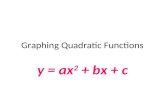Polynomial and Rational Functions … · quadratic function in the form y = a(x — h)2 + k zGraph...
Transcript of Polynomial and Rational Functions … · quadratic function in the form y = a(x — h)2 + k zGraph...

Polynomial and Rational Functions
Chapter 3

Quadratic Functions and Models
Section 3.1

Quadratic Functions
Quadratic function: Function of the form
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
(a, b and c real numbers, a ≠ 0)

Quadratic Functions
Example. Plot the graphs of f(x) =
x2, g(x) = 3x2 and
-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
-30
-20
-10
10
20
30

Quadratic Functions
Example. Plot the graphs of f(x) =
—x2, g(x) = —3x2 and
-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
-30
-20
-10
10
20
30

Parabolas
Parabola: The graph of a quadratic function
If a > 0, the parabola opens up
If a < 0, the parabola opens down
Vertex: highest / lowest point of a parabola

Parabolas
Axis of symmetry: Vertical line passing through the vertex

-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10
Parabolas
Example. For the function
f(x) = —3x2 +12x — 11
(a) Problem: Graph the function
Answer:

Parabolas
Example. (cont.)
(b) Problem: Find the vertex and axis of symmetry.
Answer:

Parabolas
Locations of vertex and axis of
symmetry:
Set
Set
Vertex is at:
Axis of symmetry runs through vertex

Parabolas
Example. For the parabola defined by
f(x) = 2x2 — 3x + 2
(a) Problem: Without graphing, locate the
vertex.
Answer:
(b) Problem: Does the parabola open up
or down?
Answer:

x-intercepts of a Parabola
For a quadratic function
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c:
Discriminant is b2 — 4ac.
Number of x-intercepts depends on the
discriminant.
Positive discriminant: Two x-intercepts
Negative discriminant: Zero x-intercepts
Zero discriminant: One x-intercept
(Vertex lies on x-axis)

x-intercepts of a Parabola

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example. For the function
f(x) = 2x2 + 8x + 4
(a) Problem: Find the vertex
Answer:
(b) Problem: Find the intercepts.
Answer:

-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10
Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example. (cont.)
(c) Problem: Graph the function
Answer:

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example. (cont.)
(d) Problem: Determine the domain and range of f.
Answer:
(e) Problem: Determine where f is increasing and decreasing.
Answer:

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example.
Problem: Determine the quadratic function whose vertex is (2, 3) and whose y-intercept is 11.
Answer:
-14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
-14
-12
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10
12
14

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Method 1 for Graphing
Complete the square in x to write the quadratic function in the form y = a(x — h)2 + k
Graph the function using transformations

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Method 2 for GraphingDetermine the vertex
Determine the axis of symmetry
Determine the y-intercept f(0)
Find the discriminant b2 — 4ac.If b2 — 4ac > 0, two x-intercepts
If b2 — 4ac = 0, one x-intercept (at the vertex)
If b2 — 4ac < 0, no x-intercepts.

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Method 2 for Graphing
Find an additional point
Use the y-intercept and axis of symmetry.
Plot the points and draw the graph

Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example. For the quadratic function
f(x) = 3x2 — 12x + 7
(a) Problem: Determine whether f has a maximum or minimum value, then find it.
Answer:

-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10
Graphing Quadratic Functions
Example. (cont.)
(b) Problem: Graph f
Answer:

Quadratic Relations

Quadratic Relations
Example. An engineer collects the following data showing the speed s of a Ford Taurus and its average miles per gallon, M.

