer, et al. Arth Rheum. 1997;40:1829–1837.

Cons Effective for mild-to-moderate RA Contraindicated in patients with sulfa
intolerance Toxicities: myelosuppression,
gastrointestinal, CNS Rate of AEs is dose-dependent CBC every 2-4 weeks for 3 months,
then every 12 weeks
Pros Clinical effectiveness
demonstrated in short-term use
Mild level of toxicity
Selection of an Initial DMARD: Sulfasalazine

Cons Lack of clinical
experience Toxicities:
hepatotoxicity, gastrointestinal
Selection of an Initial DMARD: Leflunomide
Pros Early onset of action (~ 4
weeks) Stabilized benefit for long-
term use Selectively targets
autoimmune lymphocytes to reduce untoward AEs

Cons High risk for severe leukopenia and/or
thrombocytopenia Other toxicities: hepatotoxicity, may increase
cancer risk, high risk for opportunistic infections, macrocytic anemia, severe bone marrow depression
Requires monitoring every 1-2 weeks with dosage change, every 1-3 months thereafter
Selection of an Initial DMARD: Azathioprine
Pros Effective in refractory
RA

Combination DMARD Therapy Combination DMARD regimen
u Does not increase toxicity levelsu Long-term outcome more favorableu Superior efficacy to single-DMARD regimen
Possible combinationsu Methotrexate/sulfasalazine/hydroxychloroquineu Cyclosporine/methotrexateu Leflunomide/methotrexate

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatment New Options—Combinations
Methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine
Superior to any one or two alone for ACR 50% improvement response and maintenance of the response
Side effects no greater0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
2-Year Outcome
Per
cent
With
50%
AC
R R
espo
nse
TripleRX
SSZ+HCQ
MTX

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Drug Treatment Options
• NSAIDs • Symptomatic relief, improved function
• No change in disease progression• Low-dose prednisone (10 mg qd)
• May substitute for NSAID • Used as bridge therapy!!!• If used long term, consider prophylactic
treatment for osteoporosis• Intra-articular steroids
• Useful for flaresPaget. Primer on Rheum Dis. 11th edition. 1997:168.

Cons
Does not affect disease progression !!!!
GI toxicity common Renal complications (eg, irreversible
renal insufficiency, papillary necrosis)
Hepatic dysfunction CNS toxicity
Pros
Effective control of inflammation and pain
Effective reduction in swelling
Improves mobility, flexibility, range of motion
Improve quality of life
Relatively low-cost
Pros and Cons of NSAID Therapy

RA: Unknown Case 1 68-year-old woman with 3-year history of RA She presents with 4 weeks of increasing fatigue,
dizziness, dyspnea, and anorexia Her joint pain and stiffness are mild and
unchanged Managed with ibuprofen and hydroxychloroquine
until 4 months ago, when a flare caused a switch to piroxicam and prednisone

RA: Unknown Case 1 (cont’d) Past history: Peptic ulcer 10 years ago and mild
hypertension Exam shows a thin, pale apathetic woman with
Temp 36.6ºC, BP 110/65, pulse 110 bpm Symmetrical 1+ synovitis of the wrist, MCP, PIP,
and MTP joints Exam of the heart, lungs, and abdomen is
unremarkable

RA: Unknown Case 1 (cont’d)
Which system in this patient is currently predominantly affected?
A. Cardiovascular
B. Neuropsychological
C. Endocrine
D. Gastrointestinal

RA: Unknown Case 1 (cont’d)
Don’t Miss It
NSAID gastropathy is sneaky and can be fatal

RA: Unknown Case 1 (cont’d)
• Clues of impending disaster• High risk for NSAID gastropathy• Presentation suggestive of blood loss
• Pale, dizzy, weak• Tachycardia, low blood pressure
• No evidence of flare in RA to explain recent symptoms of increased fatigue

Singh. Am J Med. 1998;105(suppl B):31S–38S.
Key Point: Know the Risk Factors for NSAID Ulcers
Older age Prior history of peptic ulcer or GI symptoms with
NSAIDs Concomitant use of prednisone NSAID dose: More prostaglandin suppression =
greater risk of serious events Disability level: The sicker the patient the higher
the risk

Cons
Does not conclusively affect disease progression!!!
Low doses result in skin thinning, ecchymoses, and Cushingoid appearance
Significant cause of steroid-induced osteopenia
Pros
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects
Can be used to bridge gap between initiation of DMARD therapy and onset of action
Intra-articular injections can be used for individual joint flares
Pros and Cons of Corticosteroid Therapy

Therapeutic Window of Opportunity of DMARDs is limited
O’Dell JR. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:283-285.Van der Heijde DM. Br J Rheum. 1995;34 (suppl 2):74-78.

Biologic DMARD’s – Genetically Engineered Targeted Molecules Similar or Identical to
Naturally Occurring Molecules
TNFα antagonists:u Adalimumab (Humira)u Etanercept (Enbrel)u Infliximab (Remicade)
Interleukin-1 antagonistu Anakinra (Kineret)
Suppress T-Cell activationu Abatacept (Orencia)
Anti B-Cell monoclonal antibodyu Rituximab (Rituxan)

Characteristics of Biologics
Etanercept
Enbrel
Infliximab
Remicade
Adalimumab
Humira
Anakinra
Kineret
Abatacept
Orencia
Rituximab
Rituxan
Target TNF TNF TNFIL-1
ReceptorT-Cell
ActivationB-Cell
Half Life 3-5 Days 8-10 Days 10-20 Days 4-6 Hrs 13-16 Days 19 Days
Construct Human Chimeric Human Human Human Chimeric
DosingOnce
Biweekly-weekly
Once every 4-8 weeks
Once every 1-2 weeks
Once Daily Once Monthly
Twice every 6-12 months
Route Sub-Cut I.V. Sub-Cut Sub-Cut I.V. I.V.

