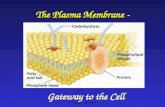
Plasma Membrane
Click here to load reader
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane

Plasma Membrane:Plasma Membrane:The Gate KeeperThe Gate Keeper
Ms. PolsonMs. Polson
BiologyBiology
October October 18,200918,2009

Plasma MembranePlasma MembraneLesson ObjectivesLesson Objectives
Students will be able to:Students will be able to:
Use vocabulary related to transport across the plasma Use vocabulary related to transport across the plasma membranemembrane
Differentiate between active and passive transportDifferentiate between active and passive transport
Identify membrane structures that permit transportIdentify membrane structures that permit transport
Understand the function of the plasma membrane as a Understand the function of the plasma membrane as a “gate keeper”“gate keeper”

What is a Plasma What is a Plasma Membrane?Membrane? All living cells have themAll living cells have them
Selective permeabilitySelective permeability
AsymmetricAsymmetric
Gives cell structureGives cell structure
Cell-cell recognitionCell-cell recognition
Fluid mosaic modelFluid mosaic model– Lipid movement in bilayerLipid movement in bilayer
Maintains homeostasisMaintains homeostasis

Animal and PlantAnimal and PlantPlasma (cell) Membrane Plasma (cell) Membrane

Plasma MembranePlasma MembraneFunctionFunction
Separate inside organelles from external Separate inside organelles from external environmentenvironment
Regulate entrance and exit of substancesRegulate entrance and exit of substances Transfer informationTransfer information Establishment of electric potential differenceEstablishment of electric potential difference Site of biological activitiesSite of biological activities Attachment between cellsAttachment between cells Removal of wasteRemoval of waste

Plasma MembranePlasma MembranePhotograph: Cell MembranePhotograph: Cell Membrane

Plasma MembranePlasma MembraneStructureStructure
LipidsLipids– Phosphlipids, Glycolipids, SteroidsPhosphlipids, Glycolipids, Steroids– Hydrophilic and hydrophobic propertiesHydrophilic and hydrophobic properties– Gives flexibilityGives flexibility
ProteinsProteins– Integral - transport channelsIntegral - transport channels– Peripheral - recognition sitesPeripheral - recognition sites– Determines membranes specific functionsDetermines membranes specific functions
SugarsSugars

Lipid Bilayer ModelLipid Bilayer ModelCross SectionCross Section
Gorter and Grendel, Gorter and Grendel, 19251925
Two sheets of lipidsTwo sheets of lipids– 7.5 nm thick7.5 nm thick
Found around cellFound around cell
Embedded with Embedded with proteinsproteins
Strengthened with Strengthened with cholesterol cholesterol molecules (animal)molecules (animal)

Lipid Bilayer ModelLipid Bilayer ModelPhospholipid Phospholipid
HydrophilicHydrophilic– Water lovingWater loving– Phosphate endPhosphate end– Outside and inside Outside and inside
HydrophobicHydrophobic– Water fearingWater fearing– Lipid tail regionLipid tail region– CenterCenter

Plasma MembranePlasma MembraneHydrophilic and HydrophobicHydrophilic and Hydrophobic

Passive TransportPassive TransportSimple DiffusionSimple Diffusion
Result of inherent Result of inherent kinetic energykinetic energy– Thermal motion or Thermal motion or
heatheat
No energy neededNo energy needed
Diffusion and osmosisDiffusion and osmosis
High concentration to High concentration to low concentration: low concentration: small molecules small molecules – OO2 2 , CO, CO22, H, H22OO

Simple DiffusionSimple Diffusion

Passive TransportPassive TransportFacilitatedFacilitated DiffusionDiffusion
Proteins act as tunnelsProteins act as tunnels
Carrier proteins help Carrier proteins help larger polar molecules larger polar molecules cross membranecross membrane– GlucoseGlucose
Moves materials along Moves materials along concentration concentration gradientgradient

Active TransportActive Transport
Energy Energy isis needed needed
Low concentration to Low concentration to high concentrationhigh concentration
Movement of molecules Movement of molecules up concentration up concentration gradient gradient
Sodium-potassium Sodium-potassium pumppump

Active TransportActive Transport
Movement of large substances by vesiclesMovement of large substances by vesicles
– Endocytosis – taking into cellEndocytosis – taking into cell PhagocytosisPhagocytosis PinocytosisPinocytosis Receptor mediateReceptor mediate
– Exocytosis – expelling from cellExocytosis – expelling from cell ER or Golgi ApparatusER or Golgi Apparatus

Types of SolutionsTypes of Solutions
IsotonicIsotonic– Concentration of dissolved substances are the Concentration of dissolved substances are the
same inside and outside the cellsame inside and outside the cell
HypotonicHypotonic– Concentration of dissolved substances are lower Concentration of dissolved substances are lower
outside than insideoutside than inside
HypertonicHypertonic– Concentration of dissolved substances are higher Concentration of dissolved substances are higher
outside than insideoutside than inside

HomeostasisHomeostasisPlasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Maintains constant internal environmentMaintains constant internal environment
Controls movement of materials in and out of Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell as a “gate keeper”the cell as a “gate keeper”– Dynamic equilibriumDynamic equilibrium
Separates cellular organelles from external Separates cellular organelles from external environment environment

Vocabulary ReviewVocabulary Review
Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane HomeostasisHomeostasis Passive TransportPassive Transport Simple DiffusionSimple Diffusion Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion Active TransportActive Transport HydrophilicHydrophilic
HydrophobicHydrophobic EndocytosisEndocytosis ExocytosisExocytosis IsotonicIsotonic HypertonicHypertonic HypotonicHypotonic

Questions…Questions…
Comments…Comments…
Thoughts?Thoughts?








![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)