[PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE -...
Transcript of [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE -...
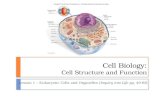
Cell Theory• All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all
living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells
through cell division.
Plasma (Cell) Membrane• Outer membrane of cell;
control movement via selective permeability
• Structure:• Transparent, Lipid bilayer• Cholesterol to stabilize • Receptors• Binding sites• Pores and carriers• Microvilli
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Plasma (Cell) Membrane• Function:• To regulate the flow
of materials both in and out
• Act as a barrier• Communication
channel between inside and outside of the cell
Nucleus
• Directs cell activities – “Headquarters”• Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear
membrane• Contains genetic material - DNA
Nucleus • 3 main structures:
1. Nuclear membrane – lipid bilayer, with pores for transport2. Nucleoli – clusters of DNA and site of ribosomal subunits3. Chromosomes – 46 present, 23 inherited from each parent, genetic materials
Nuclear Membrane• Surrounds nucleus• Is selectively permeable• Made of two layers• Openings allow material
to enter and leave nucleus
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Chromosomes• In nucleus• Made of DNA• Contain instructions
for traits & characteristics
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Nucleoli• Inside nucleus• Contains RNA to build
proteins
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Cytoplasm• Gel-like mixture - cytosol• Surrounded by cell membrane• Contains hereditary material • Site of organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum “network” (ER)
• “Mini circulatory system”• Smooth ER (SER): lacks
ribosomes; detox• Rough type, pictured (RER):
ribosomes embedded in surface
• Uses a cistern formation to move materials around the cell
• Ex. – pancreas for enzyme productionhttp://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Ribosomes• Each cell contains
thousands• Make (synthesize)
proteins
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Golgi Apparatus• “Traffic Director”• Protein 'packaging
plant'• Move materials in
and out of the cell• Modify and package
proteins• Think UPS
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Mitochondria• “The Powerhouse”• Produces energy through
manufacturing ATP• Controls level of water and
other materials in cell• Recycles and decomposes
proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Lysosomes• “Demolition Sites”• “Breakdown Bodies”• Breaks down worn out
cell parts and foreign substances
• Transports undigested material to the cell membrane for removal
• Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
![Page 1: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/1.jpg)
![Page 2: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/2.jpg)
![Page 3: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/3.jpg)
![Page 4: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/4.jpg)
![Page 5: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/5.jpg)
![Page 6: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/6.jpg)
![Page 7: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/7.jpg)
![Page 8: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/8.jpg)
![Page 9: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/9.jpg)
![Page 10: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/10.jpg)
![Page 11: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/11.jpg)
![Page 12: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/12.jpg)
![Page 13: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/13.jpg)
![Page 14: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/14.jpg)
![Page 15: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/15.jpg)
![Page 16: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/16.jpg)
![Page 17: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/17.jpg)
![Page 18: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/18.jpg)
![Page 19: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/19.jpg)
![Page 20: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/20.jpg)
![Page 21: [PPT]Cell Structure & Function - NHSPE - homenhspe.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cell_structure_function... · Web viewCell Structure & Function Cell Theory All living things are made](https://reader039.fdocuments.net/reader039/viewer/2022020302/5aa4d86e7f8b9a517d8c79d6/html5/thumbnails/21.jpg)