**PLEASE START A NEW PAGE** 5.4.11 classification We will read and complete section reviews to...
-
Upload
austen-lee -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
1
Transcript of **PLEASE START A NEW PAGE** 5.4.11 classification We will read and complete section reviews to...

**PLEASE START A NEW PAGE**5.4.11 classification
• We will read and complete section reviews to understand classification of organism and review dichotomous keys
• TEK 6.12 and 7.11• Warm up: what is the difference between a
prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell?

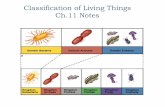
Define: 1.Classification2.Taxonomy3.Kingdom4.Genus5.Species6.Dichotomous
key
7. Archaebacteria8. Eubacteria9. Protista10. Plantae11. Fungi12. animalia

• Recall: Carolus Linnaeus founded taxonomy• Summary: At first, living things were classified
as either plants or animals• Out: come up with a nuenomic for the levels
of classification

5.5.11 Classification
• We will read and answer questions on classification in our journals
• TEK 6.12 and 7.11• Warm up: which of these are elements and
which are compounds? (TEK6.5c)CCoCO

Use complete sentences to answer the following questions:
1. Why do scientist use scientific names for organims?
2. List seven levels of classification3. Name the six kingdoms4. Explain how the kingdom system changed as
greater numbers of organisms became known5. Explain different ways that plants, fungi and
animals obtain nutrients6. Why are protists placed in their own kingdom7. Which kingdom do humans belong in? EXPLAIN
your logic!

• Recall: classification refers to the arrangement of things into orderly groups based on their similarities
• Summary: modern classification takes into account shared characteristics among organisms
• OUT: plants most fungi and animals are complex, many celled living things. Plants perform photosynthesis. Fungi break down material outside their body and then absorb the nutrients. Animals eat food which is digested inside their body

5.6.11 Shape Island
• We will conduct a lab to identify an “animal” species.
• TEK 6.12• Warm up: letters that represent elements are
called ______________ ______________

• Record and complete the lab from page 306-307 in the through portion of your journal.

• Recall: all organisms are made up of one or more cells
• Summary: the broadest taxonomic classification of living organisms is divided into currently recognized domains
• OUT: identify (define) ProkayoticUnicellularAutotrophicAsexual