Product Hand Out
-
Upload
rachit-shiv -
Category
Documents
-
view
29 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Product Hand Out
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
Product/Brand Management
Responsibility
1. Improving / Maintaining Profit2. Increasing Market Share3. Growth4. Increasing Customers satisfaction5. Develop brand equity
Functions
1. Prepare and implement Marketing plan2. Formal observation of competitors’ activities3. Consistent update on market information and research4. Administer marketing mix elements5. Packaging and price fixation of a brand for market
effectiveness6. Recommend product improvements7. Inform a sales approved marketing strategy to field staff8. Ensure that sales forecasts are met9. Ensure fair amount of sales force time for brand he is
handling.
Functions (contd)
10. Recommend selling prices and volume discounts.11. Ensure production understand plan.12. Consult production for feasibility of product changes.13. Ensure balance between inventory and production plans.14. Fit marketing plan into corporate plan.
15. Synergy between marketing strategy and company philosophy.
16. Recommend new products /selling methods/ new markets.
Functions (contd)
17.Do Strategic appraisal-Integrate planning assumption, identify key issues, opportunity, threat,indetify commercial opportunity
18.Selling knowledge and skills.-Analysis of data
19.Time Management-reduce procrastination, Handle daily works Have one project at one time, prioritize activity,
20.Project Management-Be focused and bring accountability, Provide resources in different areas, Manage new product development team
21.Product Manager score card:Business skills-Marketing plan, Financial knowledge, Selling skillsDeliver Results through People-Communication, developing others, interaction
with peopleEnsure market driven direction-customer relation, market research skills, Competitive intelligence, leading cross functional teamsGuide Product fit function-Technical understanding, QC knowledge,Product
portfolio analysis, New product development.Manage Multiple project-Time management, project management
Changing job function of a PM/BM
PM
Government
Profit Market
CoordinationProducts
TechnologyPricing
Sharp timely decision
Promotion
PlanningPR
Packaging
BRAND’S INNER AND OUTER CORE BRAND’S INNER AND OUTER CORE
INNER CORE The spiritual
central/brand essence/brand
soul.
Product
Packaging
Personality
Brand name
OUTER CORE Design
Character
Logo/symbol
Slogan
BRAND VALUE PROPOSITION
BRAND IDENTIFY – PARACHUTE BRAND IDENTIFY – PARACHUTE
INNER CORE:
Expertise in Coconuts
Brand lineage
Experience
BRAND IDENTIFY – PARACHUTE BRAND IDENTIFY – PARACHUTE
OUTER CORE:
Personality: Innovative, confident, trustworthy, young
Product focus: Coconut oil, coconut perfumed hair oil, coconut anti-dandruff hair oil
Price/quality: Value for money
User profile: Men/women, 18-45 years, SEC-B
Extensions: Parachute Coconut Hair Oil, Parachute Jasmine, Parachute Dandruff Solution.
Symbol/Logo: Flag shaped logo with a coconut tree against a blue background.
Heritage: Has been in coconut business for decades
Discrimination: Expertise – Parachute Dream centre
VALUE PROPOSITION:
Essential coconut nourishment
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
What is Product………Product is a Bundle ofTangible & Intangible
Benefits
Core Benefits
In – Tangible benefitsEg: Brand Name, Delivery, Credit, services
Tangible BenefitsEg: Colour, Design, Quality,
Price, Durability
Characteristics of ProductThere are 3 aspects to any product/service: 1. Core Benefit
[In-use benefit, psychological benefit etc]
2. Tangible product or service:[Benefits and product attributes and features]
3. Intangible product and service:[Brand name, delivery etc]
Theodore Levitt of Havard observed: “A product is not a product unless it sells. Otherwise its merely a museum piece”
Definitions• Philip Kotler – A product is anything that can be
offered to a market to satisfy a want or need.
• William Stanton – A product is a set of tangible attributes including packaging, colour, price, quality and brand plus the services and reputation of the seller. A product may be a good, service, place, person or idea.
• Skinner – A product is any good, service or idea that satisfies a need or wants and can be offered in an exchange.
