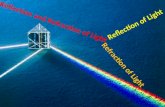
Reflection and Refraction of Light. Reflection We see objects because light bounces off them. This...
-
Upload
alvin-tucker -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Reflection and Refraction of Light. Reflection We see objects because light bounces off them. This...

Reflection and Refraction of LightReflection and Refraction of Light

ReflectionReflection
• We see objects because light bounces off them. This ‘bouncing off is known as Reflection. For example: the image of something as reflected by a mirror.

Picture:Picture:

Laws of ReflectionLaws of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
The incident ray, the normal, and the reflected ray are coplanar.
• Specular reflection (regular reflection) occurs when incident parallel rays are also reflected parallel from a smooth surface. Diffuse reflection (irregular reflection), the irregular surface can be considered to be made up of a large number of small planar reflecting surfaces positioned at slightly different angles.

RefractionRefraction
• The bending or change in direction of light is known as Refraction. The change in direction results from a change in the speed of light as it leaves one medium and enters another.

Example:Example:
• Here in the first picture we see a straight rod used for cleaning pools.
• In the second picture, by placing the rod into the swimming pool, we see that it appears to bend. This is refraction at work!

Image in a Plane MirrorImage in a Plane Mirror
• A plane mirror makes images of objects in front of it; these images appear to be behind the plane in which the mirror lies. The image formed by the plane mirror is always virtual (meaning that the light rays do not actually come from the image), upright, and of the same size as the object.

Reflection in a Plane MirrorReflection in a Plane Mirror

Features of Image in a Plane MirrorFeatures of Image in a Plane Mirror
• The image is virtual
• The image is same size as the object
• The image is the same distance behind the mirror as the object in front
• The image is upright
• The image is laterally inverted

Image Formed in a Plane MirrorImage Formed in a Plane Mirror

Refraction of Light RaysRefraction of Light Rays
Two ways how light rays are refracted:
• Light Rays travelling from one medium into an optically denser medium is bent towards the normal.
• Rays travelling into an optically less dense medium are bent away from the normal.

Example using Diagram:Example using Diagram:
• The refracted ray is bent towards the normal when travelling into a denser medium.
• mediums and is refracted.
•

Example using Diagram:Example using Diagram:
• The refracted ray is bent away from the normal when travelling into a less dense medium.
• Here light bends away from the normal. The red arrow is meant to

THE END !!!THE END !!!