Power Supplies - WordPress.com · 2010-06-28 · POWER SUPPLIES Professor Gupta 301-802-9066...
Transcript of Power Supplies - WordPress.com · 2010-06-28 · POWER SUPPLIES Professor Gupta 301-802-9066...

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
The power supply is an often-underrated part of a computer. Electroniccomponents require a steady electrical current, free of surges or drops. The powersupply is the part responsible for providing clean, constant current.
A standard power supply draws power from a local, alternating current (AC) source(usually a wall outlet) and converts it to either 3.3 or 5 volts direct current (DC), foron-board electronics, and 12 volts DC for motors and hard drives.
Most PC power supplies also provide the system's cooling and processor fans thatkeep the machine from overheating.If the computer's power supply is providing reliable,clean power and its own cooling fan works, all is well. Ifthe power supply or its fan should fail or cause erraticbehavior by the PC, the power supply must bereplaced.
Many newer supplies have a universal input that willaccept either 110 VAC (volts alternating current), 60 Hz(U.S. standard power), or 220 VAC, 50 Hz(European/Asian standard).
When replacing a power supply, there are threethings to consider:1. physical size,2. wattage, and3. connectors.

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066A hertz is a measure of unit frequency: one cycle per
second equals one hertz. A kilohertz (Kz) is 1000 cycles persecond; a megahertz (Mz) is a million cycles per second.
A hertz is a measure of unit frequency: one cycle persecond equals one hertz. A kilohertz (Kz) is 1000 cycles persecond; a megahertz (Mz) is a million cycles per second.
Power supplies are rated according to the maximumsustained power (given in watts) that they canproduce.
A watt is a unit of electrical power equivalent to onevolt-ampere. It is important to keep in mind that thepower supply must produce at least enough energy tooperate all the components of the system at one time.
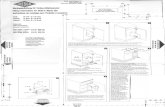
AT-Style Connections tothe Motherboard
ATX Motherboard ConnectionsMolex connector
Mini connector

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
Problem Description
SurgesThese are brief (and sometimes catastrophic) increases in the voltage source (very high voltagefor a very short time). They can originate with the power source (the local power company),but most often are due to lightning strikes.
SpikesSpikes are very short overvoltage conditions. Spikes are measured in nanoseconds, while asurge is measured in milliseconds.
Sags These are brief decreases of voltage at the power source.
BrownoutsIf a sag lasts longer than one second, it is called a brownout. The overloading of a primarypower source can cause brownouts. Some brownouts are "scheduled" by power companies toprevent overloading of circuits and potential catastrophic failure of the system.
BlackoutThis is a complete power failure, which can be caused by equipment failure (local or regional)or accidental cutting of power cables. When the power returns after a blackout, there is apower spike and danger of a power surge.
Power supplies are affected by the quality of the local power source. Commonpower delivery problems such as spikes, surges, sags, brownouts, and blackoutsaffect the stability and operation of the main power supply and are passed on to thecomputer.
While most users don't notice sudden changes in the quality of electrical power,computers and other sensitive electronics do and while we can't fully control theseproblems, there are a few things we can do to protect our equipment and data andensure a reasonably clean electrical supply.

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
Surge suppressorsare devices used tofilter out the effects ofvoltage spikes andsurges that are presentin commercial powersources and smoothout power variations.
A good surgesuppressor will protectyour system from mostproblems, but if youpurchase an economymodel, it might notwork when you need itmost.
Keep in mind thatalmost nothing willshield your hardwarefrom a very closelightning strike.
A UPS is an inline battery backup. When properlyinstalled between a computer and the wall outlet, a UPSdevice protects the computer from surges and acts as abattery when the power dips or fails.
It also provides a warning that the power is out ofspecification (above or below acceptable levels). Manymodels can also interact with the computer and initiate asafe shutdown in the event of a complete power failure.
Power-Supply ProblemsThe flow of power into a computer must be managed inorder to prevent damage and/or loss of data.Surge suppressors will eliminate some higher-than-normal voltage problems.
High-quality UPS devices will eliminate most powerfluctuations caused by too much or too little voltage.
Check power supplies when there are unusualproblems with memory and PC operations that do notquickly point to another cause.
partner-puFORID:10