TYPES OF BRANDTYPES OF BRAND
Functional Symbolic Mixed
Hero Honda
‘Fill it, shut, it forget it’
Raymond
‘Complete man’
Johnson Tiles
‘Not just tiles, lifestyles’
Disprin
‘Quick relief from pain’
Classic
‘Discover or passion’
Opel Carsa
‘Achtung baby’
Surf Excel
‘Surf Excel hai na’
Ell 18
‘Be your self’
Hero Honda Passion
‘When style matters’
Nirma
‘Doodh jaisi safedi’
Louis Philippe
‘Upper crest’
Liril
The freshness soap
Captain Cook
‘Free flow salt’
Carbon
‘Very provocative’
Dove
‘With ¼ moisturing cream’
Bajaj Aspire
‘110% bike’
Lacoste
‘Be what you are’
Nescafe
‘The taste that gets you stated’
Bisleri
‘Play safe’
Cortier
‘Opulence’
Cadbury Dairy milk ‘Khane walon ka khane..?
Functional Symbolic Mixed
Dettol
‘100% bath’
Thumps up
‘Have you grown up to Thumps up yet’
woodland
‘Leather that weathers’
Complan
‘The complete planned food’
American Express
‘Quite frankly American Express card is not for everyone’ (earlier)
Rexona Deo
It keeps working
Panasonic
‘First & Fast Telecom Solutions’
Wills Sport
‘Be a sport’
Honda Accord
‘Style and substance’
TYPES OF BRANDTYPES OF BRAND
TYPES OF BRANDTYPES OF BRAND
Functional Symbolic Mixed
Kelvinator
‘The coolest one’
Nike
‘Just do it ’
Alto
‘The hottest little car in town’
Moove
‘Ah se aaha tak’
Allen Solly
Friday dressing
BMW
Ultimate driving machine
Vim Bar
‘Bas thoda sa vim bar’
Boss
Hugo Boss
Indica
‘More car per car’
Mant Blanc
Art of writing
PRODUCT V/S BRANDProduct Brand
Refers to a commodity Refers to a mindset
A product is something that is made in a factory
A brand is something that is bought by a customer.
A product can be copied by a competitor.
A brand is unique.
A product can be quickly outdated.
A successful brand is timeless.
A product is something tangible
A brand is a set of values and associations that exist only in the mind of consumers
Leads to customer satisfaction
Leads to customer loyalty
What is Brand Equity?What is Brand Equity?Brand equity is a set of brand assets and liabilities linked to a brand, its name, and a symbol, that add to or subtract from the value provided by a product or service to a firm or to that firm’s customers.
David Aaker TheoryDavid Aaker Theory
““Brand equity is the brand assets or liabilities Brand equity is the brand assets or liabilities linked to a brand’s name and symbol that add to linked to a brand’s name and symbol that add to or subtract from a product or a service. or subtract from a product or a service. These assets can be grouped into 4 dimensions These assets can be grouped into 4 dimensions – brand awareness, perceived quality, brand – brand awareness, perceived quality, brand associations and brand loyalty.”associations and brand loyalty.”
- David Aaker
Brand Equity ……………….
┘ Value of a Brand Name or Symbol
Sets of Assets & Liabilities linked with a Brand
Incremental Value of a Business above Physical Asset┘
┘
Higher Market Share Does Not Mean Higher
Brand Equity
Brand EquityBrand Equity
Perceived Brand Quality
BrandAwareness• Brand Name• Symbols
BrandLoyalty
OtherProprietaryBrand Assets•Patents•Trademarks•Channel relationships
Brand Associations• Attributes• Benefits• Attitudes
Provides Value to Customerby Enhancing:• Interpretation/processing of information• Confidence in the Purchase Decision• Use Satisfaction
Provides Value to Firm by Enhancing:• Efficiency and Effectiveness of Marketing Programs• Brand Loyalty• Prices/margins• Brand extensions • Trade Leverage• Competitive Advantage
What is Brand Equity?What is Brand Equity?
Source: Aaker (1991) “Managing Brand Equity”Source: Aaker (1991) “Managing Brand Equity”
Higher Loyalty
Name awareness
Lower Marketing Cost
Excellent Channel Relationship
Competitive AdvantageSTRONGBRANDEQUITYHigh perceived quality Can be sold at higher price
Strong brand association
STEPS IN DEVLOPING BRAND EQUITY
Identify product attributes
What is USP / UCP
Market Segment – which is more attractive?
Developing positioning based on segment / USP /UCP/ Psychographic Profile
Does it tally with company’s image and strength?
Develop campaign on new product
Top Ten Brands of Asia
1. Coca cola
2. Kelloges
3. McDonalds
4. Kodak
5. Marlbro
6. IBM
7. American Express
8. Sony
9. Mercedes
10. Nescafe
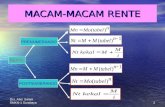
Measuring brand equityMeasuring brand equity
a) Sales value X 1.1-- 2
b) Book Value X 2 or 3 or 4
c) Profit X 10 or 15 .