Rituximab: Mechanism of Action
Rituximab initiates complement-mediated B-cell lysis
Rituximab initiates cell-mediated cytotoxicity via macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells
Rituximab induces apoptosis caspase-3,-9
CD20
Rituximab
Clynes RA et al. Nat Med. 2000;6:373-374; Reff ME et al. Blood. 1994;83:435-445.
B cell
B-cell lysis
Apoptosis
Complementcascade
Macrophage
B cell

CTLA4lg (Abatacept) Effectively Blocks CD28 Dependent Costimulatory Signals
Antigen Presenting Cell T Lymphocyte
TCRMHC II
Signal 1
CD80 CD28 Signal 2CD86 CD28
ClonalProliferation
CytokineProduction IL-2 IL-4 IL-5 TNF-
Full Activation
Antigen specific
Costimulation
CTLA4lg
Abatacept Fusion proteinFirst in the new class of “costimulation blockers” for treatment of RAPrevents T-cell activation via binding CD80 and CD86 on antigen-presenting cells

Safety Considerations with Biologic DMARD’s
Serious Infections Opportunistic
infections (TB) Malignancies/
lymphoma Demyelination Hematologic
abnormalities
Administration reactions
Congestive heart failure
Hepatic Autoantibodies and
drug induced lupus Vaccination

Biologics: Relative Contraindications
Active Hepatitis B Infection
Multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis
Active serious infections
Chronic or recurrent infections
Current neoplasia
History of TB or positive PPD (untreated)
Congestive heart failure (Class III or IV)

ACR Algorithm for Management of RA
ACR Subcommittee on RA Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:328-346.
Diagnosis• Establish early diagnosis of RA• Document baseline disease activity and damage• Estimate prognosis of patient
Initiate therapy• Patient education• Start disease-modifying agent within 3 months• Consider NSAID and/or local or low-dose steroids• Physical/occupational therapy
Subjective criteria
Physical exam
Laboratory tests
Radiography
DMARDs
Biologics
Periodically assess disease activity

ACR Algorithm for Management of RA
ACR Subcommittee on RA Guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:328-346.
Periodically assess disease activity
Adequate response with disease activity
Inadequate response(ongoing disease activity)
Change or add disease-modifying drugs
Methotrexate naive
Methotrexate Othermonotherapy
Suboptimal methotrexate response
Combinationtherapy
Biologics

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 1 34-year-old woman with 5-year history of RA Morning stiffness = 30 minutes Synovitis: 1+ swelling of MCP, PIP, wrist, and
MTP joints Normal joint alignment Rheumatoid factor positive No erosions seen on x-rays

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 1 (cont’d)
• Assessment• Current activity—mild• No sign of damage after 5 years• Type 2 minimally progressive course
• Treatment• NSAID + safer, less potent drugs, eg,
• Hydroxychloroquine, or sulfasalazine• Education and exercises

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 2 34-year-old woman with 1-year history of RA Morning stiffness = 90 minutes Synovitis: 1+ to 2+ swelling of MCP, PIP, wrist,
knee, and MTP joints Normal joint alignment RF positive Small erosions of the right wrist and two MCP
joints seen on x-rays

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 2 (cont’d)
Early erosion at the tip of the ulnar styloid

A. Soft-tissue swelling, no erosions
B. Thinning of the cortex on the radial side and minimal joint space narrowing
C. Marginal erosion at the radial side of the metacarpal head with joint space narrowing
How fast is joint damage progressing?
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 2 (cont’d)
ACR Clinical Slide Collection, 1997.

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 2 (cont’d)
• Assessment of case 2• Moderate disease activity• Many joints involved• Clear radiologic signs of joint destruction early
in disease course• Type 3 progressive course
• Treatment should be more aggressive• NSAID, MTX, SSZ, and hydroxychloroquine
would be a good choice

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 3
• 34-year-old woman with 3-year history of RA• Morning stiffness = 3 hours• 2 to 3+ swelling of MCP, PIP, wrist, elbow,
knee, and MTP joints• Ulnar deviation, swan neck deformities,
decreased ROM at wrists, nodules on elbows• RF positive, x-rays show erosions of wrists and
MCP joints bilaterally• Currently on low-dose prednisone + MTX, SSZ,
and hydroxychloroquine

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case 3 (cont’d)
• Assessment• Very active disease in spite of aggressive
combination therapy• Evidence of extensive joint destruction
• Treatment options are many• Step-down oral prednisone, 60 mg qd tapered
to 10 mg qd over 5 weeks, can be used for immediate relief of symptoms
• Use other cytotoxics or cyclosporine • Consider TNF inhibitor or leflunomide

Treatment Summary
Early appropriately aggressive intervention in patients with inflammatory arthritis: critical to best possible outcome.
The combination of a biologic plus MTX is frequently more effective than either agent alone.

Conclusion
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a serious disease Early diagnosis is key to good outcomes Advent of new therapies have major impact in
altering disease progression