Rheumatic Fever Ок
-
Upload
ali-baker-algelane -
Category
Documents
-
view
251 -
download
0
Transcript of Rheumatic Fever Ок
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
1/45
Rheumatic
fever
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
2/45
Rheumatic feveris acute systemic disease of
the connective tissue immune
inflammatory genesis,characterised mainly by
arthritis, carditis, chorea,
subcutaneous nodules and
erythema marginatum.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
3/45
Rheumatic fever(RF)
is common world-wide and is
responsible for many causesof damage heart valves.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
4/45
Etiology:
Group A, hemolytic streptococcus(strains 3,5,18,24,28,49 ) is the maine
etiologycal factor. RF occurs about 2weeks after exudative tonsi l i tis
(quinsy,soa throat), scar let
fever,streptodermia or otherstreptococcus infections, if it goes
without treatment.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
5/45
Person who has high hyperensitivi ty toimmune system on streptococcus
suffered more frequently. This
hypersensibil i ty of immune systemgenotype determinate with HLA system
antigen A11, B
27, B
35, CW
2, CW
5, DR
5,
DR7.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
6/45
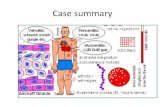
Pathogenesis:
On the basis of pathogenesis RF is
immunoinflamatory reaction
(reaction antigen-antibody) with
edema,
hyperemia,
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
7/45
lymphocyte infiltration of
connective tissue heart (valvule,endocardium, myocardium,
pericardium), brain, vessels,
synovial membrane of joints,skin,
other organ and formatione
rheumatic granuloma (Aschoffsnodule) in connective tissue.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
8/45
Immunoinflamatory reaction (react ion
ant igen-ant ibody) is always
accompanied by elimination ofinflammatory mediators: histamine,
bradikinin, prostaglandin E2 and
other.Histamin is dilated capillares andbring on oedema, hyperemia,
infiltratione connective tissue with
cells of immune response
(lymphocytes, plasmatic cells, mast
cells, eosinophils, basophils).
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
9/45
Prostaglandin E2 - causeincrease to C.
Cluster circulate immune
complex in connective tissue
is cause formation ofpointing necroses in
particular area.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
10/45
during immunoinflamatory
reaction morphologically we are
different 4 stages:
mucoid swelling;fibrinoid swelling;
granulomatosis;sclerosis and hyalinosis.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
11/45
Outcome of the
immunoinflammatory reaction
are sclerosis,hialinosis,deformation,calcification
valvulas and formatione
anatomical defects (valvula
heart d isease) .
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
12/45
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
13/45
Sclerosis of myocardium -
myocard iosc leros is(cardiacinsufficiencyheart failure,
arrhythmias, blockades).
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
14/45
Clinical PICTURE
symptoms and signs ar ise 2 weeks
after pharyngitis or tonsi l l i tis (soa
throat) or scarlet fever.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
15/45
major cr i ter ia (manifestation)of RF are:
1.Migratory polyarthritis
2.Carditis
3.Chorea
4.Subcutaneous nodules
5.Erythema marginatum
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
16/45
m ino r cr i ter ia o f RF are:
high toC;abdominal pain, anorexia;
heart failure;
epistaxis;
pneumonia;
asthenia;malaise;
fatigue.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
17/45
Migratory polyarthritis is the most
common clinical manifestation,monoarthritis can also occur. Joints
become painful and tender ,red, hot,
swollen, sometimes with effusion.
Knees, elbows or wrists are most
commonly involved. It leaves nopermanent joint deformility.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
18/45
Cardit is
(involves 2 or 3 wall of heart)endocarditis+myocarditis=
rheumocard i t is :
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
19/45
Rheumatic myocarditis, mature Aschoff nodule
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
20/45
CLINICAL SIGNS OF CARDITIS:
Cardiac failureChanges heart sounds
Cardiac enlargement
Murmurs;
1. systolic myocardial murmur;
2. murmurs of VS, MI, AS, AI.
pericardial rub.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
21/45
ChoreaSydenhamS chorea
emotional instability,muscular weakness and
rapid, uncoordinated jerky
movements affecting
primarily the face, foot and
hands.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
22/45
Subcu taneus nodu les
These are firm,
colorless, painlessnodules 1-2 cm in size,
near the tendens orbony prominences of
joints, especially elbow.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
23/45
Subcutaneous nodules (rheumatic fever
nodules/Aschoff nodules)
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
24/45
Erythema marg inatum
This is a nonpruritic, flat,
circular or serpigious rash
on thoraxic trunk and near
joints.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
25/45
DIAGTOSTICS
For diagnostic we use:
* major and minor rheumatic criterias* rheumatic anamnesis
* markers of streptococcus infection
* laboratory findings* ECG
* Doppler USG of heart.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
26/45
2 major criteria or one major criteria
and 2 minor criteria with markers of
streptococcus infection are basement
for support the diagnosis of RF.
NB!
