Plasma membrane
description
Transcript of Plasma membrane

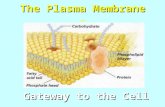
Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Hormone receptor
Adenylate cyclase
ATP
Active Protein Kinase A
PO4
G
cAMP Inctive Protein Kinase A
PO4
Active pKA enters the nucleus and phosphorylates CREB on Serine 133
Hormone
G-protein
Core promoter
Phosphorylation of CREB: - stimulates interactions with several core promoter proteins - induces binding of HAT and acetylation of histones
Signaling mediated by cAMP and protein kinase A

ATP cAMP(3’,5’cyclic AMP)
PPi
2Pi
H2Opyrohosphatase
Adenylate cyclase
AMP
phoshodiesteraseH2O
cAMP formation cAMP hydrolysis
NO
O
OHO
PO
OH
N
NN
NH2
NO
O
OHOH
P
O
OH
P
O
O
OH
OH
OH
O
O
P N
NN
NH2

Substrate-OH
O ║
Substrate─O ─ P ─ O─
│ OH
Kinase
ATP ADP
Protein-OH
O ║
Protein ─ O ─ P ─ O─
│ OH
Protein Kinase
ATP ADP
Serine-OH
O ║
Serine ─ O ─ P ─ O─
│ OH
Protein Kinase A
ATP ADPSeveral specific Proteins
Including CREB
Several specific proteins
including CREB

CREB and Memory

Signaling by calcium ions
Ca++enters cell
Ca++ activates calmodulin
CaM kinases phosphorylate multiple targets including
ser 133 of CREB
Calmodulin activates CaM kinases

CREB and Memory

CREB and
Memory( in Aplysia,
a slug)
Bailey, Kandel & Kausik (2004) Neuron 44:49-57
Stimulates long term memory
Inhibits long term memory
Amplification:C/EBP is another transcription factor.It activates many genes. (CCAAT box enhancer binding protien)
Two forms of CREB:CREB1 stimulates transcriptionCREB2 represses transcription
A.
B.

A model promoter
TGACTCA GACGTC GGGCGG
SP-1
CREBFos Jun CREB
AP-1 (Fos-Jun binding site)Regulation bygrowth factors,stress, and varioustransmembranesignals
CRE (Cyclic AMPResponse Element)Regulation by cAMP,and by Ca+. Interacts withcore promoter (through CREB Binding Protein)and modifies chromatin structure (through HAT).
SP-1 SiteProvides basalunregulatedtranscriptionalactivity. Manygenes have multiple SP-1 sites
Core PromoterBinds generaltranscriptionalmachinery
TATAAA
Positions of these elementsare relatively unimportant
HAT Histone Acetyl Transferase
HRENR NR
HRE (HormoneResponse Element)Regulation by hormonessuch as estrogen which enter the cell
NR=“nuclear receptor”

Nuclear receptors: An important class of transcription factors
Nuclear receptors include:Steroid hormone receptors:
Glucocorticoid receptorEstrogen receptors α and βAndrogen receptorProgesterone receptorMineralocorticoid receptor
Vitamin D receptorThyroid hormone T3 receptorFatty acid receptors
PPARα, PPARδ and PPARγBile salt receptorOxysterol receptorMany others

Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoid receptor
receptor +
glucocorticoid
Example of Nuclear receptor functionStimulation of transcription by glucocorticoids
Binds to specific DNA sequences and stimulates transcription of
glucocorticoid-responsive genes

DNA binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor (a zinc finger protein)

Activation of steroid receptors
The “LLXXL” domain (Leu Leu X X Leu) of the coactivator.
Binding of estrogen moves helix 12, allowing binding of the
coactivator’s LLXXL helix
Tamoxifen inhibits the
movement of helix 12
The cooactivator functions to recruitother factors that
stimulate transcripton such as CBP
Example: estrogen

HAT
Phosphorylation of CREB and the CREB binding protein (CBP)
HRENR NR
p160 p160coactivator

SERMS Selective estrogen receptor modifiers
SERM Bone Breast Cardio- Uterus vascular17-Estradiol + + + +ICI 182,780 (antiestrogen) - - - -Tamoxifen + - + +Raloxifene + - + -
+ Agonist- Antagonist

