Renal Arteriogram
-
Upload
guestcd8394 -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.060 -
download
0
Transcript of Renal Arteriogram

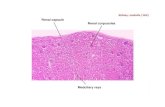
A Renal Arteriogram is also commonly called a renal angiogram A arteriogram is a X-ray image of the arteries or blood vessels of a particular organ in this case it would be the Kidneys(Renal). A Fluoroscopic image of the Kidneys can also be done to see the movement of the kidneys

You Can’t eat or drink the night before the procedure so that you stomach is completely empty of all food.
You have to tell the doctor a list of your medication or any medication you may be allergic to.
An IV(intervenous) will be placed in you hand


The catheter will be removed you should lie completely still to stop any bleeding that may occur.
You can begin to eat and an IV fluid will be given to help flush all the dye that is left.
Your Blood pressure an other vital signs remained monitored.
Some renal angiograms take half an hour others can take longer like an hour or two.

• Procedure: Translumbar Puncture Projection: Posteroanterior(PA)
Patient Position : Patient Prone, Centered to table, arms at side of body head in lateral position shins supported, slight internal rotation of legs
Central ray : Vertical beam to center of film, through midsagittal plane at level of kidney hilum
Anatomy : Renal arteries, aorta and associated major branches.

The translumbar puncture is not commonly used for a renal angiogram for several reasons.
• The patient must lay in the prone position during the procedure
• Another reason is that the opening of the renal vessels are located dorsally, and to make the vessels radiopaque so they can show up on the x-ray is made more difficult due to the position of the patient and the specific gravity of the contrast agent.

The Position of the patient is limited to the prone position. The needle location makes it impossible for any other position or excessive movement.
The patient is centered to the table with his arms alongside the body in a comfortable position.
The shins should be supported, and the legs should be placed in internal rotation.
The kidneys generally extend between the 12th thoracic and 3rd lumbar vertebras when the patient is recumbent.
The central ray should be positioned to the hilum of the kidney

Procedure: Percutaneous catheter (Seldinger Method)
Projection : Anteroposterior(AP)
Patient Position : Patient prone, centered to table, arms at side of body, head in lateral position, shins supported, slight internal rotation of legs
Central Ray : Vertical beam to center of film at level of kidney hilum
Anatomy : Renal arterial supply, accessory renal arteries

A Percutaneous Catherization or Seldinger method is a specialty procedure that is only done under the supervision of a radiologist.
A Seldinger method is done by first having the radiologist inserts a wire into a large
artery of the groin. The wire has a small tube called a catheter attached to it the catheter is lead into the kidneys where the doctor will insert a dye through the catheter and into the patients kidneys. Once the dye has settled an x-ray will be taken this x-ray will bring contrast to the arteries which will make for an easy diagnosis.

The most common position will be the recumbent supine.
The technique of catheter placement, however, allows more flexibility in patient positioning than the previous method.
Obliques may be required for a better demonstration of the origin of the renal vessels.
The central ray is again at the level of the kidney hilum

The injection equipment required for a renal angiogram varies
In the translumbar approach, the contrast agent can be injected by hand or by the use of an automatic injector.
Sterile trays and packs are required for the procedure.
For the catheterization procedure a special catheterization pack is required. In a renalangiogram a curve in the catheter is required.
As in any angiogram emergencies may happen so you need emergency equipment and supplies.

Aneurysm- This disease most commonly is found in arteries.
An aneurysm is a bulge of bloodIn an artery this can become dangerousIf the artery breaks
Aneurysm only symptom is pain and Is usually detected through x-rays.
Treatment is drugs or surgery Depending on the size of the Aneursm.

Stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of blood vessels
Renal artery stenosis can become serious when left untreated
The kidneys release a hormone know as renin to decrease blood pressure if the kidneys can continue to release renin this can result in hypertension

Renovascular hypertension is the narrowing of the blood vessels in the kidneys
It is easily seen on a renal angiogram and can be treated by angioplasty or stenting (man made tube inserted into the artery) of the renal arteries.

arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between artery and veins it arises the embryo.
Arteriovenous malformation usually shows no symptoms and is found during autopsy but can be discovered in a renal angiogram. This type of disorder can cause serious damage to the spinal cord and brain.

Thrombosis is a blood clot that blocks an artery and disrupts theflow of blood.
Thrombosis can be caused by a blow to theabdominal area or a tumor that obstructs therenal artery or vein
Treatment of thrombosis is anticoagulation medication

Since renal angiogram deals with x-ray there is always a risk of too much radiation exposure since multiple x-rays will be taken
There is always a risk when you deal with a blood vessel especially arteries which are high pressured blood vessel
Hemorrhage due to a punctured blood vessel Injury to nerves Embolus-clot of a blood vessel Hematoma Infection Kidney Failure