Brand EquityBrand Equity
d) Basis of the Stock Value
RKS Model
MEASUREMENT OF BRAND EQUITYCOST – BASED
HISTORICAL COST
REPLACEMENT COST
MARKET VALUE METHOD
INTERBRAND METHOD
PRICE-BASED
PRICE PREMIUM
EQUALIISATION PRICE
INDIFFERENT PRICE
CONSUMER-BASED
ATTRIBUTE RATING
BLIND TEST
Cost based methodsHistorical cost
Money spent till date on the brand Eg: Rs.100mn. Have been spent so far in creating a brand “X”. So, value at which
brand can be sold is Rs.100mn.
Disadvantage : 1. No guarantee of realization.
2. Cost incurred in brands are no measure of the efficiency with which the money was spent.
Eg:
3. May or may not be adequate measure of brand’s future potential even when the costs are adjusted to the current prices.
Interbrand INTER-BRAND METHOD
Valuation Method Is Based On Brand Earnings Approach.Brand Earnings Are Determined By Using Brand Index- A Combination Of Seven Variables
STEPS USED TO MEASURE BRAND EQUITY
a) The weighted average of the last three years profits of the brand is computed
b) This figure when multiplied with a number gives the value of brand equity. The number is arrived at by multiplying the P/E of the company or industry in which the company operates and a factor called Brand Strength.
c) Brand strength is dependent on Brand Index which consists of certain variables like leadership, stability, etc . Of the brand.
BRAND EQUITY = (weighted average of brand profits X P/E of the Industry X Brand strength)
CONSIDER A BRAND X, WHOSE PROFITS ARE GIVEN BELOW
YEAR PROFITS
(Rs. Million)
WEIGHTAGE
1998
1999
2000
15
20
30
1
2
3
AVERAGE PROFIT = 15X1+ 20X2 + 30X3/1+2+3 = Rs. 24.2 million
FACTORS IMPLICATION MAXIMUM SCORE
SCORE FOR BRAND X
Leadership
Stability
Geographic Spread
Support
Protection
Market
Trend
Is The Brand Leader In Market Share, Pricing
Does The Brand Have Stable Market Share
What Is The Brand Acceptance Level Internationally
Is The Brand Actively Supported And Promoted By The Company
Is It Adequately Supported By Trademark
Is The Market In Which Brand Operates Is Stable
Long Term Future For The Brand
25
15
15
15
5
5
20
13
7
1
8
2
2
10
TOTAL 100 43
BRAND STRENGTH SCORE = 43/100 = 0.43
SUPPOSE THE P/E VALUE OF THE INDUSTRY IS 15, THEN BRAND STRENGTH SCORE X P/E = 0.43 X 15 = 6.45
BRAND EQUITY = 6.45 X 24.2= 156.09 million
This is the recommended price at which brand X can be sold.
ADVANTAGES
IT IS WIDELY ACCEPTED
IT TAKES ALL ASPECTS OF BRANDING IN ACCOUNT IN VALUATION
DISADVANTAGES
BRAND STRENGTH COMPUTATION RESTS MORE OR LESS ONSUMJECTIVE JUDGEMENT.
VALUME BUSINESS
RANK IN MARKET
MARKET SIZE
RELATIVE PRICE
MARKETING EXPENSE TO TOTAL SALES RATIO
HOW TO MEASURE BRAND EQUITY--- RKS model
ACTUAL QUALITY SATISFACTION SCORE
STATUS OF THE PRODUCT ON PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
PRICE ELASTICITY
PROFITABILITY
SCOPE FOR LINE EXTENTION
HOW TO MEASURE BRAND EQUITY
Measuring Brand Equity (RKS Model)
Factors Score ( a )
( b )1 2 3 4 5
WeightedScore
( a x b ) Value Business of product
Rank in the market( 1-3- = 10 – 15 <3 = 10 )
Market Share
( > 5% = 10 - 15< 5% = 10)
10
Perceived Value
(Higher - 10 - 15Lower - 10)
15
15
15
Measuring Brand Equity (RKS Model)
Factors Score ( a )
( b )1 2 3 4 5
WeightedScore
( a x b ) Profitability
(> 60% GM – 10- 15> 60% GM – 10)
Marketing Expense
to total Sales
Status of product on
Life cycle
15
10
10
Measuring Brand Equity (RKS Model)
Factors Score ( a )
( b )1 2 3 4 5
WeightedScore
( a x b ) Scope of life Extension
Total
Total Weighted Score ( a x b)
Index Scores = ---------------------------------------- X 100
500
B Eq. = Profit X Index Score % = -------------- crore
10
100
Brand Equity Valuation RKS MODEL
• ROOSTER 25 Cr.• NORMAXIN 15.4 Cr.