A model promoter
TGACTCA GACGTC GGGCGG
SP-1
CREBFos Jun CREB
AP-1 (Fos-Jun binding site)Regulation bygrowth factors,stress, and varioustransmembranesignals
CRE (Cyclic AMPResponse Element)Regulation by cAMP,and by Ca+. Interacts withcore promoter (through CREB Binding Protein)and modifies chromatin structure (through HAT).
SP-1 SiteProvides basalunregulatedtranscriptionalactivity. Manygenes have multiple SP-1 sites
Core PromoterBinds generaltranscriptionalmachinery
TATAAA
Positions of these elementsare relatively unimportant
HAT Histone Acetyl Transferase
HRENR NR
HRE (HormoneResponse Element)Regulation by hormonessuch as estrogen which enter the cell

The Cell CycleM (Mitosis) 2 hours
S (DNA synthesis) 6 hours
G112 hours
G24 hours
G0indefinite

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Growth factorReceptor
SRFSerum regulatory factor
Growth factor Receptor
Fos geneOther genes:
Ras-GDP

Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma, using HER2/ErbB2 (29D8) Rabbit mAb
HER2 FISH
HER2: Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Growth factorReceptor
TFIID
SRFSerum regulatory factor
Growth factor Receptor
Fos geneOther genes:
Growth factor
Growth factor receptors form dimers
Growth factor binds
Ras-GDP

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Growth factorReceptor
SRFSerum regulatory factor
Growth factor Receptor
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
One receptor’s tyrosine kinase activity phosphorylatesthe other receptor.
Ras-GDP

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Grb2
SRFSerum regulatory factor
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SH2 domain
Grb2 binds to phosphorylated receptor (via SH2 domain)
Ras-GDP

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Grb2
SRFSerum regulatory factor
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SH2 domain
2) SOS exchanges GDP on Ras for GTP
SH3 domain
SOS Ras-GTP
GTP GDP
1) GRB2 changes conformation and binds SOS

Ras-GTPRas-GDP
GTP GDP
sos
SOS is a GTP exchange protein. It removes the GDP and replaces it with GTP
Ras-GTP Ras-GDP
H20 Pi
A. Activation of Ras
B. Inactivation of Ras
Ras contains a GTPase activity(it continually hydrolyzes the associated GTP)

Plasma membrane
Nuclear membranes
Grb2
SRFSerum regulatory factor
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
A Series of kinases are activated by phopshorylation

ATP ADP
Activating a chain of MAP kinases(mitogen activated protien kinases)
MAP kinase kinase MAP kinase kinase
MAP kinase MAP kinaseMAP kinase kinase
ATP ADP
Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
MAP kinase
Substrate proteins
ATP ADP
Pi
Pi
Pi
Pi
PiSubstrate proteins
OH
OH
OH
A.
B.
C.

Transcription factors are activated by phosphorylation
Plasma membraneGrb2
SRFSerum regulatory factor
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol IIThe Fos protein is synthesized

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
Fos/Jun stimulates transcription of many genes

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
New proteins are formed
Cell Division
Some of the new proteins stimulate cell division

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
H2O Pi

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivation

Plasma membraneGrb2
HO
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Jun
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivation

Plasma membraneGrb2
HO
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranesJun
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivationFos mRNA & protein degraded

Plasma membraneGrb2
HO
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Cell Division
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivation
Fos mRNA & protein degraded

Plasma membraneGrb2
HO
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivationFos mRNA & protein degraded

Plasma membraneGrb2
HO
Fos geneOther genes:SO
S Ras-GDPRaf (a kinase)
Pi
H2OMAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Deactivating the pathway
Grb2
inactivationFos mRNA & protein degraded

Plasma membraneGrb2
PO4
Fos geneOther genes:
PO4PO4
SOS Ras-GTPRaf (a kinase)
ATP
ADP
MAP Kinases
Nuclear membranes
Fos pre mRNA
Fos protein Fos mRNA
Pol II
Jun
Cell Division
Problems that can lead to cancer