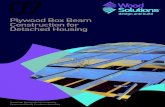
Regulatory Model of Dramatic Life Span Increase
-
Upload
dr-mike-changaris -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
113 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Regulatory Model of Dramatic Life Span Increase

Cell Maintanance Factors
Repilac1on Factors
Cell Mortality Factors
Interac1ng vectors push body systems in different direc1ons forming a stable ballanced regulatory plane of system states.
Outside the stable regulatory plane body systems behave chao1cally and 1ssue can destablize (e.g. illness/death).
80 Yr. Life Span
New Regulatory Plane > Life Span > 160 Yr. ???
Change in Regulatory Vectors
Tissue Spacific Life Span Regula1on
Stable Regulatory
Plane Tissue Spa. Stable
Regulatory Plane
Tissue Spa. Stable
Regulatory Plane
Mul1ple Body
Systems Co-‐regulate Crea1ng a Global
Regulatory Complex Defining a Plane
of Life-‐Span Regula1on for the Body as a whole.

Adverse Childhood Experiences
(ACEs)
Autonomic Dysregula1on
Allosta1c Load
Telomerase Telemeres
ROS, CASP9, CREB, Bcl2 etc.
Apoptosis Regulators
Cell Markers of Cell Health and Self
Removal of Healthy Cells
Neuroplas1c Immunofunc1ons
Neuroplas1c Changes
Remove Brake On Plas1city
Increase Rate of Brain Tissue Change
Glial Func1oning • Glutamate Reuptake • Immune Barrior • Synap1c Plas1city • Apop1c Signal
Rapid Tissue Loss
Cell Repair Cycles • Neurogenesis • LTP • Cell Repair
Lesion Regrowth
Metabolic Changes
(e.g. Sugar/Insulin, Mitochondria fxn)
Model of Mul1ple Sclerosis
Balance
Decrease Cell Replacement And Reduced Cell Health
Gene1c & Other Factors