Protein Synthesis: Transcription. Objectives What is the Central Dogma of biology? What are the...
-
Upload
suzanna-logan -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
0
Transcript of Protein Synthesis: Transcription. Objectives What is the Central Dogma of biology? What are the...

Protein Synthesis: Protein Synthesis: TranscriptionTranscription

Objectives
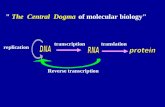
What is the Central Dogma of biology?
What are the steps of transcription?

Recall Recall
Why do we need proteins? Why do we need proteins? Muscles, hair, nails cartilage, tendons, Muscles, hair, nails cartilage, tendons,
ligamentsligaments EnzymesEnzymes Hemoglobin Hemoglobin AntibodiesAntibodies

Central Dogma Central Dogma

What are proteins made of?What are proteins made of?
Amino Acids Amino Acids are the individual building are the individual building blocksblocks Together to make one Together to make one ProteinProtein
There are There are 20 20 types of amino acids, sometypes of amino acids, some
There are infinite combinations of amino There are infinite combinations of amino acidsacids
These long chains are called These long chains are called polypeptide polypeptide chainschains

Protein synthesisProtein synthesis is the process in is the process in which a cell makes protein based on which a cell makes protein based on the message contained within its the message contained within its DNA.DNA.
However:However: DNA is only found in the nucleusDNA is only found in the nucleus Proteins are Proteins are onlyonly made outside the made outside the
nucleus – in the cytoplasm.nucleus – in the cytoplasm.
Protein Synthesis

Protein SynthesisProtein Synthesis
How do the many different messages How do the many different messages within the DNA molecule get to the within the DNA molecule get to the many ribosomes outside the many ribosomes outside the nucleus?nucleus?
A molecular cousin of DNA – A molecular cousin of DNA – RNARNA – is – is used to carry these messages.used to carry these messages.

Ribonucleic Acids - RNA Ribonucleic Acids - RNA
The job ofThe job of RNA RNA (ribonucleic acid) is (ribonucleic acid) is to to carry messagescarry messages from the from the DNADNA (in the nucleus) to the (in the nucleus) to the ribosomesribosomes (in (in the cytoplasm).the cytoplasm).

Differences between RNA and Differences between RNA and DNADNA
DNADNA Double-strandedDouble-stranded
Deoxyribose Deoxyribose sugar groupsugar group
Nitrogen Base PairsNitrogen Base Pairs A-T, C-GA-T, C-G
RNARNA Single StrandedSingle Stranded
Ribose sugar Ribose sugar groupgroup
Nitrogen Base PairsNitrogen Base Pairs A-U, C-GA-U, C-G


Types of RNATypes of RNA
mRNA: carries the mRNA: carries the mmessage from the essage from the DNA to the cytoplasm DNA to the cytoplasm
tRNA: tRNA: ttransports amino acids to the ransports amino acids to the mRNA to make the protein mRNA to make the protein
rRNA: make up the rRNA: make up the rribosomes, which ibosomes, which help make the proteinhelp make the protein

Protein Synthesis Process Protein Synthesis Process
Occurs in Occurs in TWO TWO steps:steps:1.1. TranscriptionTranscription – the genetic information – the genetic information
from a strand of DNA is copied into a from a strand of DNA is copied into a strand of strand of mRNAmRNA
2.2. TranslationTranslation

Steps of TranscriptionSteps of Transcription 1. 1. DNA unwindsDNA unwinds
Enzymes help Enzymes help split apart base pairssplit apart base pairs to open the to open the DNA double helix.DNA double helix.
Transcription complex: RNA polymerase and Transcription complex: RNA polymerase and proteins proteins
Uses one strand as a templateUses one strand as a template 2. 2. Bases line upBases line up
Free nucleotides in the cell Free nucleotides in the cell find their find their complementary base pairscomplementary base pairs on the DNA template on the DNA template strand strand
What will be different?? What will be different??


Steps of TranscriptionSteps of Transcription
3. 3. RNA formedRNA formed The growing RNA strand hands greely as it is The growing RNA strand hands greely as it is
transcribed. transcribed. DNA strand must close back up DNA strand must close back up
4. 4. The completed RNA strand The completed RNA strand separates from the DNA templateseparates from the DNA template

Steps of TranscriptionSteps of Transcription
http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/transcription.swf

Try It!Try It!What will the RNA Strand What will the RNA Strand
be? be?
TACGCATGGCATGCAATACGCATGGCATGCAA

Try It!Try It!What will the RNA Strand What will the RNA Strand
be? be?
TACGCATGGCATGCATACGCATGGCATGCAAUGCGUACCGUACGUAUGCGUACCGUACGU

Think, Pair, Share Think, Pair, Share
1. What is the purpose of Protein Synthesis?1. What is the purpose of Protein Synthesis?
2. List 2. List 22 differences between DNA and RNA differences between DNA and RNA
3. Where in the cell does the process of transcription occur?3. Where in the cell does the process of transcription occur?
4. What enzyme completes the process of transcription? 4. What enzyme completes the process of transcription?
5. What molecule is produced from transcription? 5. What molecule is produced from transcription?
6. Where does this molecule go after it is made? 6. Where does this molecule go after it is made?

