Plasma Membrane
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane

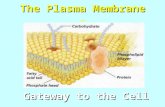
Plasma Membrane
- Surrounded the cells
- Basic structure: - Phospholipids - Protein- Carbohydrate- Cholesterol

2

3
Membrane Function:
-To control the intracellular milieu-The enzymes catalyze reactions-As cytoskeleton fibers cell shape-A passageway for molecules- Protein as a receptor-Enclose the cell separate the cells-Cell binds to each other tissue

4

5
General architecture
All membranes contain lipid and protein, with vary ratio every cell and organellesExp.Mitochondrial membrane is 76 % proteinThe myelin membrane is 18 % protein
Lipid as phospholipids, predominantly phosphoglycerides, which have a glycerol backbone.

6
- Phospholipids are amphipathic or amphiphilic,
head hydrophilic tails hydrophobic
- Hydrophilic pole water – loving polar
Hydrophobic pole water – hating non polar

7

8

• Phospholipids predominate in the plasma membrane of many mammalian cell
• The tail groups:• Fattyacyl chains have usually 16, 18 or
20 number of carbon atoms Saturated straight chain
• Unsaturated fattyacyl chain normally have one double bond, but some have 2, 3, or 4 Unsaturated a rigid kink
• Differences in length and saturation affect the fluidity
9

10
• Head Phosphatidyl-choline, Phosphatidylethanolamin, SphingomyelinPolar (no net electric charge )
Negative charge Phosphatidyl-serineInositol phospholipid smaller quantities cell signaling

11

12

13

14
- Shape and Amphipathic nature of the lipid molecule :-Bilayer or micelles spontaneously
in aqueous solution lipid molecule surrounded on all sides by water shape of lipid molecule

15

16

17
Fluidity
The fluidity depends on:Composition of the lipid Temperature
- Cis-double bonds kinks in hydrocarbon chain difficult to pack together fluid in lower temperature

18
- At normal temperature fluid-Lower temperature:- unsaturated fluid state, - saturated gel like state.
- Heat: gel like fluid like- Van der Waals interaction fluidity.- The lipid molecules can migrate: lateral diffusion, flexion, rotation and very rarely flip-flop

19

20

21
Cholesterol and glycolipid
Membrane contain large amount of cholesterol up to one molecule for every phospholipids molecule
Cholesterol molecule enhance the permeability barrier properties in molecule lipid bilayer

22

23
•Membrane Protein
- Protein usually: 50%
-On the surface peripheral
-Within membrane integral

24

25

26
Glycoproteins and Glycolipid-Carbohydrates found in many membranes: covalently bound either to protein glyco protein; or to lipid glycolipid.
-Abundant in the plasma membrane of eukaryo tic cells,but are abscent in inner mitochondrial membrane,chloroplast lamellae, etc
.-Increase the hydrophilic character of lipids and proteins.
-Stabilize the membrane protein.

27

28
Carbohydrate components are oligosacharides:
Galactose, mannose, fructoseN.acethylneuraminic(sialic acid),N.acethylgalactosamine, N.acethyl glucosamine,

29
Glycolipids :located in the cell surface membrane.
-Blood group antigens immune reaction glycoproteins or glycolipids blood group A, B, AB and O.-Antigenic determinant genetically deter- mined-All people have enzymes that synthesizes the O antigen.
-The O antigen is a chain of fructose, galactose, glucose and N.acethylglucosamine.

30
•The A antigen is similar to O, except that the A antigen contains an N-acetylgalactosamine attached to the outer galactose residue;• the B antigen is also similar to O, except for an extra galactose residue attached to the outer galactose.• All people have the enzymes that synthesize the O antigen. People with type A blood also have the enzyme that adds the extra N-acetylgalactosamine; those with type B blood have the enzyme that adds the extra galactose. •People with type AB blood synthesize A and B antigens; those with type O make only the O antigen.

31

32

33
•Erythrocyt have an usual plasma membrane that is tightly anchored to the cytosceleton.




37
Membrane Organization-Integral protein bind asymetrically to the li- pid bilayer.-Integral protein single, specific orientation to cytosolic and exoplasmic faces.-The two membrane leaflet have different lipid composition.-Glycolipid are always found in exoplasmic leaflet.-Integral proteins and lipids are mobile-Some protein interact with cytoskeletal compound.

38
-In specialized plasma membrane intestinal epithelial cells apical and basolateral region different function.-Microvilli extensions of the cell surface.-Glycocalyx a loose network , in the outer membrane surface oligosaccharide glycoproteins or glycolipids.







![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)