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
27/45
LABORATORY FINDINGS:
General blood analysis (blood test)anemia, leycocytosis, shift in leycocyt formulaleft, accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR);
biochemical blood analysis:
reumoprobs:
Level of C-reactive protein;
Level of Seromucoids
Level of Glycoproteins
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
28/45
positive throat culture;
elevated level of antistreptolisin O,
antistreptokinaze or other streptococcalantibody.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
29/45
ECG findings:
PQ prolongation more than 0,18-0,20 sec;
Signs of enlargement of atria or
ventricules;
Signs of pericarditis.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
30/45
Doppler USG heart:
Thickening of walls
Patological blood flows
(regurgitatione)
Enlargement atrium or ventricles;
Signs of effusion in pericardium.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
31/45
Treatment regimenthe patient must take rest
before normalizaton of his temperature ;
Diet N10;
Ethyologycal treatment: :- ant istreptoc cocal ant ib iot ics
- Benzilpenicillini-natrii 1,21,5 million U
per day,
- Benzathine penicillini G 1,2 million U perday
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
32/45
Or Amoxicillin 0,5 - 4 times per day;
Ampicillin 0,5 - 4 times per day
If the patient have allergic to penicillinwe use:
Erytromicinum Cephalexin 50mg/kg
Cephadroxil 50mg/kg
2 times per day
Azithromycin 15mg/kg
Clarithromicin 15mg/kg
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
33/45
One of this ant ib iot ics adm inister
du r ing 10 day, than we change
ant ib io t ic and prescr ibe pro longate
ant ib iot ics:
Bicillinum-3 (1,5 million U forone injection weeks;
Or Bicillinum-5 (1,5 milliom U
one jnjectione for 3 weeks
during the year)
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
34/45
4. Anti-inflammatory drugs:(NONSTEROID ANTI INFLAMMATORY
DRUGS)NSAID This drugs
blocked Pr a2.NONSELECTIVE:
1) Sal icy l ic Ac id:Acetylsalicylic acid;Sodium salicylate;Mg salicylate.
2) A t l i id
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
35/45
2) An tray l ic ac id-Mefenamic acid 0,250,5;
- Flufenamic acid;
- Meclofenamic acid.
3) A ry lbenzene ac ids-Diclofenac Sodium ( Voltaren,
ortofen ) - tablets 0,0250,05;
-ampules 0,075; suppository 0,05;
gel 1 %;-Alclofenac;
-Fenclofenac;
- Fentiazak.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
36/45
4) Prop ion ic acids :
Ibuprofen ( brufen )Dragee 0,2;
FlorbiprofenDragee 0,05;
Ketoprofen;
Naproxen;
Fenoprofen;
Fenbufen;
Piridofen.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
37/45
INDOL DERIVATIVES :
Indomethacin ( Metindol, Indosid )Dragee 0,025 Suppository 0,05;
SulindacTablets 0,2.
PYRAZOLE DERIVATI VES :
Butadion ( Phenylbutazone );
Analgin;
Amidopirin.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
38/45
SELECTIVE COX2
BLOKERS:OXICAMSPiroxicam ( Felden ) Tablets 0,01
Izoxicam
Sudoxicam
Meloxicam ( Movalis )
COXI BS :Celecoxib ( Celebrex, Rancelex
Rofecoxib ( Rofica )
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
39/45
5. Cort icos teroid therapy :
Prednizoloni 0,5-1 mg/kg orally 3times daily(during 3-5 week) with
decrease dose step by step on
regime 5 mg for weeks.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
40/45
6.Symptomatical therapy:
If the patient have signs of carditis and
heart failure we administrate:
diuretic drugs:
furosemid 20-40 mg orally daily in the
morning before meal;
Hypothyazidi 50-100 orally daily.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
41/45
- Cardiotonic drugs such as
Digoxin 0,0001 1-2 times orally
daily.
If the patient has arrhythmiasahtiarrhythmic drugs.
If the patient has signs vasculitis we
are administed ac. Ascorbinici 0,53times orally daily.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
42/45
Prognos is :
In case of initial RF with advantage arthritisand initial carditis prognosis will be favourable
if the patient receive adequate therapy.
In cases severe RF with arthritis, severe
carditis, chronic rheumatic disease, heartvalvule diseases are observed.
If RF is not treated, chronic rheumatic disease
and heart valvule diseases are always occur. Arthritis, chorea, subcutaneous nodulus
erythema marginatum have favorable outcome.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
43/45
Prophylaxis (prevention):
Primary prevention:is prevention from
streptococcal infection (tonsilitis,
pharingitis, scarlet fever).
Secondary prevention:
---Antistreptococcal prophylaxis should
be conducted after attack of acute RF in
order to prevent recurrence.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
44/45
---Bicillini-5 1,5milliom U (or Benzilinepenicillin 6 1,2 million) one injection for
month due to 3 month
---Aspirini 0,54 times daily
orally during 3 weeks or other
NSAID.
-
8/10/2019 Rheumatic Fever
45/45