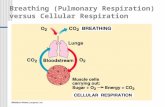
Breathing (Pulmonary Respiration) versus Cellular Respiration.
Respiration
-
Upload
ferdinand-reilly -
Category
Documents
-
view
13 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Respiration

RespirationReleases energy from glucose ATP

Respiration
Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + ATP
C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 38 ADP + 38 Pi 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP
http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/12580-the-science-of-life-cellular-respiration-video.htm (introduction, 1.5min)

• Rod shaped
• Double membrane
• Inner membrane folded extensively into cristae to increase surface area for reactions

ATP (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate)
Adenosine Diphosphate phosphate
ADP + Pi + energy ATP
High energy phosphate bonds
Universal energy carrier
Quick easy source of energy (compared to glucose)

PiAdenosine Pi Pi
PiPiAdenosine
Pi
Energy from Glucose
Energy for Life

Respiration – 3 phases
1. Glycolysis (cytoplasm) Glucose 2 pyruvate
2. Krebs Cycle (matrix) Pyruvate CO2 & H
3. Electron transfer chain (mitochondrial membrane). Electrons are passed along a series of carriers. Oxygen is the final acceptor of H+ and e- to make water.

cytoplasm matrix membranes
GLUCOSE
PYRUVATE
2ATP
GLYCOLYSIS
2ATP 34ATP
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION
CO2
NADH2
NAD FAD
NADH2 FADH2
KREB’S CYCLE
NAD
O2
H2O
ELECTRON TRANSPORT
CHAIN

Glycolysis
• Glucose too large to diffuse into mitochondria
• Glucose (6C) 2 pyruvate (3C)
• NAD NADH + H+
• 2 ATP
• Does not require oxygen

Cytoplasm Membrane Mitochondrion
Glucose (6C)
Alcohol & CO2
Lactic acid
yeas
t fe
rmen
tatio
n lactic
fermentation
Pyruvate (3C)
low oxygennormal
2 ATP
4 ADP
4 ATP
CO2 + H2O
36 ADP
36 ATP
GLYCOLYSIS

Kreb’s (citric acid) Cycle
• Pyruvate acetyl coA in mitochondria
• acetyl-coA 2 CO2 (waste) + coA (recycled) + H2
– NAD + H2 NADH2
– FAD + H2 FADH2

Krebs Cycle
Pyruvate
Acetyl coA
CO2
(waste)
coA
NAD & FADA co-enzyme carrier molecule
NADH2
FADH2

Electron Transfer Chain
• NADH2 + FADH2
NAD + FAD + H+ + high energy electrons
• e- transferred along a series of electron carriers, cytochromes, in the cristae. Energy from the electrons is used to produce ATP at each move.
• Oxygen is the final hydrogen acceptor water

NADH+
H+
e-
e-
e-
e- e-
e- e-
e-
O
ATP
ATP
ATP
ATP
NADH2
e-
e-
H2H2O
34 ATP
This cannot occur without oxygen!!!!!

Rate of respiration1. ↑Temperature ↑reaction rate (up to an optimum temp.)
(↑ energy of enzymes and substrate ↑collisions).
2. ↑ Body’s energy demands ↑ rate of respiration (Eg running muscle cells need more energy)
3. Poisons. Eg Cyanide prevents O2 combining with hydrogen ( ↓ respiration).

Where would you expect to find the most mitochondria?
eg Muscle and liver cells
Active cells with high energy needs

MENU
Key Words
Exercises
Quick Quiz
MCQ
Videos

Key words• respiration• mitochondria• cristae• surface area• matrix• ATP• glycolysis• Kreb’s cycle• citric acid cycle• electron transport chain• glucose• pyruvate• electron carrier• final acceptor
• acetyl coA• NADH2
• FADH2
• oxidative phosphorylation• lactic fermentation• yeast fermentation• anaerobic
Back to menu

QUICK QUIZ1. Cellular respiration takes place in the ____
2. Glucose is broken down into ____ during ____
3. ____ is small enough to enter the mitochondrion
4. ____ in the matrix catalyse the reactions of the ____ cycle
5. The inner mitochondrial membrane is folded to increase ____
6. NAD and FAD carry ____ to the electron transport chain
7. ____ is the universal energy carrier
8. Most ATP is produced in the ____ stage
9. ____ respiration yields 34-38 ATP
10. ____ respiration occurs in the absence of sufficient oxygen
11. Yeast undergoes ____ under anaerobic conditions
12. Animals produce ____ under anaerobic conditions
Back to menu
Answers

QUICK QUIZ1. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria
2. Glucose is broken down into pyruvate during glycolysis
3. pyruvate is small enough to enter the mitochondrion
4. enzymes in the matrix catalyse the reactions of the Krebs cycle
5. The inner mitochondrial membrane is folded to increase surface area
6. NAD and FAD carry electrons to the electron transport chain
7. ATP is the universal energy carrier
8. Most ATP is produced in the electron transport chain stage
9. aerobic respiration yields 34-38 ATP
10. anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of sufficient oxygen
11. Yeast undergoes fermentation under anaerobic conditions
12. Animals produce lactic acid under anaerobic conditions
Back to menu

Exercise
• Workbook pp 67-72, all questions• Pathfinder p45 q5
Back to menu
READING• Pathfinder p43• Excellence in Biology 126-130

VideosBack to menu
These videos contain more detail than you need, but the basics are very good!
• http://www.5min.com/Video/Glycolysis-and-the-Krebs-Cycle-150946257 (summary, Wolfe, 8 min)
• http://www.5min.com/Video/Oxidative-Phosphorylation-150626566 (ATP, 10min)
• http://www.articlesbase.com/videos/5min/150626157 (Glycolysis, 14min)

proteins lipidspolysaccharides
amino acids monosaccharides fatty acids + glycerol
pyruvate
acetyl coA
NADH2 + FADH2
wastes - CO2 + H2O
Krebs

Location Needs Makes ATP yield
Glycolysis
Krebs cycle
Electron transfer
chain
Location Needs Makes ATP yield
Glycolysis cytoplasm Glucose Pyruvic acid & hydrogen
2
Krebs cycle
matrix Pyruvate(or acetyl
coA)
Cyclic but releases ATP & hydrogen
(CO2 as waste)
2
Electron transfer
chain
cristae Hydrogen and oxygen
ATP & water 32-4