POW
ER S
UPP
LIES
Prof
esso
r Gup
ta 3
01-8
02-9
066
1. Power supply rating2. AC Input voltage levels3. DC output levels by type4. 3.3V and 5V output andpeak output5. Hazard warnings6. Product certifications
1. Power supply rating2. AC Input voltage levels3. DC output levels by type4. 3.3V and 5V output andpeak output5. Hazard warnings6. Product certifications
Most power supplies aredesigned to handle twodifferent voltage ranges:■ 110–120V/60Hz■ 220–240V/50Hz
Most power supplies aredesigned to handle twodifferent voltage ranges:■ 110–120V/60Hz■ 220–240V/50Hz
partner-puFORID:10

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
What happens if you connect devicesthat require more wattage than a powersupply can provide?
This is a big problem called an overload. Anoverloaded power supply has two major symptoms:■ Overheating■ Spontaneous rebooting (cold boot with memory test)due to incorrect voltageon the Power Good line running from the power supplyto the motherboard.
NOTE if the fan has failed because of ashort circuit or incorrect input voltage,you will not see any picture onscreenbecause the system cannot operate.
NOTE if the fan has failed because of ashort circuit or incorrect input voltage,you will not see any picture onscreenbecause the system cannot operate.
You can do the following toimprove air flow inside thecomputer:
■ Use cable ties to secure excessribbon cable and power connectorsout of theway of the fans and the powersupply.
■ Replace any missing slot covers.
■ Make sure that auxiliary case fansand CPU fans are working correctly.
■ Use Serial ATA drives in place ofconventional ATA hard drives(assuming the system supportsSerial ATA); Serial ATA drives usevery narrow data cables.
When you open a system for any kind ofmaintenance, look for the following:
■ Dirt, dust, hair, and gunk clogging the case vents
■ A thin layer of dust on the motherboard andexpansion slots
■ Dirt and dust on the power supply vent and fans

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
Replacing Power Supply Form Factors and Connectors
There are two major types of power connectors on motherboards:■ 20-pin, used by older motherboards in the ATX family■ 24-pin, used by recent ATX/BTX motherboards requiring the ATX12V 2.xpower supply standard
Some motherboards use power supplies that feature severaladditional connectors to supply added power, as follows:■ The four-wire ATX12V connector provides additional 12V power to themotherboard; this connector is sometimes referred to as a “P4” or “Pentium4” connector.■ Many recent high-end power supplies use the eight-wire EPS12V connectorinstead of the ATX12V power connector.■ Some older motherboards use a six-wire AUX connector to provide additionalpower.
The power supply also powers various peripherals, such as thefollowing:■ PATA hard disks, CD and DVD optical drives, and case fans that do not pluginto the motherboard use a four-pin Molex power connector.■ 3.5-inch floppy drives use a reduced-size version of the Molex power supplyconnector.■ Serial ATA (SATA) hard disks use an L-shaped thin-line power connector.

Testing Power Supplies with a Multimeter
Multimeters are designed toperform many different types ofelectrical tests, including thefollowing:■ DC voltage and polarity■ AC voltage and polarity■ Resistance (Ohms)■ Diodes■ Continuity■ Amperage
A multimeter consists of two probes, an analogor digital meter, and a multiposition switch toselect the type of test you wish to perform.
Testing AC PowerOn any new building installation, failure to properlytest AC outlets can result in damaged or destroyedequipment, as well as possible injury andelectrocution. In the event a wiring error was madethat causes the voltage to be outside of thespecifications (either two high or too low), problemsare sure to arise. Don't take for granted that thebuilding power supply provides the correct voltage, orthat all of the other inputs are wired correctly.
When testing an AC power source, check thesethree things:1. Is the hot wire sending the correct voltage, and is
it wired to the correct pin?2. Is the neutral wire connected to ground and to the
correct pin?3. Is the ground wire connected to ground and to the
correct pin?