Million $ 1. COKE 70453 2. MICROSOFT 651743. IBM 510874. INTEL 311125. MCDONALD 245996. MARLBRO 22183
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
BRAND IDENTITY CONFUSION BRAND IDENTITY CONFUSION
• BRAND IMAGE : How the brand is now perceived
• BRAND IDENTITY : How strategists want the brand to be
perceived
• BRAND POSITION : The part of the brand identity and value
proposition to be actively communicated to a target audience
Identity and Image
Image: The way a
public perceive the company or its product
Identity: The way a company aims to
identify or position itself.
BRAND IDENTITY CONFUSION BRAND IDENTITY CONFUSION
Brand identity strives to support the relationship between
customer and brand by generating a value proposition that can
include functional, emotional and self expressive benefits
Sales
Brand ImageHi
Low
HiLow
HealthyBrand
VulnerableDyingBrand
UnrealizedPotential
Brand Image vs Sales
BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL
Continue
Core Extended
Brand Essence
Brand as Product
1. Product scope
2. Product attributes
3. Quality / Value
4. Uses
5. Users
6. Country of origin
Brand as Symbol
11. Visual image and metaphors
12. Brand heritage
Brand as person
9. Personality (e.g., genuine, energetic, rugged)
10. Customer/ brand relationships
Brand as a organization
7. Organization attributes (e.g., innovation, consumer concern, trustworthy)
8. Local versus global
BRAND IDENTITY
BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL
Continue
VALUE PROPOSITION
• Functional
benefits
• Emotional
benefits
• Self-expressive
benefits
CREDIBILITY
Support other brands
RELATIONSHIP
BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL BRAND IDENTITY PLANNING MODEL
BRAND IDENTITY IMPLEMENTATION SYSTEM
BRAND IDENTITY ELABORATION
BRAND POSITION
The part of the brand identity and value proposition that is to be actively communicated to the target audience
BRAND-BUILDING PROGRAMS
TRACKING
BRAND’S INNER AND OUTER CORE -identityBRAND’S INNER AND OUTER CORE -identity
INNER CORE The spiritual
central/brand essence/brand
soul.
Product
Packaging
Personality
Brand name
OUTER CORE Design
Character
Logo/symbol
Slogan
BRAND VALUE PROPOSITION
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
Brand Personality
Expression of the core values & characteristics of a brand with emphasis on human personality traits e.g. friendly, intelligent, innovative
Process of transforming brand into a person or humanizing the brand.
Acts as brand differentiator &offers sustainable competitive advantage
Personaity
• Brand personality describe brands in terms of human characteristics and was seen as a factor in increasing brand awareness and attachment in much the same ways as people related and bonded themselves to other people. (Aaker J.L.(1997).
Brand Personality Dimensions-David Aaker
• Sincerity– down-to-earth, honest, wholesome, cheerful
• Excitement– daring, spirited, imaginative, up-to-date
• Competence– reliable, intelligent, successful
• Sophistication– upper class, charming
• Ruggedness– outdoorsy, tough CRESS
1. SINCERITY :
DOWN-TO-EARTH – Family oriented, Small town,
Conventional, Blue-collar, All Indian
HONEST – Real, Ethical, Thoughtful, Caring.
WHOLESOME – Original, Genuine, Ageless, Classic, Old-
fashioned.
CHEERFUL – Sentimental, Friendly, Warm, Happy.
2. EXCITEMENT:
DARING – Trendy, Exciting, Off-beat, Flashy,
Provocative.
SPIRITED – Cool, Young, Lively, Outgoing,
Adventurous.
IMAGINATIVE – Unique, Humorous, Surprising,
Artistic, Fun.
UP-TO-DATE – Independent, Contemporary,
Innovative, Aggressive.
3. COMPETENCE:
RELIABLE – Hardworking, Secure, Efficient,
Trustworthy, Careful.
INTELLIGENT – Technical, Corporate, Serious.
SUCCESSFUL – Leader, Confident, Influential.
4. SOPHISTICATION:
UPPER CLASS – Glamorous, Good Looking,
Pretentious, Sophisticated.
CHARMING – Feminine, Smooth, Sexy, Gentle.