Quadratic Relations
Speed, s Miles per Gallon, M
30 18
35 20
40 23
40 25
45 25
50 28
55 30
60 29
65 26
65 25
70 25

Quadratic Relations
Example. (cont.)
(a) Problem: Draw a scatter diagram of the data
Answer:

Quadratic Relations
Example. (cont.)
(b) Problem: Find the quadratic function of best fit to these data.
Answer:

Quadratic Relations
Example. (cont.)
(c) Problem: Use the function to determine the speed that maximizes miles per gallon.
Answer:

Key Points
Quadratic Functions
Parabolas
x-intercepts of a Parabola
Graphing Quadratic Functions
Quadratic Relations

Polynomial Functions and Models
Section 3.2

Polynomial Functions
Polynomial function: Function of the form
f(x) = anxn + an —1x
n —1 + ⋅⋅⋅ + a1x + a0
an, an —1, …, a1, a0 real numbers
n is a nonnegative integer (an ≠ 0)
Domain is the set of all real numbers
Terminology
Leading coefficient: an
Degree: n (largest power)
Constant term: a0

Polynomial Functions
Degrees: Zero function: undefined degree
Constant functions: degree 0.
(Non-constant) linear functions: degree 1.
Quadratic functions: degree 2.

Polynomial Functions
Example. Determine which of the following are polynomial functions? For those that are, find the degree.
(a) Problem: f(x) = 3x + 6x2
Answer:
(b) Problem: g(x) = 13x3 + 5 + 9x4
Answer:
(c) Problem: h(x) = 14
Answer:
(d) Problem:
Answer:

Polynomial Functions
Graph of a polynomial function will be smooth and continuous.
Smooth: no sharp corners or cusps.
Continuous: no gaps or holes.

Power Functions
Power function of degree n:
Function of the form
f(x) = axn
a ≠ 0 a real number
n > 0 is an integer.

Power Functions
The graph depends on whether n is even or odd.

Power Functions
Properties of f(x) = axn
Symmetry:
If n is even, f is even.
If n is odd, f is odd.
Domain: All real numbers.
Range:
If n is even, All nonnegative real numbers
If n is odd, All real numbers.

Power Functions
Properties of f(x) = axn
Points on graph:
If n is even: (0, 0), (1, 1) and (—1, 1)
If n is odd: (0, 0), (1, 1) and (—1, —1)
Shape: As n increases
Graph becomes more vertical if |x| > 1
More horizontal near origin

-4 -2 2 4
-4
-2
2
4
Graphing Using Transformations
Example.
Problem: Graph f(x) = (x — 1)4
Answer:

-4 -2 2 4
-4
-2
2
4
Graphing Using Transformations
Example.
Problem: Graph f(x) = x5 + 2
Answer:

Zeros of a Polynomial
Zero or root of a polynomial f:
r a real number for which f(r) = 0
r is an x-intercept of the graph of f.
(x — r) is a factor of f.

Zeros of a Polynomial

Zeros of a Polynomial
Example.
Problem: Find a polynomial of degree 3 whose zeros are —4, —2 and 3.
Answer:
-10 -5 5 10
-40
-30
-20
-10
10
20
30
40

Zeros of a Polynomial
Repeated or multiple zero or root of f:
Same factor (x — r) appears more than once
Zero of multiplicity m:
(x — r)m is a factor of f and (x — r)m+1 isn’t.

Zeros of a Polynomial
Example.
Problem: For the polynomial, list all zeros and their multiplicities.
f(x) = —2(x — 2)(x + 1)3(x — 3)4
Answer:

-4 -2 2 4
-40
-20
20
40
Zeros of a Polynomial
Example. For the polynomial
f(x) = —x3(x — 3)2(x + 2)
(a) Problem: Graph the polynomial
Answer:

Zeros of a Polynomial
Example. (cont.)
(b) Problem: Find the zeros and their multiplicities
Answer:

Multiplicity
Role of multiplicity:
r a zero of even multiplicity:
f(x) does not change sign at r
Graph touches the x-axis at r, but does not cross
-4 -2 2 4
-40
-20
20
40

Multiplicity
Role of multiplicity:
r a zero of odd multiplicity:
f(x) changes sign at r
Graph crosses x-axis at r
-4 -2 2 4
-40
-20
20
40

Turning Points
Turning points: Points where graph changes from increasing to decreasing function or vice versa
Turning points correspond to local extrema.
Theorem. If f is a polynomial function of degree n, then f has at most n — 1 turning points.

