Population
description
Transcript of Population

Population
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sc4HxPxNrZ0&feature=related

Population density is the measure of the number per unit area. It is commonly represented as people per square mile. which is derived simply by dividing... total area population / land area in square miles

Kolkata, India

Rajasthan, India

Overpopulation is when there are too many people relative to available resources. Simple density is not the determinant.


World and Country Population Totals
Distribution and Structure: 3/4 of people live on 5% of earth's surface!
Total: 7,059,735,689 as of now.
Five most populous regions and countriesREGION POPULATION COUNTRY POPULATION
East Asia 1.6 billion China 1.3 billion South Asia 1.5 billion India 1.1 billion Europe 1 billion U.S. 300 million SE Asia 600 million Indonesia 250
million Canada 27.5 million Brazil 188 million

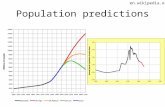
Human Population Growth
How many people will the planet eventually support?
The U.S. Census Bureau and the United Nations Statistics Division both agree that world population will level off somewhere between 9 and 11 billion people and then start to fall.


Rates of Natural Increase

Doubling Time• How long will it take for a population of a given area to double in size?• Doubling time assumes the population will grow at a given annual rate• Approximated by dividing the annual rate of population increase into 70
World = 50U.S. = 35MDC = 550LDC = 40Honduras = 22Denmark = 700Russia = never?
Example: Bangladesh70 / R.N.I. => 70/2.09 = 33.5 years
Bangladesh with a population of 144.3 million people in 2005 will have approximately 288.6million people in 2038, if the population continues to grow at current rates.
Source: National Geographic Magazine

Total Fertility Rate 2006

Total Fertility Rate 1950

Infant Mortality Rate – the number of deaths of children under the age of one per thousand live births. The rate ranges from as low as 3 (Singapore, Iceland) to as much as 150 (Sierra Leone, Afghanistan). The U.S. rate is just over 6. High infant mortality tends to result in higher fertility rates as families seek “insurance” for the loss of children.

World Death Rates Epidemiological Transition is the shift
from infectious to degenerative diseases that occurs with development.
Infectious diseases (developing world)– HIV/AIDS– SARS– Malaria– Cholera
Degenerative diseases (developed countries)– Obesity– Tobacco use

Life Expectancy
Rapid increase throughout world
Infant mortality rate declining in most countries
Antibiotics/immunization
Increasing standards of living

Life Expectancy





Demographic Transition Model- was highly predictive for most countries

Demographic Transition Model
Stage one (preindustrial/pre-agricultural)– Crude birth/death rate high– Fragile, but stable, population
Stage two (improved agriculture and medicine)– Lower death rates– Infant mortality rate falls– Natural increase very high
Stage three (attitudes change)– Indicative of richer developed countries– Higher standards of living/education– Crude birth rate finally falls
Stage four – Crude birth/death rates low– Population stable– Populations aging

Population pyramids are used to show information about the age and gender of people in a specific country.
Male Female
Population in millions
In this country
there is a high Birth
Rate
There is also a high
Death Rate.
This population pyramid is typical of countries in poorer parts of the
world (LEDCs.)

In some LEDCs the government is
encouraging couples to have smaller
families. This means the birth rate has
fallen.

Male Female
Population in millions
In this country the number of people in each age group is
about the same.
The largest category of
people were born about 40
years ago.
In this country there is a low Birth Rate and a low Death Rate.
This population pyramid is typical of countries in the richer parts of the
world (MEDCs.)

Population in millions
Male Female
In this country the birth rate is decreasing.
In the future the elderly people will
make up the largest section of the
population in this country.
This is happening more and more in
many of the world’s richer
countries.

Male Female
Population in thousands
This country has a large number of temporary
workers. These are people who migrate here
especially to find a job.

Population pyramid for Mozambique.
Population pyramid for Iceland.
What type of countries are represented here?

What happens next?


What is going to happen to Japan’s population in the future?
Why does this matter?

?

?

?


Pop
ula
tion
an
d R
eso
urc
e
Con
sum
pti
on

Technology, Energy Consumption, and Environmental Impact
There has been a dramatic increase in:
• individual energy use over time: 3,000 kcal/person - 300,000 kcal/person
• the power of technology to change the environment: think stone axe versus bulldozer versus atomic bomb.
• The scope and severity of environmental impacts.

Demographics
characteristics of human populations and population segments

MOVEMENT

WHY DO WE MOVE?
PUSH FACTORS (things that would push us to leave the area)
Weather and Climate- Texas in August
Cost of living – a house in Cali costs $450,000
Personal Safety – WAR, plague, famine
Environmental Catastrophes – tsunami, earthquakes, hurricanes
Emigration/Emigrant

PULL FACTORS (things that would pull us want to an area)
availability of jobs
religious or political freedom
SafetyImmigration/Immigrant

Where do we move to?
Rural

UrbanMexico City Pop. 18,836,045
8th largest city in the World

The End