posterior triangle of neck
-
Upload
drpratik-mistry -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
117 -
download
1
Transcript of posterior triangle of neck

Posterior triangle of Posterior triangle of neckneck
Dr Pratik Mistry

22
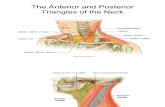
STERNOCLEIDOMASTOIDSternocleidomastoid is a strap muscle.It extends obliquely across the side of the neck. It forms a prominent surface landmark.It divides the side of the neck into anterior & posterior triangles

33
The neck is divided into anterior and posterior triangles by sternocleidomastoid
Anterior triangle lies in front of the muscle
Posterior triangle lies behind it.
TRIANGLES OF THE NECK

Torticollis (wry neck)Torticollis (wry neck)

55
Boundaries of the Posterior triangle:
Anteriorly: posterior border of sternomastoid
Posteriorly: anterior border of trapezius
Inferiorly: middle third of the clavicle.

66
OMOHYOID MUSCLEThe omohyoid
muscle has:
Inferior belly Intermediate
tendon
Superior belly.

77
The inferior belly of omohyoid subdivides the posterior triangle into:
a large occipital triangle above
a small supraclavicular triangle below.

88
The roof of the triangle is covered by:
Skin. superficial fascia, which
contains: platysma, cutaneous branches of
cervical plexus External jugular vein Investing layer of deep
cervical fascia.


1010
PLATYSMA MUSCLEThe platysma can be seen as a sheet of muscle by asking the patient to clench the jaws firmly. It extends from the body of the mandible downward over the clavicle onto the anterior thoracic wall.

1111
Running across the triangle in its covering: the cutaneous branches of cervical plexus


1313
BRANCHES OF THE CERVICAL PLEXUS
The cervical plexus is formed by the anterior rami of C1,C2,C3 & C4.Several cutaneous nerves emerge from under the middle of the posterior border of the sternomastoid muscle.They innervate parts of the skin in the head and neck region.

1414
LESSER OCCIPITAL NERVEThe lesser occipital nerve is a branch of C2.It hooks around the accessory nerve and ascends along the posterior border of the sternomastoid muscle It supply the skin over the lateral part of the occipital region and the medial surface of the auricle.

1515
GREAT AURICULAR NERVEThe great auricular nerve is a branch of C2 & C3.It ascends across the sternomastoid where it divides into branches that supply the skin over the angle of the mandible, the parotid gland, and the auricle.

1616
TRANSVERSE CERVICAL NERVETransverse cervical nerve of the neck is a branch of C2 and C3. It emerges from behind the middle of the posterior border of the sternomastoid.It passes forward across that muscle and divides into branches that supply the skin on the anterior and lateral surfaces of the neck, from the body of the mandible to the sternum.

1717
SUPRACLAVICULAR NERVESThe supraclavicular nerves are branches of C3 and C4. They emerge from beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and descend across the side of the neck. They pass onto the chest wall and shoulder region, down to the level of the second rib.

1818
EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEINThe External jugular vein begins just behind the angle of the mandible by the union of the posterior auricular vein with the posterior division of the retromandibular vein.


2020
TRIBUTARIES Posterior auricular vein.Posterior division of the retromandibular vein.Transverse cervical vein.Suprascapular vein.Anterior jugular vein. Posterior external jugular vein, a small vein that drains the posterior part of the scalp and neck and joins the external jugular vein about halfway along its course.

Notice:
The cutaneous branches of cervical plexus & the external jugular vein are contents and in the same time they run in the roof of the triangle

Parts of Deep cervical fascia:
Investing layer.Prevertebral layer.Pretracheal layer.Carotid sheath.

2323
The FLOOR of the triangle is covered by the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia. It is formed from below upward by the:
– Scalenus medius. – Scalenus posterior– Levator scapulae– Splenius capitis, &
Semispinalis capitis, A small part of the scalenus anterior may be present, but it is usually overlapped and hidden by the sternocleidomastoid.