Testing AC Outlets with a MultimeterThe first step when testing an AC outlet isto set up the multimeter. Then you need toknow how to read the meter. You can alsouse special equipment if the multimeterdoes not provide enough information.
Setting Up the Meter1. Attach the black test lead to the negative (-)
marked hole. In some low-cost meters, leadsare permanently attached to the meter.
2. Attach the red test lead to the volts (+) hole.Be careful-if this lead is placed in the wronghole (ohm or amp) it can cause permanentdamage to the meter.
3. Set the selector switch to AC volts (thischoice is often denoted by red lettering). Ifthere are multiple selections, use the highestsetting possible (if voltage is unknown), orselect one level higher than the estimatedvoltage. For standard household outlets, 200VAC is a good selection. Some digitalmeters use "Auto-range" and don't need anyselection except AC volts.
Reading the MeterAfter the meter is set up, you are ready totest a wall outlet. There are three tests toperform. With AC voltage, it does notmatter which lead is placed in whichconnector:
Hot to Neutral: Place one lead in hot(smaller of the two vertical slots) and theother in neutral (larger of the verticalslots). The reading should be between 110and 120 volts AC.
Hot to Ground: Place one lead in hot(smaller of the two vertical slots) and theother in ground. The reading should bebetween 110 and 120 volts AC.
Neutral to Ground: Place one lead inneutral (larger of the two vertical slots) andthe other in ground. The reading should be0 volts.
POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066

Testing AC RippleThe function of the power supply is to convertAC to DC voltage. When working properly, apure DC signal will be produced. However,sometimes, as the power supply ages, its abilityto produce pure DC falters. A power supplyuses electrolytic capacitors (discussed later inthis lesson) to filter or smooth the voltage afterit has been converted from AC to DC. Thesecapacitors are second only to fuses as the partof a power supply most likely to fail. When anelectrolytic capacitor begins to fail, it allowsmore and more AC voltage to pass through.This small amount of AC voltage issuperimposed on top of the DC voltage andcalled noise or ripple. To test for ripple, set ameter to read AC. Then connect a .1mfd(microfarad) capacitor to the red lead. With thepower turned on, measure the DC voltage. Anyripple present will be displayed as AC voltage.
Testing ResistanceResistance is an opposition to the flowof current through a conductor.Resistance is measured in ohms. Thesymbol for an ohm is W. Resistance ismeasured by placing one lead of themeter on each side of the circuit orcomponent to be measured. Takingresistance measurements for acomponent while it is still soldered in itscircuit can lead to inaccurate readingsbecause any other componentconnected to the circuit can affect thetotal resistance measured. Unlikevoltage checks, you should testresistance with the power off. If a meteris set up to read resistance, you willdamage it if you connect it to anelectrical outlet.
POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066

Testing ContinuityContinuity is a term used to indicate whether ornot a connection exists between one point in acircuit and another. It is used to determine thepresence of breaks in wires and electricalcircuits.If no continuity setting is available, use theresistance setting (see the next section). If themultimeter measures infinite resistance, there isno continuity. This indicates a break in the line.If the multimeter shows little or no resistance,there is continuity and the circuit is complete.
Testing DC VoltageTesting for DC voltage is the same astesting for AC voltage, but with oneimportant difference: DC voltage issensitive to polarity. As mentionedearlier, DC voltage has a positive pole(+) and a negative pole (-). Whenmeasuring DC voltage, it is importantto place the positive (red) lead on thepositive side and the negative (black)lead on the negative side of the circuit.If the leads are positioned backwards,the polarity of the reading will be theopposite of what it should be.
POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066