End Behavior
Theorem. [End Behavior]
For large values of x, either positive or negative, that is, for large |x|, the graph of the polynomial
f(x) = anxn + an—1x
n—1 + L + a1x + a0
resembles the graph of the power function
y = anxn

End Behavior
End behavior of:
f(x) = anxn + an—1x
n—1 + L + a1x + a0

Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Example. For the polynomial:
f(x) =12x3 — 2x4 — 2x5
(a) Problem: Find the degree.
Answer:
(b) Problem: Determine the end behavior. (Find the power function that the graph of f resembles for large values of |x|.)
Answer:

Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Example. (cont.)
(c) Problem: Find the x-intercept(s), if any
Answer:
(d) Problem: Find the y-intercept.
Answer:
(e) Problem: Does the graph cross or touch the x-axis at each x-intercept:
Answer:

-4 -2 2 4
-80
-60
-40
-20
20
40
60
80
Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Example. (cont.)
(f) Problem: Graph f using a graphing utility
Answer:

Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Example. (cont.)
(g) Problem: Determine the number of turning points on the graph of f. Approximate the turning points to 2 decimal places.
Answer:
(h) Problem: Find the domain
Answer:

Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Example. (cont.)
(i) Problem: Find the range
Answer:
(j) Problem: Find where f is increasing
Answer:
(k) Problem: Find where f is decreasing
Answer:

Cubic Relations

Cubic Relations
Example. The following data represent the average number of miles driven (in thousands) annually by vans, pickups, and sports utility vehicles for the years 1993-2001, where x = 1 represents 1993, x = 2 represents 1994, and so on.

Cubic Relations
Year, x Average Miles Driven, M
1993, 1 12.4
1994, 2 12.2
1995, 3 12.0
1996, 4 11.8
1997, 5 12.1
1998, 6 12.2
1999, 7 12.0
2000, 8 11.7
2001, 9 11.1

Cubic Relations
Example. (cont.)
(a) Problem: Draw a scatter diagram of the data using x as the independent variable and M as the dependent variable.
Answer:

Cubic Relations
Example. (cont.)
(b) Problem: Find the cubic function of best fit and graph it
Answer:

Key Points
Polynomial Functions
Power Functions
Graphing Using Transformations
Zeros of a Polynomial
Multiplicity
Turning Points
End Behavior
Analyzing Polynomial Graphs
Cubic Relations

The Real Zeros of a Polynomial Function
Section 3.6

Division Algorithm
Theorem. [Division Algorithm]If f(x) and g(x) denote polynomial functions and if g(x) is a polynomial whose degree is greater than zero, then there are unique polynomial functions q(x) and r(x) such that
where r(x) is either the zero polynomial or a polynomial of degree less than that of g(x).

Division Algorithm
Division algorithm
f(x) is the dividend
q(x) is the quotient
g(x) is the divisor
r(x) is the remainder

Remainder Theorem
First-degree divisor
Has form g(x) = x — c
Remainder r(x)
Either the zero polynomial or a polynomial of degree 0,
Either way a number R.
Becomes f(x) = (x — c)q(x) + R
Substitute x = c
Becomes f(c) = R

Remainder Theorem
Theorem. [Remainder Theorem] Let f be a polynomial function. If f(x) is divided by x — c, the remainder is f(c).

Remainder Theorem
Example. Find the remainder if
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 + 2x — 6
is divided by:
(a) Problem: x + 2
Answer:
(b) Problem: x — 1
Answer:

Factor Theorem
Theorem. [Factor Theorem] Let f be a polynomial function. Then x — c is a factor of f(x) if and only if f(c) = 0.
If f(c) = 0, then x — c is a factor off(x).
If x — c is a factor of f(x), then f(c) = 0.

Factor Theorem
Example. Determine whether the function
f(x) = —2x3 — x2 + 4x + 3
has the given factor:
(a) Problem: x + 1
Answer:
(b) Problem: x — 1
Answer:

Number of Real Zeros
Theorem. [Number of Real Zeros]A polynomial function of degree n, n ≥ 1, has at most n real zeros.