Contents of occipital triangleContents of occipital triangle
Spinal part of Spinal part of accessory nerveaccessory nerveC3 & C4 nervesC3 & C4 nervesNerve to Nerve to rhomboidusrhomboidusFour cutaneous Four cutaneous branches of cervical branches of cervical plexusplexusUpper trunk of Upper trunk of brachial plexusbrachial plexusOccipital arteryOccipital artery

2525
ACCESSORY NERVE (SPINAL PART)
The spinal part of the accessory nerve enters the posterior triangle by emerging from beneath the middle of the posterior border of sternomastoid.It runs downward and laterally across the posterior triangle on the levator scapulae muscle

2626
OCCIPITAL ARTERYIt is a branch of the external carotid artery. It enters the posterior triangle at its superior angle, appearing between the sternomastoid & trapezius muscles. Then, it ascends in a tortuous course over the back of the scalp, accompanied by the greater occipital nerve.

Contents of supraclavicular triangleContents of supraclavicular triangleThird part of Third part of subclavian arterysubclavian arterySubclavian veinSubclavian veinExternal jugular External jugular veinveinTrunks of brachial Trunks of brachial plexusplexusSuperficial cervical Superficial cervical arteryarterySuprascapular a.Suprascapular a.Dorsal scapular a.Dorsal scapular a.Supraclavicular LNSupraclavicular LN

2828
THIRD PART OF THE SUBCLAVIAN ARTERYThe subclavian artery is divided into three parts by the scalenus anterior muscle, which crosses in front of the artery. First part medial to
scalenus anterior. Second part lies
behind the muscle. Third part extends
from the lateral border of the muscle to the outer border of the first rib; where, it is continuous as the axillary artery.

2929
The third part of the subclavian artery enters the anteroinferior angle of the posterior triangle and disappears behind the middle of the clavicle.

3030
BRACHIAL PLEXUSThe brachial plexus is formed from the anterior rami of the C 5th, 6th, 7th,& 8th &T 1st . It lies in the subclavian triangle of the posterior triangle.

3131
The trunks of the brachial plexus enter the posterior triangle of the neck through the interval between the scalenus anterior and the scalenus medius muscles.

Branches of supraclavicular part of Branches of supraclavicular part of brachial plexus in the trianglebrachial plexus in the triangle
Nerve to Nerve to rhomboidsrhomboidsNerve to serratus Nerve to serratus anterioranteriorNerve to subclaviusNerve to subclaviusSuprascapular Suprascapular nervenerve

3333
SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL ARTERY
It is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, of the first part of the subclavian artery. It runs across the lower part of the posterior triangle and disappears deep to the trapezius muscle.

3434
SUPASCAPULAR ARTERYThe suprascapular artery is also a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. It runs across the lower part of the posterior triangle. It follows the suprascapular nerve into the supraspinous fossa and takes part in the anastomosis around the scapula.

Supraclavicular lymph nodesSupraclavicular lymph nodes
In relation with In relation with inferior belly of inferior belly of omohyoidomohyoidDrain lymph from Drain lymph from back of scalp, neck back of scalp, neck and from upper and from upper deep cervical, deep cervical, axillary nodesaxillary nodesEmpty into the Empty into the jugular lymph jugular lymph trunktrunk

Clinical anatomyClinical anatomySubclavian steal syndromeSubclavian steal syndrome

Cervical ribCervical rib

Swellings in the posterior Swellings in the posterior trianglestriangles
Tuberculosis of cervical vertebraTuberculosis of cervical vertebraEnlarged supraclavicular lymph Enlarged supraclavicular lymph nodes (Virchow's nodes) as seen in nodes (Virchow's nodes) as seen in many infections like TB, Lymphoma, many infections like TB, Lymphoma, malignancies of breast, stomach, malignancies of breast, stomach, testis and other abdominal organstestis and other abdominal organs

External jugular veinExternal jugular veinInjury to EJV in the Injury to EJV in the supraclavicular supraclavicular space cause air space cause air embolism and embolism and sudden death.sudden death.JVPJVPRaised in right Raised in right sided heart failuresided heart failure


THANK YOUTHANK YOU