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
EXTENSION
• What is line Extension?Occurs when original brand name is extended by
modifying features within the existing product category. Ex,Coke,Diet Coke
• What is Brand extension ?-is using the leverage of a well known brand
name in one category to launch a new product in a different category.” –ponds cold cream ponds telcum powder
1.Line Extension-approach
Product
Existing New
Existing Line extension
For Better Penetration
Eg : Different packs.
Existing Brand with little modification. eg: LUX Liquid soap.
New New UsersBrand development activityGrocery shop to club shop/Petrol shopLiquor shop to bars
Diversification
eg:Cocktail Drinks.
(Breeze)
Alcoholic drink
Cust
omer
Diversification
Market Penetration Market Development
Product Development
Existing Markets New Markets
Exis
ting
Prod
ucts
New
Pr
oduc
ts
2.Igor Ansoff’s Matrix (Product/Market Matrix)
Colgate Dental Cream Tata Tea
Ujala Supreme
Ariel Liquid with fabric softener
Bru Cappuccino
Tanishq
Line ExtensionDannon Yogurt Flavors
MultibrandsSeiko Lasalle & Pulsar
Brand ExtensionBarbie Electronics
New BrandsWindex (by acquisition)B
rand
Nam
e
Existing New
Product Category
Existing
New
3.Four Brand Extension Strategies
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
TEN COMMANDMENTS OF PRODUCT LAUNCH
Do not try introducing a new product if you have no:
1) Market Research
2) Free availability of raw material.
3) Clear knowledge of regulatory formalities.
4) Capability of in house manufacturing facilities.
5) Clear cut product differentiations.
6) Good positioning slot.
7) Worthwhile USP./UCP
9) Well planned launch.
10) Well developed feedback systems
8) Good training programme.
TEN COMMANDMENTS OF PRODUCT LAUNCH
Do not try introducing a new product if you have no:
1) Market Research
2) Free availability of raw material.
3) Clear knowledge of regulatory formalities.
4) Capability of in house manufacturing facilities.
5) Clear cut product differentiations.
6) Good positioning slot.
7) Worthwhile USP./UCP
9) Well planned launch.
10) Well developed feedback systems
8) Good training programme.
HOW TO SELECT A NEW PRODUCT
1. Follow company Objective
2. Off patent Product / Patent Office
8. Existing Molecules With Longer PLC
10. Smaller niche Market
6. Customer Feed back / Suppliers / Licensing Agents
4. Usage Of Precise Models
11. MD idea/ New Marketing Recruits / Production foremen/ Sales Personnel
9. Tie Ups
5. Indian Research lab – Company Venture / International Literature
7. National Product
3. Top ten therapeutic Market Segment
13. Exhibition / Merger / Acquisition
What kind of product to select ?
Application of RKS Model in new product selection Relevance to company Whether product is different than others. Will product benefit to customer. Will it answer – why should he change and buy your product. Production Expertise. Market competitive level.
High Margin : 200 – 300% to Sales or COG = 25 – 35%
What are customer perceptions about product ? High volume sales.
USP of product - can we differentiate
Niche market product
NEW PRODUCT INTRODUCTION SYSTEMNEW PRODUCT INTRODUCTION SYSTEM
PRODUCT CONCEPT
TEST MARKET
CHECK POINT
CHECK POINT
CHECK POINT
8 Weeks---------------8 Weeks---------------
6 Weeks
4 Weeks RSRS RS
RS RS RS RS RS RS RS
RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS
RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS RS
BASIC MARKET DATA
IDEAS IDEAS
CONS. SCREENING
Concept Test
Concept use Test
PACKDEVTEST
ADVDEVTEST
TIMINGTIMING IDEASIDEAS EXPENSEEXPENSE
NATIONAL SALES
MODEL - IIRating Scale 0 1 2 3 4 5
1. Product offers something new to consumer.
2. Product will improve or change the habits
3. Product offers advantages over the existing competitive
products.
5. Matching of product profile with current requirement of consumer which is not yet fully filled.
6. Product profile can be communicated is communication effectively.
7. Product profile does not require concept selling.
4. Perceived benefits scores over the price.
35 ----- X 100 = 100%35
NEW PRODUCT – MARKETABILITY INDEX Model 1
A. MARKETABILITY FACTORS
1) MARKET SHARE CONCENTRATION RATIO
2) PRICE / QUALITY ADV.
3) COMPETITION ADV. SPENDING INDEX
4) IMPACT ON EXSTING PRODUCT SALES
5) DISTRI. NETWORK VS COMP.