Introns and Exons
The DNA that is copied contains both…
Introns: sequences of nucleotides not involved in coding for proteins.
AND
Exons: DNA sequences that code for proteins

Objectives
By the end of the day today you should:
1. Know the steps of translation
2. Identify the differences in transcription and translation

Translation Translation
Now that the mRNA has been made, the Now that the mRNA has been made, the next step is for itsnext step is for its’’ message to be made message to be made into a proteininto a protein
Translation: the Translation: the mRNAmRNA, with the help of the , with the help of the ribosomeribosome, forms a , forms a chain of amino acidschain of amino acids (eventually forming a (eventually forming a proteinprotein) based on the ) based on the information contained on the mRNA.information contained on the mRNA. Occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomeOccurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome


ProteinsProteins Proteins are made of amino acids Proteins are made of amino acids
20 different amino acids total20 different amino acids total
Adult humans can only make 12 out Adult humans can only make 12 out of the 24 amino acids of the 24 amino acids How do we attain the other 8 amino acids?How do we attain the other 8 amino acids?

TranslationTranslation
One ProblemOne Problem There are 20 amino acids There are 20 amino acids There are 4 RNA bases There are 4 RNA bases
How can just four nucleotides—A, U, How can just four nucleotides—A, U, C, G—be translated into so many C, G—be translated into so many different amino acids? different amino acids?

Language of RNA Language of RNA Just like the alphabet, 26 letters can make more than 26 Just like the alphabet, 26 letters can make more than 26
words words Letters of RNA are put together in different ways.Letters of RNA are put together in different ways.
CodonCodon: three nucleotide sequence which codes for the : three nucleotide sequence which codes for the
insertion of a unique amino acid insertion of a unique amino acid Language of the genetic codeLanguage of the genetic code Multiple codons for the same amino acid Multiple codons for the same amino acid
AnticodonAnticodon: : on one end of tRNAon one end of tRNA complementary to a complementary to a specific mRNA codonspecific mRNA codon tRNA molecules carry different amino acids tRNA molecules carry different amino acids


Genetic CodeGenetic Code
• Start Codon – signals the start of translation (AUG- Methionine)
• Stop codon – signal the end of the amino acid chain (3 total)


TranslationTranslation
Before translation begins, a ribosome will be Before translation begins, a ribosome will be assembled from two ribosomal subunits (large and assembled from two ribosomal subunits (large and small). The ribosome contains three attachment small). The ribosome contains three attachment sites for tRNA molecules.sites for tRNA molecules. On the large subunit: E site, A site and P siteOn the large subunit: E site, A site and P site On the small subunit: mRNA joinsOn the small subunit: mRNA joins

Step 1: mRNA attaches to the small ribosomal unit. Step 1: mRNA attaches to the small ribosomal unit. The large subunit attaches to the small subunit. The The large subunit attaches to the small subunit. The first codon is aligned at the P site. first codon is aligned at the P site.

Step 2: A tRNA carrying the amino acid Step 2: A tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine attaches to the start codon, methionine attaches to the start codon, AUG,AUG, on the mRNA. This happens at on the mRNA. This happens at the P site on the large ribosome the P site on the large ribosome

Step 3: Attachment of the first amino Step 3: Attachment of the first amino acid carrying acid carrying tRNA to A binding tRNA to A binding sitesite. .

Step 4: The ribosome forms a Step 4: The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the two peptide bond between the two amino acidsamino acids and breaks the bond and breaks the bond between the first tRNA and its amino between the first tRNA and its amino acid. acid.

Step 5: Step 5: The ribosome pulls the The ribosome pulls the mRNA the length of one codonmRNA the length of one codon. . The tRNA and polypeptide chain The tRNA and polypeptide chain move to the P site. The first tRNA is move to the P site. The first tRNA is shifted to the E site. shifted to the E site.

Step 6: Step 6: tRNA is ejectedtRNA is ejected from the E from the E binding site and returns to the binding site and returns to the cytoplasm. The A site is now open for cytoplasm. The A site is now open for another tRNA. another tRNA.

Step 7: This process continues to Step 7: This process continues to translate the translate the mRNA strand until it reaches a stop codonmRNA strand until it reaches a stop codon. . The protein is released and the large and small The protein is released and the large and small ribosome disassemble. ribosome disassemble.

st. olaf transcription animation whfreeman animation http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini
/flashanimat/molgenetics/translation.swf

Mutations

Objectives
What are different types of mutations that can occur during
protein synthesis?

Mutations Mutations Mutations are changes in the DNA Mutations are changes in the DNA
sequencesequence1.1. DNA damage from environmental DNA damage from environmental
agents:agents:1.1. UV LightUV Light
2.2. Chemicals Chemicals
2.2. Mistakes that occur when DNA is copied Mistakes that occur when DNA is copied before cell divisionbefore cell division
Point Mutation:Point Mutation: a change in a single a change in a single base pair of a gene base pair of a gene

No Mutation: No Mutation: DNA Sequence: DNA Sequence: TACAAG TACAAG mRNA Sequence: AUGUmRNA Sequence: AUGUUUC C Amino Acid Chain: Met – PhenAmino Acid Chain: Met – Phen
Point Mutation: Point Mutation: DNA Sequence:DNA Sequence: TACA TACATTGG mRNA Sequence: AUGUmRNA Sequence: AUGUAACC Amino Acid Chain: Met – TyrAmino Acid Chain: Met – Tyr

Other Types of Mutations Substitution
change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced.
change a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced

Other Types of Mutations
Insertions mutations in which extra base pairs
are inserted into a new place in the DNA

Other Types of Mutations
Deletion mutations in which a section of DNA is
lost, or deleted.