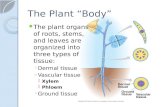
Plants cont. Vascular Tissue. Vascular Tissue Cells Series of tubes that transport fluids throughout...
-
Upload
peregrine-paul -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Plants cont. Vascular Tissue. Vascular Tissue Cells Series of tubes that transport fluids throughout...

Plants cont.Plants cont.
Vascular TissueVascular Tissue

Vascular Tissue Cells
• Series of tubes that transport fluids throughout the plant
• 2 types of vascular tissue: xylem and phloem.

Vascular Tissue Cells
• Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves
• Phloem carries sugar produced in the leaves to all parts of the plant
• Xylem and phloem together are called vascular bundles

Xylem Tissue• Moves water and dissolved minerals
from the roots up to the leaves • Thick walled tubes (provide support)
– Cylindrical cells fuse– Cytoplasm breaks down & Cells die– Non living cell walls become thin tubes

Phloem Tissue• Transports sucrose and other
dissolved sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plant– Formed from sieve tube cells making a
continuous duct– Alive! But do not have nucleus– Connected to small nucleated companion
cells that direct their activities

Phloem Tissue

Phloem Tissue

Xylem and Phloem animation
Xylem and Phloem animation

The rest of the plantThe rest of the plant
Beyond the leafBeyond the leaf

Epidermis (Dermal Tissue)
• Outer layer of all surfaces• One cell layer thick • Not in woody plants in woody
plants this is replaced by bark on the stem

Link

Use of sugar traveling in the phloem
• Provides energy for cellular processes– Protein manufacturing– Stored as starch in the roots (Carrots, and
sweet potatoes) stems (ginger, potatoes) leaves (green onions, rhubarb)
– Making cellulose • Forms the cell wall• Fibrous structures• Provide strength and support• Can be associated with the lignin in
the formation of wood