6) PROFITABILITY
B. DURABILITY FACTORS
7) MARKET SIZE
8) MARKET GROWTH RATE
9) LIFE CYCLEDURATION
10) SENSITIVITYTOECONOMIC FLUCTUATION
C. PRODUCTION ABILITY FACTORS
11) EQUIPMENT NECESSARY
12) PERSONNEL NECESSARY
13) RAW MATERIALS
TOTAL
MARKETABILITY INDEX (MI)
VG = 80 % - G = 71% - 80% AV = 60% - 70%
BELOW AV = 50% - 59% POOR = < 50%
WEIGHT (Wi) RATING SCORE (Ri)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Wted Score
10 20
7 42
7 7
7 63
9 45
10 60
8 72
10 70
6 36
8 48
6 54
6 54
6 54
100 625
= 625 ------ X 1001000= 62.5%
Livon RKS MODEL Rating (0 – 5)
Product offers something new to the consumer 5
Product will improve or change the habits like usage,
buying pattern 5
Product offers advantages over the existing competitive products
5
Perceived benefits scores over the price 3Product matches with current requirements of
consumer, which is not yet fully filled 5
Product profile can be communicated in communication media effectively
5
Product does not require concept selling 3
WELCOME
TO
Lecture
DR.R.K.SRIVASTAVA
Prof.-University of Mumbai-150 years of
standing
Categories of New Products
New-To-The-WorldNew-To-The-World
New Product LinesNew Product Lines
Product Line Additions
Product Line Additions
Improvements/Revisions
Improvements/Revisions
Repositioned Products
Repositioned Products
Lower-Priced Products
Lower-Priced Products
SixCategories
ofNew
Products
SixCategories
ofNew
Products
Mobile MovieMobile Movie
Gatorade- Propel
WaterGatorade- Propel
Water
McDonalds Value Meals
McDonalds Value Meals
New look Honda City
New look Honda City
MilkmaidMilkmaid
Wheel BarWheel Bar
New-Product StrategyNew-Product Strategy
Idea GenerationIdea Generation
Idea ScreeningIdea Screening
Business AnalysisBusiness Analysis
DevelopmentDevelopment
Test MarketingTest Marketing
CommercializationCommercialization
New-Product New-Product Development ProcessDevelopment Process
AdvertisingAdvertising
PackagingPackaging
ProductProductBudget LevelsBudget Levels
Positioning Positioning
DistributionDistributionPricingPricing
BrandingBranding
Elements that May be Test
Marketed by a Company
Test Marketing is the Stage Where the Product and Marketing Program are Introduced into More Realistic
Market Settings.
New Product Development Process New Product Development Process Step 7. Test MarketingStep 7. Test Marketing
Product Positioning is creating a desired product concept based on consumer perceptions.
Segmentation Segmentation isis grouping of people grouping of people by needs or wants.by needs or wants.
Positioning: Positioning: is the way consumers perceive the brand relative to its competitors DUE TO competitive advantage bycompetitive advantage by
- Differentiating the product &Differentiating the product &- Stressing salient characteristicsStressing salient characteristics
Positioning – What?
Positioning is the act of designing the company’s Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinct and valued offering and image to occupy a distinct and valued place in the target customers mindplace in the target customers mind – Philip Kotler – Philip Kotler
DO PERCEPTUAL MAPPINGDO PERCEPTUAL MAPPINGCosmetic
Medicinal
Good Taste Poor Taste
o Anchor
o Colgate Gel
o Close Up
Colgate o
o Colgate Cibaca
o Pepsodent
o Colgate Total
o Meswak
Babool o
Emoform o
Types Of Positioning Strategies
Types
Benefit Positioning- Imax Adlabs Dome
Attribute Positioning- Gillette Mach 3
Use/Application Positioning
- Maggi
Quality/Price Positioning- Maruti VFM
Users Positioning- Mercedes
Competitor Positioning- 5paisa.com
New Product Launch Process
Product selected
Name
Trade Mark clearance
Packaging – Design etc.
Fore casting
Mfg Product specification (MKT)
Samples /
Sales
Yearly
Monthly
3 months –Placement stocks
Trade margin Price
Pricing
Inform sales
Get feed back
Finally announce the price - Raw Material
- Batch Size
New Product Launch Process
Finished product
Bonded store
Distribution/ Depot
Stockiest / Distributor / C&F /CA/ Depot
Retailers
Consumer
Marketing Activity
Product : MKT plan
Product concept Testing