Basic Voltage TestThe only purpose of this test is toverify the existence and value ofvoltages. With time, most powersupplies show their age by areduction in voltage. This voltagedrop will show itself in both the 5-voltand the 12-volt outputs, but is morepronounced on the 12-volt side.
Prepare the Meter for the TestAgain, meter preparation is quitesimple:Connect the black lead to thecommon (-) connector and the redlead to the voltage (+) connector.Turn the test selector to DC volts. Ifthe meter has an AC/DC switch, besure it is set to DC. If the meter does"auto range," set the range to 15-to-20 volts.
Testing the VoltagesThe best place to check voltage is at thepower supply's P8/P9 or ATX powerconnectors. For P8/P9 systems use theinstructions below:1. Place the meter's black (ground) lead
on the black wire connection and its red(positive) lead on the yellow (+12 volt)connection.
2. Record the voltages. A good powersupply will provide a voltage between11 and 13 volts DC.
3. Replace the power supply if the voltagereading is less than 10.
The voltage regulator receives the low-voltage AC outputs of the transformer andconverts them to clean DC power.
The voltage regulator receives the low-voltage AC outputs of the transformer andconverts them to clean DC power.
POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
Avoiding Power Supply Hazards
■ Never disassemble a power supply orpush metal tools through the openingsin the case - Long after you shut off thesystem, the wire coils inside the power supplyretain potentially fatal voltage levels. If you wantto see the interior of a power supply safely,check the websites of leading power supplyvendors such as PC Power and Cooling.
■ If you are replacing the power supplyin a Dell desktop computer, determinewhether the computer uses a standardATX or Dell proprietary ATX powersupply - Many Dell computers built fromSeptember 1998 to the present use anonstandard version of the ATX power supplywith a different pinout for the power connector.Install a standard power supply on a systembuilt to use a Dell proprietary model, or upgradefrom a Dell motherboard that uses theDell proprietary ATX design to a standardmotherboard, and you can literally cause apower supply and system fire!
Look for the following features to beuseful in preventing powerproblems:■ A low TVSS let-through voltage level (400V ACor less). This might seem high compared to the115V standard, but power supplies have beentested to handle up to 800V AC themselveswithout damage.■ A covered-equipment warranty that includeslightning strikes (one of the biggest causes ofsurges and spikes).■ A high Joule rating. Joules measure electricalenergy, and surge suppressors with higher Jouleratings can dissipate greater levels of surges orspikes.■ Fusing that will prevent fatal surges from gettingthrough.■ Protection for data cables such as telephone/fax(RJ-11), network (RJ-45), or coaxial (RG6).■ EMI/RFI noise filtration (a form of lineconditioning).■ Site fault wiring indicator (no ground, reversedpolarity warnings).■ Fast response time to surges. If the surgesuppressor doesn’t clamp fast enough, the surgecan get through.■ Protection against surges on hot, neutral, andground lines.

POWER SUPPLIESProfessor Gupta 301-802-9066
Battery Backup Units (UPS and SPS)
A true UPS runs your computer from its batteryat all times, isolating the computer and monitorfrom AC power.
There is no switchover time with a true UPSwhen AC power fails because the battery isalready running the computer.
A true UPS inherently provides powerconditioning (preventing spikes, surges, andbrownouts from reaching the computer) becausethe computer receives only battery power, notthe AC power coming from the wall outlet.
True UPS units are sometimes referred toas line-interactive battery backup units becausethe battery backup unit interactswith the AC line, rather than the AC line goingdirectly to the computer and othercomponents.
An SPS (standby power supply) is also referredto as a UPS, but its design is quitedifferent.
Its battery is used only when AC power fails.
A momentary gap in power(about 1ms or less) occurs between the loss ofAC power and the start of standbybattery power; however, this switchover time is farfaster than is required to avoidsystem shutdown because computers can coastfor several milliseconds before shutting down.
SPS-type battery backup units are far lessexpensive than true UPSs, but work just as wellas true UPSs when properly equipped withpower-conditioning features.