Prokaryotic Cells Power Point
-
Upload
chelsea-kojaian -
Category
Documents
-
view
68 -
download
0
Transcript of Prokaryotic Cells Power Point

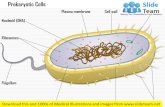
Prokaryotic cells
Cells with no membrane bound nucleus or organelles

• Similarities to eukaryotic cells– contain cell membranes that are lipid bilayers
– Both have DNA that encode genetic information

• DifferencesStructural – eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles and nucleus
Prokaryotic cells lack these

• Chemicalcell wall of bacteria contains
peptidoglycan
ribosomes are comprised of distinct subunits

• Size – Generally eukaryotes are 10 X larger than
prokaryotes.– Why is this important?• Small cells have larger surface to volume ratio – greater
contact with the environment therefore nutrients can enter and be distributed faster.• cells can be simpler and grow faster• Exception:

• Shapes:
• Round cocci• Rod bacilli• Spiral spirilla
Cocci may form chains tetrads or clusters depending upon the plane of division

Bacterial envelope
• Plasma membrane• Cell wall • Outer membrane
Gram negative bacteria have all 3 layersGram positive bacteria lack the outer
membrane

Bacterial envelope

• Plasma membrane
Regulates what enters and exits a bacteria
More protein in bacteria membranes than in eukaryotic membranes No mitochondria are present therefore ATP is generated by enzymes located on the cell membrane
No sterols in bacterial membrane

• Cell wall – Forms a chain mail like covering over the bacteria– Made up of peptidoglycan• Peptide units are made up of 4 amino acids and differ
between species• Glycan units are made of alternating chains of
N acetylglucosamine and N acetylmuramic acid

• Cell wall– Function is to provide shape and support • Some bacteria have turgor pressures of 350 lbs/square
inch• All bacteria have cell walls except a group of bacteria
called mycoplasmas. – Mycoplasmas are isotonic to their environment – – Antibiotics can damage some bacteria turning them into
L-forms – they lose their ability to make cell walls.
Mycoplasma pneumonia causes “ walking pneumonia”

• Differences in cell wall of GN and GP bacteria– Gram negative bacteria are 1 layer thick– Gram positive bacteria are many layer thick and
contain techoic acid • Techoic acids may function as passage ways for moving
ions inside and outside of cell – involve in structural integrity

Gram positive envelope


• Outer membrane – Gram negative bacteria only– Consists of a bi layer• Inner layer is phospholipid• Outer layer is lipopolysaccharide
– Act as barriers to polar as well as nonpolar molecules– Only H2O and gasses pass through this membrane

• How do nutrients get into gram negative cell?– PORINS – small pores in membrane formed by
proteins• Porins are embedded in membrane and act as
transport molecules


• LPS is known as endotoxin • LPS is toxic and highly reactive to humans
causing fever and vasodilation

• Some bacteria have a polysaccharide capsule which surrounds the bacteria
• Function – Protection against moisture loss– To adhere to surfaces for growth– Agent of pathogenicity – protects bacteria against
phagocytosis by host cells

• How do bacterial cells enlarge?• They produce enzymes called autolysins that
break the cross linking peptide bonds• New peptidoglycan units attach and enzymes
called transpeptidases reseal the breaks
• Why is this important??• Penicillin binds to transpeptidase enzymes
preventing resealing of the peptidoglycan during growth. The cell wall never reforms. Penicillin is effective against actively growing bacteria.

Bacterial appendagesPili made of proteins called pilin
Function: adhesion sex pilus- attaches during bacterial
sexresponsible for the specificity of
some pathogenic bacteria to certain host cells
if pili are destroyed, bacterial are no longer pathogenic
All Gram negative bacteria have pili, many gram positive bacteria do not


Bacterial appendageFlagella
function: locomotion by rotationstructure: 3 parts
filament hookBasal body

Arrangements of flagella:
Monotrichous
Lophotrichous
Amphitrichous
Peritrichous

• Flagella allow for movement in response to a stimulus
chemotaxisaerotaxisphototaxismagnetotaxis

• Spirochetes have axial filaments – do not extend outside of their body
– Allows movement like a corkscrew– Move best in viscous fluids