Rational Zeros Theorem
Theorem. [Rational Zeros Theorem]Let f be a polynomial function of degree 1 or higher of the form
f(x) = anxn + an—1x
n—1 + L + a1x + a0
an ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0, where each coefficient is an integer. If p/q, in lowest terms, is a rational zero of f, then p must be a factor of a0 and q must be a factor of an.

Rational Zeros Theorem
Example.
Problem: List the potential rational zeros of
f(x) = 3x3 + 8x2 — 7x — 12
Answer:

Finding Zeros of a Polynomial
Determine the maximum number of zeros.
Degree of the polynomial
If the polynomial has integer coefficients:
Use the Rational Zeros Theorem to find potential rational zeros
Using a graphing utility, graph the function.

Finding Zeros of a Polynomial
Test values
Test a potential rational zero
Each time a zero is found, repeat on the depressed equation.

Finding Zeros of a Polynomial
Example.
Problem: Find the rational zeros of the polynomial in the last example.
f(x) = 3x3 + 8x2 — 7x — 12
Answer:

Finding Zeros of a Polynomial
Example.
Problem: Find the real zeros of
f(x) = 2x4 + 13x3 + 29x2 + 27x + 9
and write f in factored form
Answer:

Factoring Polynomials
Irreducible quadratic: Cannot be factored over the real numbers
Theorem. Every polynomial function (with real coefficients) can be uniquely factored into a product of linear factors and irreducible quadratic factors
Corollary. A polynomial function (with real coefficients) of odd degree has at least one real zero

Factoring Polynomials
Example.
Problem: Factor
f(x)=2x5 — 9x4 + 20x3 — 40x2 + 48x —16
Answer:

Bounds on Zeros
Bound on the zeros of a polynomial
Positive number M
Every zero lies between —M and M.

Bounds on Zeros
Theorem. [Bounds on Zeros]Let f denote a polynomial whose leading coefficient is 1.
f(x) = xn + an—1xn—1 + L + a1x + a0
A bound M on the zeros of f is the smaller of the two numbers
Max{1, |a0| + |a1| + L + |an-1|}, 1 + Max{|a0| ,|a1| , … , |an-1|}

Bounds on Zeros
Example. Find a bound to the zeros of each polynomial.
(a) Problem:
f(x) = x5 + 6x3 — 7x2 + 8x — 10
Answer:
(b) Problem:
g(x) = 3x5 — 4x4 + 2x3 + x2 +5
Answer:

Intermediate Value Theorem
Theorem. [Intermediate Value Theorem]
Let f denote a continuous function. If a < b and if f(a) and f(b) are of opposite sign, then f has at least one zero between a and b.

Intermediate Value Theorem
Example.
Problem: Show that
f(x) = x5 — x4 + 7x3 — 7x2 — 18x + 18
has a zero between 1.4 and 1.5. Approximate it to two decimal places.
Answer:

Key Points
Division Algorithm
Remainder Theorem
Factor Theorem
Number of Real Zeros
Rational Zeros Theorem
Finding Zeros of a Polynomial
Factoring Polynomials
Bounds on Zeros
Intermediate Value Theorem

Complex Zeros; Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Section 3.7

Complex Polynomial Functions
Complex polynomial function: Function of the form
f(x) = anxn + an —1x
n —1 + ⋅⋅⋅ + a1x + a0
an, an —1, …, a1, a0 are all complex numbers,
an ≠ 0,
n is a nonnegative integer
x is a complex variable.
Leading coefficient of f: an
Complex zero: A complex number r with f(r) = 0.

Complex Arithmetic
See Appendix A.6.
Imaginary unit: Number i with i2 = —1.
Complex number: Number of the form z = a + bi
a and b real numbers.
a is the real part of z
b is the imaginary part of z
Can add, subtract, multiply
Can also divide (we won’t)

Complex Arithmetic
Conjugate of the complex number
a + bi
Number a — bi
Written
Properties:

Complex Arithmetic
Example. Suppose z = 5 + 2i and w = 2 — 3i.
(a) Problem: Find z + w
Answer:
(b) Problem: Find z — w
Answer:
(c) Problem: Find zw
Answer:
(d) Problem: Find
Answer:

Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Theorem. [Fundamental Theorem of Algebra]Every complex polynomial function f(x) of degree n ≥ 1 has at least one complex zero.

Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Theorem. Every complex polynomial function f(x) of degree n ≥ 1 can be factored into n linear factors (not necessarily distinct) of the form
f(x) = an(x — r1)(x — r2) L (x — rn)
where an, r1, r2, …, rn are complex numbers. That is, every complex polynomial function f(x) of degree n ≥ 1 has exactly n (not necessarily distinct) zeros.

Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Theorem. [Conjugate Pairs Theorem]
Let f(x) be a polynomial whose
coefficients are real numbers. If a + bi
is a zero of f, then the complex
conjugate a — bi is also a zero of f.

Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Example. A polynomial of degree 5 whose coefficients are real numbers has the zeros —2, —3i and 2 + 4i.
Problem: Find the remaining two zeros.
Answer:

Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Example.
Problem: Find a polynomial f of degree 4 whose coefficients are real numbers and that has the zeros —2, 1 and 4 + i.
Answer:

Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Example.
Problem: Find the complex zeros of the polynomial function
f(x) = x4 + 2x3 + x2 — 8x — 20
Answer:

Key Points
Complex Polynomial Functions
Complex Arithmetic
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Conjugate Pairs Theorem

Properties of Rational Functions
Section 3.3

Rational Functions
Rational function: Function of the form
p and q are polynomials,
q is not the zero polynomial.
Domain: Set of all real numbers except where q(x) = 0

Rational Functions
is in lowest terms:
The polynomials p and q have no common factors
x-intercepts of R:
Zeros of the numerator p when R is in lowest terms

Rational Functions
Example. For the rational function
(a) Problem: Find the domain
Answer:
(b) Problem: Find the x-intercepts
Answer:
(c) Problem: Find the y-intercepts
Answer:

Graphing Rational Functions
Graph of
-10 -5 5 10
-10
-7.5
-5
-2.5
2.5
5
7.5
10

Graphing Rational Functions
As x approaches 0, is unbounded in the positivedirection.
Write f(x) → ∞
Read “f(x) approaches infinity”Also:
May write f(x) → ∞ as x → 0
May read: “f(x) approaches infinity as xapproaches 0”

-6 -4 -2 2 4
-4
-2
2
4
Graphing Rational Functions
Example. For
Problem: Use transformations to graph f.
Answer:

Asymptotes
Horizontal asymptotes:
Let R denote a function.
Let x → —∞ or as x → ∞,
If the values of R(x) approach some fixed number L, then the line y = L is a horizontal asymptote of the graph of R.

Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes:
Let x → c
If the values |R(x)| → ∞, then the line x = c is a vertical asymptote of the graph of R.

Asymptotes
Asymptotes:
Oblique asymptote: Neither horizontal nor vertical
Graphs and asymptotes:
Graph of R never intersects a vertical asymptote.
Graph of R can intersect a horizontal or oblique asymptote (but doesn’t have to)

Asymptotes
A rational function can have:
Any number of vertical asymptotes.
1 horizontal and 0 oblique asymptote
0 horizontal and 1 oblique asymptotes
0 horizontal and 0 oblique asymptotes
There are no other possibilities

Vertical Asymptotes
Theorem. [Locating Vertical Asymptotes]
A rational function
in lowest terms, will have a vertical
asymptote x = r if r is a real zero of
the denominator q.

Vertical Asymptotes
Example. Find the vertical asymptotes, if any, of the graph of each rational function.
(a) Problem:
Answer:
(b) Problem:
Answer:

Vertical Asymptotes
Example. (cont.)
(c) Problem:
Answer:
(d) Problem:
Answer:

Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes
Describe the end behavior of a rational function.
Proper rational function:
Degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator.
Theorem. If a rational function R(x) is proper, then y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote of its graph.

Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes
Improper rational function R(x): one that is not proper.
May be written
where is proper. (Long division!)

Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes
If f(x) = b, (a constant)Line y = b is a horizontal asymptote
If f(x) = ax + b, a ≠ 0,Line y = ax + b is an oblique asymptote
In all other cases, the graph of Rapproaches the graph of f, and there are no horizontal or oblique asymptotes.
This is all higher-degree polynomials

Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes
Example. Find the hoizontal or oblique asymptotes, if any, of the graph of each rational function.
(a) Problem:
Answer:
(b) Problem:
Answer:

Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes
Example. (cont.)
(c) Problem:
Answer:
(d) Problem:
Answer:

Key Points
Rational Functions
Graphing Rational Functions
Vertical Asymptotes
Horizontal and Oblique Asymptotes

The Graph of a Rational Function; Inverse and Joint Variation
Section 3.4

Analyzing Rational Functions
Find the domain of the rational function.
Write R in lowest terms.
Locate the intercepts of the graph.
x-intercepts: Zeros of numerator of function in lowest terms.
y-intercept: R(0), if 0 is in the domain.
Test for symmetry – Even, odd or neither.

Analyzing Rational Functions
Locate the vertical asymptotes:
Zeros of denominator of function in lowest terms.
Locate horizontal or oblique asymptotes
Graph R using a graphing utility.
Use the results obtained to graph by hand

Analyzing Rational Functions
Example.
Problem: Analyze the graph of the rational function
Answer:
Domain:
R in lowest terms:
x-intercepts:
y-intercept:
Symmetry:

Analyzing Rational Functions
Example. (cont.)
Answer: (cont.)
Vertical asymptotes:
Horizontal asymptote:
Oblique asymptote:

-4 -2 2 4
-4
-2
2
4
Analyzing Rational Functions
Example. (cont.)
Answer: (cont.)

Analyzing Rational Functions
Example.
Problem: Analyze the graph of the rational function
Answer:
Domain:
R in lowest terms:
x-intercepts:
y-intercept:
Symmetry:

Analyzing Rational Functions
Example. (cont.)
Answer: (cont.)
Vertical asymptotes:
Horizontal asymptote:
Oblique asymptote:

-6 -4 -2 2 4 6
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
Analyzing Rational Functions
Example. (cont.)
Answer: (cont.)

Variation
Inverse variation:
Let x and y denote 2 quantities.
y varies inversely with x
If there is a nonzero constant such that
Also say: y is inversely proportional to x

Variation
Joint or Combined Variation:
Variable quantity Q proportional to the product of two or more other variables
Say Q varies jointly with these quantities.
Combinations of direct and/or inverse variation are combined variation.

Variation
Example. Boyle’s law states that for a fixed amount of gas kept at a fixed temperature, the pressure P and volume V are inversely proportional (while one increases, the other decreases).

Variation
Example. According to Newton, the gravitational force between two objects varies jointly with the masses m1 and m2 of each object and inversely with the square of the distance r between the objects, hence

Key Points
Analyzing Rational Functions
Variation

Polynomial and Rational Inequalities
Section 3.5

Solving Inequalities Algebraically
Rewrite the inequality
Left side: Polynomial or rational expression f. (Write rational expression as a single quotient)
Right side: Zero
Should have one of following forms
f(x) > 0
f(x) ≥ 0
f(x) < 0
f(x) ≤ 0

Solving Inequalities Algebraically
Determine where left side is 0 or undefined.
Separate the real line into intervals based on answers to previous step.

Solving Inequalities Algebraically
Test Points:
Select a number in each interval
Evaluate f at that number.
If the value of f is positive, then f(x) > 0 for all numbers x in the interval.
If the value of f is negative, then f(x) < 0 for all numbers x in the interval.

Solving Inequalities Algebraically
Test Points (cont.)
If the inequality is strict (< or >)Don’t include values where x = 0
Don’t include values where x is undefined.
If the inequality is not strict (≤ or ≥)
Include values where x = 0
Don’t include values where x is undefined.

Solving Inequalities Algebraically
Example.
Problem: Solve the inequality x5 ≥ 16x
Answer:

Key Points
Solving Inequalities Algebraically